Chemical Energy
... Vocabulary List and Definitions 1. Attracting – To draw by a physical force causing or tending to cause to approach, adhere, or unite; pull. 2. Chemical Energy – Energy which is stored within the bonds of atoms and molecules of a a. substance. Released when they are broken and the substance undergoe ...
... Vocabulary List and Definitions 1. Attracting – To draw by a physical force causing or tending to cause to approach, adhere, or unite; pull. 2. Chemical Energy – Energy which is stored within the bonds of atoms and molecules of a a. substance. Released when they are broken and the substance undergoe ...
Process
... A process or transformation is a change in the state of the system over time, starting with a definite initial state and ending with a definite final state. The process is defined by a path, which is the continuous sequence of consecutive states through which the system passes, including the initial ...
... A process or transformation is a change in the state of the system over time, starting with a definite initial state and ending with a definite final state. The process is defined by a path, which is the continuous sequence of consecutive states through which the system passes, including the initial ...
Entropy and Free Energy
... has a fundamental molecular significance: It is a measure of the disorder of a system. This disorder can be asymmetry or displacement. This significance is relevant in the sub-atomic nature of the physical universe as well. Boltzmann proposed that entropy is related to the number of different micros ...
... has a fundamental molecular significance: It is a measure of the disorder of a system. This disorder can be asymmetry or displacement. This significance is relevant in the sub-atomic nature of the physical universe as well. Boltzmann proposed that entropy is related to the number of different micros ...
Energy Vocabulary
... absorption: the stopping of light by soaking it up sound energy: a form of energy made when something moves back and forth (vibration) vibrations: a rapid motion of the particles of an elastic body or substance back and forth chemical energy: energy that can be released by a chemical change fossil f ...
... absorption: the stopping of light by soaking it up sound energy: a form of energy made when something moves back and forth (vibration) vibrations: a rapid motion of the particles of an elastic body or substance back and forth chemical energy: energy that can be released by a chemical change fossil f ...
Lecture 6 Free Energy
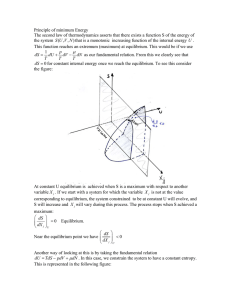
... It is the tendency of that molecular specie to chemically react, which depends on both its concentration and internal energy of the molecule. In a chemical reaction A ! B , the difference between A and B is amount of chemical energy available to do work per unit of molecule. At chemical equilibrium, ...
... It is the tendency of that molecular specie to chemically react, which depends on both its concentration and internal energy of the molecule. In a chemical reaction A ! B , the difference between A and B is amount of chemical energy available to do work per unit of molecule. At chemical equilibrium, ...
Unit 9: Thermodynamics Content Outline: The Mechanics of
... EA is greater for endothermic (non-spontaneous) reactions versus exothermic (spontaneous) reactions. Endothermic needs energy input; where as, exothermic has it already… as it will release the energy as the reaction occurs. 2. Transition State a. The state of two molecules interacting during a chemi ...
... EA is greater for endothermic (non-spontaneous) reactions versus exothermic (spontaneous) reactions. Endothermic needs energy input; where as, exothermic has it already… as it will release the energy as the reaction occurs. 2. Transition State a. The state of two molecules interacting during a chemi ...
Modes of Energy
... • A 10-N force is applied to push a block across a friction free surface for a displacement of 5.0 m to the right. W=Fd W=(10N)(5.0m) W=50J A force of 50 N acts on the block to move the block a horizontal distance of 3.0 m. How much work is done by the applied force? ...
... • A 10-N force is applied to push a block across a friction free surface for a displacement of 5.0 m to the right. W=Fd W=(10N)(5.0m) W=50J A force of 50 N acts on the block to move the block a horizontal distance of 3.0 m. How much work is done by the applied force? ...
1 Thermodynamics All biochemical and cellular processes obey the
... be predicted based simply on entropic considerations. (For example, the reaction 2 H2 + O2 → 2 H2O is usually spontaneous, in spite of the lower entropy associated with fewer products than reactants. Note, however, that if the heat released by the reaction is taken into account the overall entropy c ...
... be predicted based simply on entropic considerations. (For example, the reaction 2 H2 + O2 → 2 H2O is usually spontaneous, in spite of the lower entropy associated with fewer products than reactants. Note, however, that if the heat released by the reaction is taken into account the overall entropy c ...
Thermodynamics Energy Changes
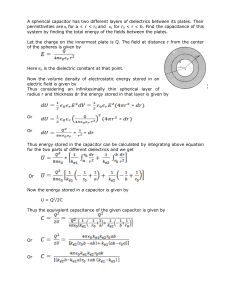
... To determine how energy is flowing we need to define the system and the surroundings. The system is the thing (chemical reaction) that we are interested in. The surroundings are everything else in the universe. Energy conversions are know as state functions, that is, only the starting and ending poi ...
... To determine how energy is flowing we need to define the system and the surroundings. The system is the thing (chemical reaction) that we are interested in. The surroundings are everything else in the universe. Energy conversions are know as state functions, that is, only the starting and ending poi ...