Chapter 4
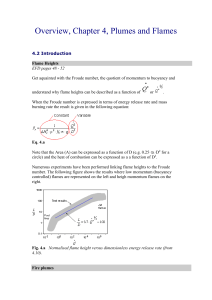
... narrow fire source and the upper solid line flame heights for an axisymmetric plume. Equations 4.34 and 4.35 can be used to calculate flame heights and plume mass flow rate for a long and narrow fire source (line source). ...
... narrow fire source and the upper solid line flame heights for an axisymmetric plume. Equations 4.34 and 4.35 can be used to calculate flame heights and plume mass flow rate for a long and narrow fire source (line source). ...
Bernoulli
... Pressure = 0 Whenever the only pressure acting on a point is the standard atmospheric pressure, then the pressure at that point can be assumed to be zero because every point in the system is subject to that same pressure. Therefore, for any free surface or free jet, pressure at that point can be ass ...
... Pressure = 0 Whenever the only pressure acting on a point is the standard atmospheric pressure, then the pressure at that point can be assumed to be zero because every point in the system is subject to that same pressure. Therefore, for any free surface or free jet, pressure at that point can be ass ...
Momentum
... When one object is moving hits an object that is moving at a different velocity some momentum is passed on or transferred. When a moving object hit a nonmoving object all the momentum is transferred to the object that was not moving. ...
... When one object is moving hits an object that is moving at a different velocity some momentum is passed on or transferred. When a moving object hit a nonmoving object all the momentum is transferred to the object that was not moving. ...
Rotary
... A particle moves in a circle of radius r. Having moved an arc length s, its angular position is θ relative to its original position, where . ...
... A particle moves in a circle of radius r. Having moved an arc length s, its angular position is θ relative to its original position, where . ...
Rotational Kinematics (Part I from chapter 10)
... combined mass M moves like an equivalent particle of mass M would move under the influence of the net external force on the system ...
... combined mass M moves like an equivalent particle of mass M would move under the influence of the net external force on the system ...