chap 6 momentum
... Very Fast objects have Greeeeat momentum Very Massive Objects have Greeeat momentum ...
... Very Fast objects have Greeeeat momentum Very Massive Objects have Greeeat momentum ...
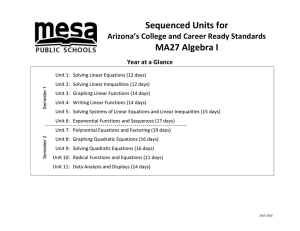
Sequenced Units for MA27 Algebra I Arizona’s College and Career Ready Standards
... students to appreciate what the broader notation enables us to do because they have not learned enough at this stage. When two equations are graphed on the same axes, we can clearly refer to f and g, versus saying “the first y =” and “the second y =.” We compose functions and have functions with mul ...
... students to appreciate what the broader notation enables us to do because they have not learned enough at this stage. When two equations are graphed on the same axes, we can clearly refer to f and g, versus saying “the first y =” and “the second y =.” We compose functions and have functions with mul ...
Momentum and Impulse Unit Notes
... IMPULSE AND MOMENTUM PREVIEW The momentum of an object is the product of its mass and velocity. If you want to change the momentum of an object, you must apply an impulse, which is the product of force and the time during which the force acts. If there are no external forces acting on a system of ob ...
... IMPULSE AND MOMENTUM PREVIEW The momentum of an object is the product of its mass and velocity. If you want to change the momentum of an object, you must apply an impulse, which is the product of force and the time during which the force acts. If there are no external forces acting on a system of ob ...
Momentum and Impulse Unit Notes
... The product of the average force acting on an object and the time during which it acts. Impulse is a vector quantity, and can also be calculated by finding the area under a force versus time curve. linear momentum The product of the mass of an object and its velocity. Momentum is a vector quantity, ...
... The product of the average force acting on an object and the time during which it acts. Impulse is a vector quantity, and can also be calculated by finding the area under a force versus time curve. linear momentum The product of the mass of an object and its velocity. Momentum is a vector quantity, ...
Chapter 11 Clickers
... 11.11.6. Joe has volunteered to help out in his physics class by sitting on a stool that easily rotates. Joe holds the dumbbells out as shown as the stool rotates. Then, Joe drops both dumbbells. Then, the angular momentum of Joe and the stool change, but the angular velocity does not change. Which ...
... 11.11.6. Joe has volunteered to help out in his physics class by sitting on a stool that easily rotates. Joe holds the dumbbells out as shown as the stool rotates. Then, Joe drops both dumbbells. Then, the angular momentum of Joe and the stool change, but the angular velocity does not change. Which ...
Lecture 18
... Motion of an object/system under a Force • We know that for a system of masses, or for a solid object, if a Force is applied to the system/object, the center of mass of the moves as if all of the mass was at the CM and the Force is applied to the CM. • But does this entirely determine the motion of ...
... Motion of an object/system under a Force • We know that for a system of masses, or for a solid object, if a Force is applied to the system/object, the center of mass of the moves as if all of the mass was at the CM and the Force is applied to the CM. • But does this entirely determine the motion of ...
Quiz 07-2 Rotation
... a) zero newtons b) 100 N c) 600 N d) 800 N e) 1000 N ____ 13. A string is wrapped around a pulley of radius 0.05 m and moment of inertia 0.2 kg • m2. If the string is pulled with a force F, the resulting angular acceleration of the pulley is 2 rad/s2. Determine the magnitude of the force F. ...
... a) zero newtons b) 100 N c) 600 N d) 800 N e) 1000 N ____ 13. A string is wrapped around a pulley of radius 0.05 m and moment of inertia 0.2 kg • m2. If the string is pulled with a force F, the resulting angular acceleration of the pulley is 2 rad/s2. Determine the magnitude of the force F. ...
Notes II for phy132
... and forth, and its motion is periodic. The questions we want to consider are: is the motion simple harmonic, and what is the equation for the period T of the motion? To answer these questions, one starts with the equation relating forces and motion. I am going to use a different variable than the te ...
... and forth, and its motion is periodic. The questions we want to consider are: is the motion simple harmonic, and what is the equation for the period T of the motion? To answer these questions, one starts with the equation relating forces and motion. I am going to use a different variable than the te ...
Chapter 7 Momentum and Impulse
... "Multiply both sides of Newton’s second law by the time interval over which the force acts: "The left side of the equation is impulse, the (average) force acting on an object multiplied by the time interval over which the force acts. "How a force changes the motion of an object depends on both the s ...
... "Multiply both sides of Newton’s second law by the time interval over which the force acts: "The left side of the equation is impulse, the (average) force acting on an object multiplied by the time interval over which the force acts. "How a force changes the motion of an object depends on both the s ...
Inertia and Momentum
... What is Momentum? Objects at rest had no impedo. A rock rolling down a hill had impedo. More faster it moved, the more impedo it had. The change in impedo depended on force and how long the force acted. ...
... What is Momentum? Objects at rest had no impedo. A rock rolling down a hill had impedo. More faster it moved, the more impedo it had. The change in impedo depended on force and how long the force acted. ...
Document
... frictionless the force it exerts is normal to the plank and makes the angle with the vertical. Its magnitude is designated F. W is the force of gravity; this force acts at the center of the plank, a distance L/2 from the point where the plank touches the floor. FN is the normal force of the floor ...
... frictionless the force it exerts is normal to the plank and makes the angle with the vertical. Its magnitude is designated F. W is the force of gravity; this force acts at the center of the plank, a distance L/2 from the point where the plank touches the floor. FN is the normal force of the floor ...