Chapter 33: The Atomic Nucleus and Radioactivity
... How does the source differ for a beam of gamma rays and a beam of X rays. Ans. Gamma rays come from the nuclei of some atoms. X rays come from the reconfiguration of electrons surrounding the nucleus of an atom. They may also be produced when an electron undergoes a large acceleration. ...
... How does the source differ for a beam of gamma rays and a beam of X rays. Ans. Gamma rays come from the nuclei of some atoms. X rays come from the reconfiguration of electrons surrounding the nucleus of an atom. They may also be produced when an electron undergoes a large acceleration. ...
Chapter 33: The Atomic Nucleus and Radioactivity
... How does the source differ for a beam of gamma rays and a beam of X rays. Ans. Gamma rays come from the nuclei of some atoms. X rays come from the reconfiguration of electrons surrounding the nucleus of an atom. They may also be produced when an electron undergoes a large acceleration. ...
... How does the source differ for a beam of gamma rays and a beam of X rays. Ans. Gamma rays come from the nuclei of some atoms. X rays come from the reconfiguration of electrons surrounding the nucleus of an atom. They may also be produced when an electron undergoes a large acceleration. ...
em waves dual nature atoms and nuclei
... 21. Draw a labeled diagram of Geiger – Marsden experiment on th scattering of α particles. How is the size of the nucleus estimated based on the experiment? 22. Derive an expression for the potential and kinetic energy of an electron in any orbit of a hydrogen atom. How does the potential energy cha ...
... 21. Draw a labeled diagram of Geiger – Marsden experiment on th scattering of α particles. How is the size of the nucleus estimated based on the experiment? 22. Derive an expression for the potential and kinetic energy of an electron in any orbit of a hydrogen atom. How does the potential energy cha ...
The Standard Model - University of Rochester
... of gluon-gluon activity Until enough energy is present in the gluon interactions to produce another quark pair So quarks can’t be separated And increasing gluon-gluon activity is why the Strong force increases with distance ...
... of gluon-gluon activity Until enough energy is present in the gluon interactions to produce another quark pair So quarks can’t be separated And increasing gluon-gluon activity is why the Strong force increases with distance ...
Overview of LENT Theory Low Energy Nuclear - Indico
... deuterons (or any other material) at high density would not behave as a mere collection of free deuterons. • Surface plasmons are generated when EM radiation in some form is adsorbed on a metallic surface leading to a coherent oscillation of the charged material on the surface • Giuliano used the EM ...
... deuterons (or any other material) at high density would not behave as a mere collection of free deuterons. • Surface plasmons are generated when EM radiation in some form is adsorbed on a metallic surface leading to a coherent oscillation of the charged material on the surface • Giuliano used the EM ...
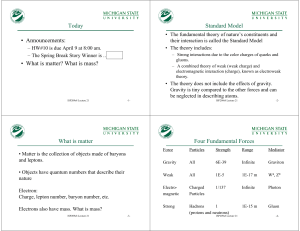
What is matter? - National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory
... Standard Model • The fundamental theory of nature’s constituents and their interaction is called the Standard Model • The theory includes: ...
... Standard Model • The fundamental theory of nature’s constituents and their interaction is called the Standard Model • The theory includes: ...
Astronomy 1010
... Positively charged protons are hold together by the strong force, which overcomes electrical repulsion. Negatively charged electrons are attracted to the nucleus. The number of protons in an atom is called the atomic number, which is unique for different chemical elements. ...
... Positively charged protons are hold together by the strong force, which overcomes electrical repulsion. Negatively charged electrons are attracted to the nucleus. The number of protons in an atom is called the atomic number, which is unique for different chemical elements. ...
The Age of the Earth
... Igneous rocks (formed from Earth’s magma solidifying) containing uranium-bearing minerals can be dated by the uranium-lead and lead-lead methods. 238U and 235U decay to the stable lead isotopes 206Pb and 207Pb, respectively. 238U decays to 206Pb with a half-life of 4.51 billion years. 235U decays to ...
... Igneous rocks (formed from Earth’s magma solidifying) containing uranium-bearing minerals can be dated by the uranium-lead and lead-lead methods. 238U and 235U decay to the stable lead isotopes 206Pb and 207Pb, respectively. 238U decays to 206Pb with a half-life of 4.51 billion years. 235U decays to ...
