ME2 – MECHANICAL COMPONENTS
... A common error used in computing the moment of inertia about an axis occurs when we approximate the body as a point mass physically located at its center of gravity and then use this point to define the distance of the body from its axis of rotation. In the case shown above, if we had used the cent ...
... A common error used in computing the moment of inertia about an axis occurs when we approximate the body as a point mass physically located at its center of gravity and then use this point to define the distance of the body from its axis of rotation. In the case shown above, if we had used the cent ...
Section 8-2 Center of Mass
... b. Center gravity – an average position at which the gravitational force of the object acts. i. In this book Center of Mass and Center of Gravity are equivalent. 12. Moment of Inertia a. Mini Lab: Moment of inertia of a rod i. Pg 285 ii. Calculate “I” for rod in each position 1. Why is it easier to ...
... b. Center gravity – an average position at which the gravitational force of the object acts. i. In this book Center of Mass and Center of Gravity are equivalent. 12. Moment of Inertia a. Mini Lab: Moment of inertia of a rod i. Pg 285 ii. Calculate “I” for rod in each position 1. Why is it easier to ...
Rigid_Body_Dynamics1..
... • We treat a rigid body as a system of particles, where the distance between any two particles is fixed • We will assume that internal forces are generated to hold the relative positions fixed. These internal forces are all balanced out with Newton’s third law, so that they all cancel out and have n ...
... • We treat a rigid body as a system of particles, where the distance between any two particles is fixed • We will assume that internal forces are generated to hold the relative positions fixed. These internal forces are all balanced out with Newton’s third law, so that they all cancel out and have n ...
Rotational Inertia and Angular Momentum
... To understand why ice skaters, divers, & gymnasts spin faster when they bring their bodies in we must discuss the Conservation of Angular Momentum. ...
... To understand why ice skaters, divers, & gymnasts spin faster when they bring their bodies in we must discuss the Conservation of Angular Momentum. ...
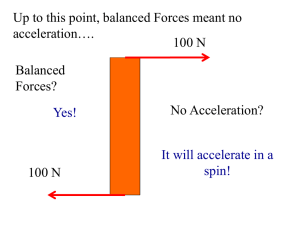
Newton`s First Law Practice
... _____ 4. The inertia of an object is determined by its speed. _____ 5. The speed of an object changes only when an unbalanced force acts it on. _____ 6. A stationary object resists movement only because of gravity. _____ 7. The tendency of an object to resist a change in motion depends on its mass. ...
... _____ 4. The inertia of an object is determined by its speed. _____ 5. The speed of an object changes only when an unbalanced force acts it on. _____ 6. A stationary object resists movement only because of gravity. _____ 7. The tendency of an object to resist a change in motion depends on its mass. ...