Rotational Kinematics
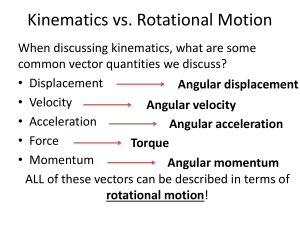
... When discussing kinematics, what are some common vector quantities we discuss? • Displacement Angular displacement • Velocity Angular velocity • Acceleration Angular acceleration • Force Torque • Momentum Angular momentum ALL of these vectors can be described in terms of rotational motion! ...
... When discussing kinematics, what are some common vector quantities we discuss? • Displacement Angular displacement • Velocity Angular velocity • Acceleration Angular acceleration • Force Torque • Momentum Angular momentum ALL of these vectors can be described in terms of rotational motion! ...
Notes
... keep on rotating until something stops rotation. A rotating object has an “inertia of rotation”. This is called Angular Momentum. It depends upon Rotational Inertia and rotational velocity. The faster something is rotating, the more angular momentum it has. The harder it was to get it started rotati ...
... keep on rotating until something stops rotation. A rotating object has an “inertia of rotation”. This is called Angular Momentum. It depends upon Rotational Inertia and rotational velocity. The faster something is rotating, the more angular momentum it has. The harder it was to get it started rotati ...
Monday, April 1, 2013
... 4. You must show the detail of your OWN work in order to obtain any credit. Monday, April 1, 2013 ...
... 4. You must show the detail of your OWN work in order to obtain any credit. Monday, April 1, 2013 ...
Ch11 - Rolling, Torque, and Angular Momentum
... 11.15 Calculate the torque due to a force on a particle by taking the cross product of the particle's position vector and the force vector, in either unit-vector notation or magnitude-angle notation. © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. ...
... 11.15 Calculate the torque due to a force on a particle by taking the cross product of the particle's position vector and the force vector, in either unit-vector notation or magnitude-angle notation. © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. ...
File
... This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permit ...
... This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permit ...
1 References Slides also Available at Some Tricks Dynamics
... • A spring has a constant of 50 N/ m. The spring is hung vertically, and a mass is attached to its end. The spring end displaces 30 cm from its equilibrium position. The same mass is removed from the first spring and attached to the end of a second (different) spring, and the displacement is 25 cm. ...
... • A spring has a constant of 50 N/ m. The spring is hung vertically, and a mass is attached to its end. The spring end displaces 30 cm from its equilibrium position. The same mass is removed from the first spring and attached to the end of a second (different) spring, and the displacement is 25 cm. ...
6-1 Rewriting Newton`s Second Law
... constant mass that we find this form of the equation to be very useful. The general form of Newton’s second law connects the net force on an object with the rate of change of the quantity . This quantity has a name, which you may already be familiar with. An object’s momentum is the product of its m ...
... constant mass that we find this form of the equation to be very useful. The general form of Newton’s second law connects the net force on an object with the rate of change of the quantity . This quantity has a name, which you may already be familiar with. An object’s momentum is the product of its m ...
... Momentum Consider a Mack truck and a roller skate moving down the street at the same speed. The considerably greater mass of the Mack truck gives it a considerably greater momentum. If the Mack truck were at rest, which would have the greater momentum? If an object is at rest, the momentum of that ...
H Ch 7 Notes - Angular Motion.notebook
... unit time. In circular motion, linear velocity is sometimes called tangential velocity because its direction is tangent to the circle. ...
... unit time. In circular motion, linear velocity is sometimes called tangential velocity because its direction is tangent to the circle. ...
Slide 1
... on an apparent breakaway for a touchdown is tackled from behind. When he was tackled by an 85-kg cornerback running at 5.5 m s in the same direction, what was their mutual speed immediately after the tackle? ...
... on an apparent breakaway for a touchdown is tackled from behind. When he was tackled by an 85-kg cornerback running at 5.5 m s in the same direction, what was their mutual speed immediately after the tackle? ...