Wade Chapter 8 Learning
... Because of his groundbreaking work B. F. Skinner is often called the greatest American Psychologist. Believed that we could study private emotions and thought by observing our own sensory responses, the verbal reports of others, and the conditions under which such events occur. Thoughts cannot expla ...
... Because of his groundbreaking work B. F. Skinner is often called the greatest American Psychologist. Believed that we could study private emotions and thought by observing our own sensory responses, the verbal reports of others, and the conditions under which such events occur. Thoughts cannot expla ...
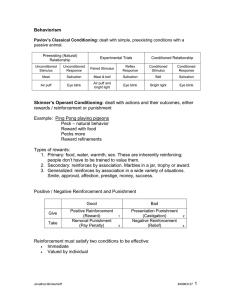
Behaviorism
... 3. Don’t get angry – keep the responsibility where it belongs. Effective: I’m sorry you’ve made the choice to loose part of your recess. Ineffective: How many times will I have to tell you to stop talking? 4. Don’t argue or debate 5. Accept feelings, then state the sad truth. I can see you’re upse ...
... 3. Don’t get angry – keep the responsibility where it belongs. Effective: I’m sorry you’ve made the choice to loose part of your recess. Ineffective: How many times will I have to tell you to stop talking? 4. Don’t argue or debate 5. Accept feelings, then state the sad truth. I can see you’re upse ...
TOPIC 1 INTRODUCTION
... between stimuli we encounter our behavioral responses to them and the reinforcement or punishment that results. Everyone history of exposure to environmental contingencies varies so each person's behavior will also differ For e.g: A person who had a frightening experience with a spider as ...
... between stimuli we encounter our behavioral responses to them and the reinforcement or punishment that results. Everyone history of exposure to environmental contingencies varies so each person's behavior will also differ For e.g: A person who had a frightening experience with a spider as ...
Learning Red
... 7 – Bill once had a blue car that was in the shop more than it was out. Since then he will not even consider owning blur or green cars. Bill’s aversion to green cars is an example of ___________. 8 – In Garcia and Koelling’s studies of taste-aversion learning, rats learned to associate taste with si ...
... 7 – Bill once had a blue car that was in the shop more than it was out. Since then he will not even consider owning blur or green cars. Bill’s aversion to green cars is an example of ___________. 8 – In Garcia and Koelling’s studies of taste-aversion learning, rats learned to associate taste with si ...
Ch.07 - Learning
... How much of the reward do I get? What are the chances of getting the reward? Is the reward worth it? ...
... How much of the reward do I get? What are the chances of getting the reward? Is the reward worth it? ...
Name two scientists famous for their studies of classical conditioning 2
... 4 – In Pavlov’s original experiment with dogs, the meat served as the (UCS, UCR, CS or CR)? 5 – During extinction, the _________ (UCS, UCR, CS, or CR) must be omitted. 6 – Bill once had a blue car that was in the shop more than it was out. Since then he will not even consider owning blur or green ca ...
... 4 – In Pavlov’s original experiment with dogs, the meat served as the (UCS, UCR, CS or CR)? 5 – During extinction, the _________ (UCS, UCR, CS, or CR) must be omitted. 6 – Bill once had a blue car that was in the shop more than it was out. Since then he will not even consider owning blur or green ca ...
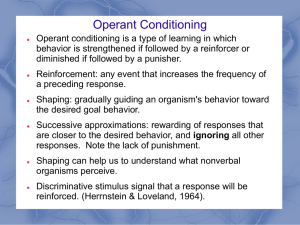
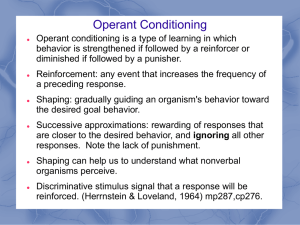
Operant Conditioning
... Operant conditioning uses operant or voluntary behavior Ask: Is the behavior something the animal can control? Does the animal have a choice in how to behave? ...
... Operant conditioning uses operant or voluntary behavior Ask: Is the behavior something the animal can control? Does the animal have a choice in how to behave? ...
Learning Chapter 7 PowerPoint
... vicarious punishment. vicarious reinforcement. modeling. mirror neurons. ...
... vicarious punishment. vicarious reinforcement. modeling. mirror neurons. ...
Chapter 6 - Learning
... – An operant conditioning procedure in which people earn a token of some sort for exhibiting a desired behavior and can later exchange the tokens for various privileges or treats • Token economies have been successful in an array of settings – Homes, hospitals, schools, mental institutions, prisons ...
... – An operant conditioning procedure in which people earn a token of some sort for exhibiting a desired behavior and can later exchange the tokens for various privileges or treats • Token economies have been successful in an array of settings – Homes, hospitals, schools, mental institutions, prisons ...
Reinforcements from the environment ∙Operant conditioning: a type of
... ∙David Premack (1962) came up with the Premack Principle-discerning which two activities someone would rather engage in means that the preferred activity can be used to reinforce a non-preferred one. *example: children prefer to watch TV instead of doing homework. So parents start with the no TV unt ...
... ∙David Premack (1962) came up with the Premack Principle-discerning which two activities someone would rather engage in means that the preferred activity can be used to reinforce a non-preferred one. *example: children prefer to watch TV instead of doing homework. So parents start with the no TV unt ...
