Neuroscience & Behavior
... Biological psychology provides insights into numerous aspects of our lives, including sleep and dreams, depression and schizophrenia, hunger and sex, stress and disease, and many others. Early approach: Phrenology. ...
... Biological psychology provides insights into numerous aspects of our lives, including sleep and dreams, depression and schizophrenia, hunger and sex, stress and disease, and many others. Early approach: Phrenology. ...
Chapter 2
... Whole-brain Association Activity Whole-brain association activity involves complex activities which require communication among association areas across the brain such as: memory language attention meditation and spirituality consciousness ...
... Whole-brain Association Activity Whole-brain association activity involves complex activities which require communication among association areas across the brain such as: memory language attention meditation and spirituality consciousness ...
Nervous System ppt
... Parkinson's disease is a disorder of the brain that leads to shaking (tremors) and difficulty with walking, movement, and coordination. Caused by loss of dopamine producing cells in brain (substantia niagra) Dopamine helps control muscle movement by releasing inhibitory function of substantia nia ...
... Parkinson's disease is a disorder of the brain that leads to shaking (tremors) and difficulty with walking, movement, and coordination. Caused by loss of dopamine producing cells in brain (substantia niagra) Dopamine helps control muscle movement by releasing inhibitory function of substantia nia ...
Gadolinium Deposition in the Dentate Nucleus: An
... osmolyte, mI contributes specificity in dementia diagnoses1, inflammation, low grade gliomas and an almost absolute specificity to hepatic encephalopathy and hyponatremic brain syndromes. Myoinositol is a precursor in the phosphatidylinositol second messenger system, and is also a glial marker. ...
... osmolyte, mI contributes specificity in dementia diagnoses1, inflammation, low grade gliomas and an almost absolute specificity to hepatic encephalopathy and hyponatremic brain syndromes. Myoinositol is a precursor in the phosphatidylinositol second messenger system, and is also a glial marker. ...
Ch. 21.1 Nervous Lecture
... 1. The “thinker” a. The more pathways the quicker information is processed—Thank you school! 2. Memory storage 3. Interpreting senses ...
... 1. The “thinker” a. The more pathways the quicker information is processed—Thank you school! 2. Memory storage 3. Interpreting senses ...
Ch 9 Sensory System
... from parts of body not actually stimulated −common with viscera pain receptors = often dull − Ex. Heart, Gallbladder, or Bladder ...
... from parts of body not actually stimulated −common with viscera pain receptors = often dull − Ex. Heart, Gallbladder, or Bladder ...
Nonlinear Behavior of Neocortical Networks
... which nerve cells transmit information. An interesting application of non-linear mathematical studies helps describe behavior in neural networks. Activity in neural networks has been shown to follow diverse patterns, including oscillations, synchrony, and waves. Recent research has revealed that spo ...
... which nerve cells transmit information. An interesting application of non-linear mathematical studies helps describe behavior in neural networks. Activity in neural networks has been shown to follow diverse patterns, including oscillations, synchrony, and waves. Recent research has revealed that spo ...
Peripheral Nervous System - UBC Psychology`s Research Labs
... the electrical current increases the firing of neurons at the tip of the electrode. ...
... the electrical current increases the firing of neurons at the tip of the electrode. ...
Slide ()
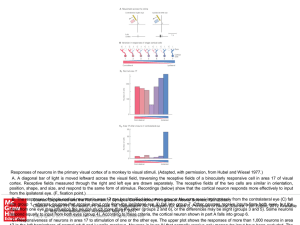
... A. A diagonal bar of light is moved leftward across the visual field, traversing the receptive fields of a binocularly responsive cell in area 17 of visual cortex. Receptive fields measured through the right and left eye are drawn separately. The receptive fields of the two cells are similar in orie ...
... A. A diagonal bar of light is moved leftward across the visual field, traversing the receptive fields of a binocularly responsive cell in area 17 of visual cortex. Receptive fields measured through the right and left eye are drawn separately. The receptive fields of the two cells are similar in orie ...
The Nervous System
... nervous system. The sympathetic nervous system is the actual system that releases energy and prepares the body for action. The body then typically restores itself back to normal after a period of time by the parasympathetic nervous system, which acts as a kind of stabilizer. ...
... nervous system. The sympathetic nervous system is the actual system that releases energy and prepares the body for action. The body then typically restores itself back to normal after a period of time by the parasympathetic nervous system, which acts as a kind of stabilizer. ...
Chapter 10 Slides
... capacity for accurate axonal growth is lost in maturity Regeneration is virtually nonexistent in the CNS of adult mammals and unlikely, but possible, in the PNS ...
... capacity for accurate axonal growth is lost in maturity Regeneration is virtually nonexistent in the CNS of adult mammals and unlikely, but possible, in the PNS ...
The Computational Brain
... perfecting how the brain is to be designed, and it would be well advised that a mechanism to simulate it would be drafted similarly. Starting with the brainstem, we devise all we need to continue to exist. This part of the brain is made of the Midbrain, Pons, and Medulla Oblongata. These control the ...
... perfecting how the brain is to be designed, and it would be well advised that a mechanism to simulate it would be drafted similarly. Starting with the brainstem, we devise all we need to continue to exist. This part of the brain is made of the Midbrain, Pons, and Medulla Oblongata. These control the ...
PRACTICE QUIZ
... 12. Olfactory neurons are frequently replaced because their lifespan is only about _________________ days. 13. Olfactory neurons synapse with mitral cells within complex structures called ______________________. 14. A bundle of mitral cell axons form _________________________ which extend from the o ...
