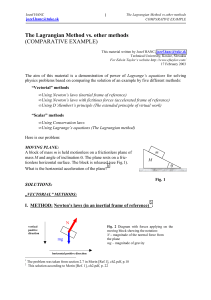
Rigid_Body_Dynamics1..
... • We treat a rigid body as a system of particles, where the distance between any two particles is fixed • We will assume that internal forces are generated to hold the relative positions fixed. These internal forces are all balanced out with Newton’s third law, so that they all cancel out and have n ...
... • We treat a rigid body as a system of particles, where the distance between any two particles is fixed • We will assume that internal forces are generated to hold the relative positions fixed. These internal forces are all balanced out with Newton’s third law, so that they all cancel out and have n ...
Lecture 18
... torque the acceleration will be less for the second scenario because I is bigger. It would be tougher to get the second dumbbell to rotate because of where we’ve put the axis of rotation, though we haven’t actually changed the masses! But what if we don’t have point masses to deal with? What if we h ...
... torque the acceleration will be less for the second scenario because I is bigger. It would be tougher to get the second dumbbell to rotate because of where we’ve put the axis of rotation, though we haven’t actually changed the masses! But what if we don’t have point masses to deal with? What if we h ...
02PCYQW_2016_Lagrange_approach - LaDiSpe
... The reason for using the term co-energy instead of the term energy , will be clarified later. B. Bona (DAUIN) ...
... The reason for using the term co-energy instead of the term energy , will be clarified later. B. Bona (DAUIN) ...
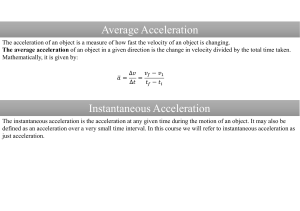
Average Acceleration Instantaneous Acceleration
... 4. At least three of the kinematic variables should have values. Be sure to read the question carefully. There may be implied data like ‘an object is accelerated from rest’, in which case we may write u = 0. 5. Often a problem is divided into parts. For instance, a car may accelerate for a period of ...
... 4. At least three of the kinematic variables should have values. Be sure to read the question carefully. There may be implied data like ‘an object is accelerated from rest’, in which case we may write u = 0. 5. Often a problem is divided into parts. For instance, a car may accelerate for a period of ...
Momentum
... Sample Questions • Which has more momentum, a 1-ton car moving at 100 km/hr or a 2-ton truck moving at 50 km/hr? ...
... Sample Questions • Which has more momentum, a 1-ton car moving at 100 km/hr or a 2-ton truck moving at 50 km/hr? ...
Unit Objectives: Understand the technique for finding center of mass
... State, prove and apply the relation between center-of-mass velocity and linear momentum, and between center-of-mass acceleration and net external force for a system of particles Define center of gravity and use this concept to express the gravitational potential energy of a rigid body in terms o ...
... State, prove and apply the relation between center-of-mass velocity and linear momentum, and between center-of-mass acceleration and net external force for a system of particles Define center of gravity and use this concept to express the gravitational potential energy of a rigid body in terms o ...
Chapter 8 Rotational Dynamics continued
... The combined moment of inertia of the dual pulley is 50.0 kg·m2. The crate weighs 4420 N. A tension of 2150 N is maintained in the cable attached to the motor. Find the angular acceleration of the dual Pulley (radius-1 = 0.600m, radius-2 = 0.200 m). ...
... The combined moment of inertia of the dual pulley is 50.0 kg·m2. The crate weighs 4420 N. A tension of 2150 N is maintained in the cable attached to the motor. Find the angular acceleration of the dual Pulley (radius-1 = 0.600m, radius-2 = 0.200 m). ...