Behaviorism Study Guide Spring 2013
... Task analysis Positive practice Notes from Guidelines: Encouraging Positive Behaviors (pg. 288): Response cost Group consequences Contingency contract Token Economy (token reinforcement system) Fading (not in text) Self-management ...
... Task analysis Positive practice Notes from Guidelines: Encouraging Positive Behaviors (pg. 288): Response cost Group consequences Contingency contract Token Economy (token reinforcement system) Fading (not in text) Self-management ...
The Tales of Operant Conditioning
... all the people in the land of Skinnerian that occurred through rewards and punishment for behavior. It was coined by it’s master creator, B.F. Skinner, which is why the land in which the people lived was known as Skinnerian, because operant conditioning was also known as Skinnerian Conditioning. ...
... all the people in the land of Skinnerian that occurred through rewards and punishment for behavior. It was coined by it’s master creator, B.F. Skinner, which is why the land in which the people lived was known as Skinnerian, because operant conditioning was also known as Skinnerian Conditioning. ...
Operant Conditioning
... Skinner wrote a novel outlining how rewards and punishments could be used to create a utopian society. Experimental communities were created based on his ideas One of these still exists. An upbeat attitude is instilled in children by only rewarding positive statements like “I like it” and “I’m ...
... Skinner wrote a novel outlining how rewards and punishments could be used to create a utopian society. Experimental communities were created based on his ideas One of these still exists. An upbeat attitude is instilled in children by only rewarding positive statements like “I like it” and “I’m ...
Module 27 Notes Operant Conditioning Operant Conditioning A type
... Type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by a reinforce or diminished if followed by a punisher. The likelihood of a behavior’s occurrence is linked to the response (consequence) that behavior receives o Rewards and Punishments (Behavior that operates on the environment to ...
... Type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by a reinforce or diminished if followed by a punisher. The likelihood of a behavior’s occurrence is linked to the response (consequence) that behavior receives o Rewards and Punishments (Behavior that operates on the environment to ...
PSY402 Theories of Learning
... More recent studies show that it can permanently suppress behavior under some conditions. Under other conditions it has no effect or only temporarily works. ...
... More recent studies show that it can permanently suppress behavior under some conditions. Under other conditions it has no effect or only temporarily works. ...
Module 21 Operant Conditioning
... gains its reinforcing power through its association with a primary reinforcer. Eg: money. Immediate reinforcers are innately satisfying rewards (food & sex); most humans need to learn delayed reinforcement as a big step to maturity. (Logue, 1998). ...
... gains its reinforcing power through its association with a primary reinforcer. Eg: money. Immediate reinforcers are innately satisfying rewards (food & sex); most humans need to learn delayed reinforcement as a big step to maturity. (Logue, 1998). ...
path to dependence
... Well-known that seatbelts save lives. Usage varies greatly. 51% in Mass 91% in Calif 78% in CT Required in CA but only suggested in MA ...
... Well-known that seatbelts save lives. Usage varies greatly. 51% in Mass 91% in Calif 78% in CT Required in CA but only suggested in MA ...
Four
... • Defined -- the application of aversive or unpleasant consequences to a behavior. A punishment reduces the likelihood of a behavior occurring. • Like a negative reinforcer, it is unpleasant but a negative reinforcer strengthens and sustains behaviors. Punishment/Discipline weakens and eliminates be ...
... • Defined -- the application of aversive or unpleasant consequences to a behavior. A punishment reduces the likelihood of a behavior occurring. • Like a negative reinforcer, it is unpleasant but a negative reinforcer strengthens and sustains behaviors. Punishment/Discipline weakens and eliminates be ...
watson skinner and operant conditioning
... rewards. Money gets us food. Clapping for an actress. Clicker training for pets. • Caveman Test ...
... rewards. Money gets us food. Clapping for an actress. Clicker training for pets. • Caveman Test ...
Conditioning and Learning Essays
... 1. Classical conditioning and operant conditioning are different learning methods. Their differences lie in a. The extent to which reinforcement depends on the behavior of the learner b. The type of behavior to which each method applies. Their similarities are that they both produce the following ba ...
... 1. Classical conditioning and operant conditioning are different learning methods. Their differences lie in a. The extent to which reinforcement depends on the behavior of the learner b. The type of behavior to which each method applies. Their similarities are that they both produce the following ba ...
Operant Conditioning
... 2 kinds of punishment Punishment weakens responses • Positive punishment: something unpleasant is added to the situation – Spanking (making sure you don’t do the wrong behavior ...
... 2 kinds of punishment Punishment weakens responses • Positive punishment: something unpleasant is added to the situation – Spanking (making sure you don’t do the wrong behavior ...
Myers Module Twenty One
... Primary reinforcer: an innately reinforcing stimulus, such as one that satisfies a biological need. Eg: food & sex. Conditionered (or secondary) reinforcer: a stimulus that gains its reinforcing power through its association with a primary reinforcer. Eg: money. Immediate reinforcers are innately sa ...
... Primary reinforcer: an innately reinforcing stimulus, such as one that satisfies a biological need. Eg: food & sex. Conditionered (or secondary) reinforcer: a stimulus that gains its reinforcing power through its association with a primary reinforcer. Eg: money. Immediate reinforcers are innately sa ...