Chapter 15: Oscillations 15-23 THINK The maximum force that can
... angular acceleration. EXPRESS We take the angular displacement of the wheel to be t = m cos(2t/T), where m is the amplitude and T is the period. We differentiate with respect to time to find the angular velocity: = d/dt = –(2/T)msin(2t/T). The symbol is used for the angular velocity of ...
... angular acceleration. EXPRESS We take the angular displacement of the wheel to be t = m cos(2t/T), where m is the amplitude and T is the period. We differentiate with respect to time to find the angular velocity: = d/dt = –(2/T)msin(2t/T). The symbol is used for the angular velocity of ...
Newtonian Mechanics
... velocity, and accleration are all vectors—mathematical quantities with both magnitude and direction. We will denote vectors by boldface symbols, e.g., x for position, v for velocity, and a for acceleration. In hand-written equations, vector quantities are usually indicated by drawing an arrow (→) ov ...
... velocity, and accleration are all vectors—mathematical quantities with both magnitude and direction. We will denote vectors by boldface symbols, e.g., x for position, v for velocity, and a for acceleration. In hand-written equations, vector quantities are usually indicated by drawing an arrow (→) ov ...
Slide 1 - SFSU Physics & Astronomy
... Time of collision is short enough that external forces may be ignored Inelastic collision: momentum is conserved but kinetic energy is not Completely inelastic collision: objects stick ...
... Time of collision is short enough that external forces may be ignored Inelastic collision: momentum is conserved but kinetic energy is not Completely inelastic collision: objects stick ...
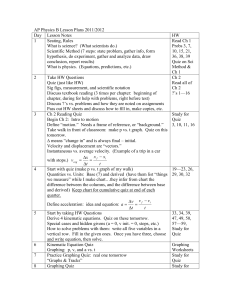
AP Physics B Lesson Plans
... Power: IV. (and others from V = IR) Unit for Power. What is a kWh? Resistors in circuits: Derive equations for series and parallel circuits: relate to equations for capacitors. Vocabulary: “tripping a circuit breaker”, “power loss due to ...
... Power: IV. (and others from V = IR) Unit for Power. What is a kWh? Resistors in circuits: Derive equations for series and parallel circuits: relate to equations for capacitors. Vocabulary: “tripping a circuit breaker”, “power loss due to ...
Dimensional Analysis and Hydraulic Similitude
... The stagnation point is created at a distance b from the source where velocities for both the flow are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. If m is volume flow rate emanating from the line of the source, U is the uniform velocity, determine; (a) Location of stagnation point ‘b’ (b) Radial a ...
... The stagnation point is created at a distance b from the source where velocities for both the flow are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. If m is volume flow rate emanating from the line of the source, U is the uniform velocity, determine; (a) Location of stagnation point ‘b’ (b) Radial a ...
Linear Momentum
... The original motion of each shell is a parabola. After the shell explodes, the individual pieces move in such a way that if you add their positive and negative momenta, they still follow the original parabolic path. ...
... The original motion of each shell is a parabola. After the shell explodes, the individual pieces move in such a way that if you add their positive and negative momenta, they still follow the original parabolic path. ...
Lect15
... CONCLUDE: Because irrotational and mass continuity satisfied Laplace equation must be satisfied ... … everywhere in plane EXCEPT at origin, location of source, where radial flow speed, is infinite- Eq. (1) ...
... CONCLUDE: Because irrotational and mass continuity satisfied Laplace equation must be satisfied ... … everywhere in plane EXCEPT at origin, location of source, where radial flow speed, is infinite- Eq. (1) ...
5, 6, 10, 13, 14, 18, 23 / 5, 7, 16, 23, 31, 34, 39, 43, 45
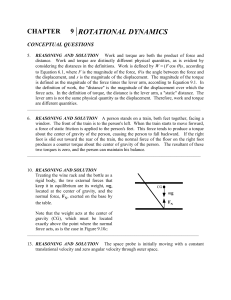
... together, the length of the cable is L/2, the final angular speed is f, and the momentum of inertia is If = 2M(L/4)2. The conservation of angular momentum indicates that I f f I 0 0 ...
... together, the length of the cable is L/2, the final angular speed is f, and the momentum of inertia is If = 2M(L/4)2. The conservation of angular momentum indicates that I f f I 0 0 ...
Dimensional Analysis Learning Objectives – Dimensional
... Gulliver’s Travels: Dimensional Analysis ...
... Gulliver’s Travels: Dimensional Analysis ...