... 12. Olfactory neurons are frequently replaced because their lifespan is only about _________________ days. 13. Olfactory neurons synapse with mitral cells within complex structures called ______________________. 14. A bundle of mitral cell axons form _________________________ which extend from the o ...
1. Which of the following is the component of the limbic system that
... 1. Which of the following is the component of the limbic system that plays an essential role in the processing of new memories? A) hypothalamus B) thalamus C) hippocampus D) medulla E) cerebellum 2. An axon is A) a cell that serves as the basic building block of the nervous system. B) a layer of fat ...
... 1. Which of the following is the component of the limbic system that plays an essential role in the processing of new memories? A) hypothalamus B) thalamus C) hippocampus D) medulla E) cerebellum 2. An axon is A) a cell that serves as the basic building block of the nervous system. B) a layer of fat ...
Neurons, Hormones, and the Brain
... center of the back • Protected by a column of bones, spinal column • Bridge between the brain and the parts of the body below the neck ...
... center of the back • Protected by a column of bones, spinal column • Bridge between the brain and the parts of the body below the neck ...
Resting potential
... 2. Carl Wernicke- studied the effects of brain disease on speech & language – All language deficits are result of damage to Broca’s area ...
... 2. Carl Wernicke- studied the effects of brain disease on speech & language – All language deficits are result of damage to Broca’s area ...
Control and Coordination
... The cerebral cortex is configured into convolutions (folds) that maximize surface area The interior white matter consists of myelinated axons of neurons that link several regions of the brain ...
... The cerebral cortex is configured into convolutions (folds) that maximize surface area The interior white matter consists of myelinated axons of neurons that link several regions of the brain ...
Control and Coordination(converted)
... The cerebral cortex is configured into convolutions (folds) that maximize surface area The interior white matter consists of myelinated axons of neurons that link several regions of the brain ...
... The cerebral cortex is configured into convolutions (folds) that maximize surface area The interior white matter consists of myelinated axons of neurons that link several regions of the brain ...
nervous system
... synapse, which cause the Na+ gates to open in the next neuron or effector Repolarization- ATP powers Na+ and K+ pump to reestablish resting potential Nerves can’t be stimulated during repolarization unless a huge stimulus occurs, “you stick your wet finger into an ...
... synapse, which cause the Na+ gates to open in the next neuron or effector Repolarization- ATP powers Na+ and K+ pump to reestablish resting potential Nerves can’t be stimulated during repolarization unless a huge stimulus occurs, “you stick your wet finger into an ...
Chapter 2 - Forensic Consultation
... activity involves complex activities which require communication among association areas across the brain such as: memory language attention meditation and spirituality consciousness ...
... activity involves complex activities which require communication among association areas across the brain such as: memory language attention meditation and spirituality consciousness ...
This newsletter is for your information only and is not a substitute for
... to turn off. These changes are most pronounced in the womb and during the first three years of life. Humans achieve their maximum brain cell density between the third and sixth month of gestation - the culmination of an explosive period of prenatal central nervous system growth. In the last trimeste ...
... to turn off. These changes are most pronounced in the womb and during the first three years of life. Humans achieve their maximum brain cell density between the third and sixth month of gestation - the culmination of an explosive period of prenatal central nervous system growth. In the last trimeste ...
Nervous System PowerPoint
... Buoyancy for the brain, c_____, chemical stability, f_____ system, clears out _____ (esp. when we sleep) Located between the _____ and _____ maters Flows uninterrupted through the CNS through the cerebrospinal canal of the spinal cord to the _____ in the _____ then exits CNS through veins draining ...
... Buoyancy for the brain, c_____, chemical stability, f_____ system, clears out _____ (esp. when we sleep) Located between the _____ and _____ maters Flows uninterrupted through the CNS through the cerebrospinal canal of the spinal cord to the _____ in the _____ then exits CNS through veins draining ...
Neuroplasticity

Neuroplasticity, also known as brain plasticity, is an umbrella term that encompasses both synaptic plasticity and non-synaptic plasticity—it refers to changes in neural pathways and synapses due to changes in behavior, environment, neural processes, thinking, and emotions – as well as to changes resulting from bodily injury. The concept of neuroplasticity has replaced the formerly-held position that the brain is a physiologically static organ, and explores how – and in which ways – the brain changes in the course of a lifetime.Neuroplasticity occurs on a variety of levels, ranging from cellular changes (due to learning) to large-scale changes involved in cortical remapping in response to injury. The role of neuroplasticity is widely recognized in healthy development, learning, memory, and recovery from brain damage. During most of the 20th century, neuroscientists maintained a scientific consensus that brain structure was relatively immutable after a critical period during early childhood. This belief has been challenged by findings revealing that many aspects of the brain remain plastic even into adulthood.Hubel and Wiesel had demonstrated that ocular dominance columns in the lowest neocortical visual area, V1, remained largely immutable after the critical period in development. Researchers also studied critical periods with respect to language; the resulting data suggested that sensory pathways were fixed after the critical period. However, studies determined that environmental changes could alter behavior and cognition by modifying connections between existing neurons and via neurogenesis in the hippocampus and in other parts of the brain, including in the cerebellum.Decades of research have shown that substantial changes occur in the lowest neocortical processing areas, and that these changes can profoundly alter the pattern of neuronal activation in response to experience. Neuroscientific research indicates that experience can actually change both the brain's physical structure (anatomy) and functional organization (physiology). As of 2014 neuroscientists are engaged in a reconciliation of critical-period studies (demonstrating the immutability of the brain after development) with the more recent research showing how the brain can, and does, change in response to hitherto unsuspected stimuli.