Lorentz violating field theories and nonperturbative physics
... be part of the “Theory of Everything.” Lorentz tests for ultrarelativistic particles like neutrinos are parameterized by the MAV. The fact that primary cosmic ray protons don’t decay into neutrons sets stronger limits on the neutrino MAV than time-of-flight ...
... be part of the “Theory of Everything.” Lorentz tests for ultrarelativistic particles like neutrinos are parameterized by the MAV. The fact that primary cosmic ray protons don’t decay into neutrons sets stronger limits on the neutrino MAV than time-of-flight ...
P. LeClair
... occupied states, so photons of energy less than this gap cannot be absorbed (since that would involve promoting an electron to a forbidden state). Thus, insulators are transparent for photon energies less than their energy gap. Metals have no such gap, and can essentially absorb photons of any energ ...
... occupied states, so photons of energy less than this gap cannot be absorbed (since that would involve promoting an electron to a forbidden state). Thus, insulators are transparent for photon energies less than their energy gap. Metals have no such gap, and can essentially absorb photons of any energ ...
From Landau levels to quantum Hall effects
... Find that a sharp Fermi surface can and does exist, but Fermi liquid is “marginal”, and has many peculiar properties. Effective mass m* is predicted to diverge (logarithmically) at low energies. Electric charge of quasiparticles is renormalized to zero, but ...
... Find that a sharp Fermi surface can and does exist, but Fermi liquid is “marginal”, and has many peculiar properties. Effective mass m* is predicted to diverge (logarithmically) at low energies. Electric charge of quasiparticles is renormalized to zero, but ...
Discovery of the atom and its components
... do not necessarily have the same number of neutrons. • Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. • One standard method of identifying isotopes is to write the mass number with a hyphen after the name of an element. • helium-3 or helium-4 ...
... do not necessarily have the same number of neutrons. • Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. • One standard method of identifying isotopes is to write the mass number with a hyphen after the name of an element. • helium-3 or helium-4 ...
Poster-Okubo - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... spin 1/2 quarks. Gail Hanson observed hadron jets and determined the jet axis by developing and applying the spheric-ity analysis to the hadrons in e+ e? events. She showed that events become more jet?like with increasing energy, contrary to what one expects from a simple phase space production mech ...
... spin 1/2 quarks. Gail Hanson observed hadron jets and determined the jet axis by developing and applying the spheric-ity analysis to the hadrons in e+ e? events. She showed that events become more jet?like with increasing energy, contrary to what one expects from a simple phase space production mech ...
Resonances and Excited States
... Particles that are unstable against decay by the strong interaction have mean lives of the order of 10 23 s and therefore cannot be detected by ordinary means. For example, if such a particle moves with nearly the speed of light, it can travel a distance of only about r = c" = 13 * 108 m>s2 110-23 s ...
... Particles that are unstable against decay by the strong interaction have mean lives of the order of 10 23 s and therefore cannot be detected by ordinary means. For example, if such a particle moves with nearly the speed of light, it can travel a distance of only about r = c" = 13 * 108 m>s2 110-23 s ...
PH1011 - Physics 1A
... The two first level modules in physics provide a balanced introduction to university physics, assuming a prior knowledge of mathematics and physics that corresponds to Higher grade passes at B in these subjects. The modules include appropriate coverage of the traditional disciplines of classical phy ...
... The two first level modules in physics provide a balanced introduction to university physics, assuming a prior knowledge of mathematics and physics that corresponds to Higher grade passes at B in these subjects. The modules include appropriate coverage of the traditional disciplines of classical phy ...
Ch 02
... *35 ssm Equipotential surface A has a potential of 5650 V, while equipotential surface B has a potential of 7850 V. A particle has a mass of 5.00 x 10-2 kg and a charge of +4.00 x 10-5 C. The particle has a speed of 2.00 m/s on surface A. An outside force is applied to the particle, and it moves to ...
... *35 ssm Equipotential surface A has a potential of 5650 V, while equipotential surface B has a potential of 7850 V. A particle has a mass of 5.00 x 10-2 kg and a charge of +4.00 x 10-5 C. The particle has a speed of 2.00 m/s on surface A. An outside force is applied to the particle, and it moves to ...