The Helmholtz Function
... Suppose W (other) 0 If we have a reversible process Q = TS and G = -W(other), so W(other) (Gi Gf ) Gf - Gi = -W (other) or The change in the Gibbs function gives the maximum energy that can be freed in an isothermal, isobaric process and made available for non-mechanical work. For this reas ...
... Suppose W (other) 0 If we have a reversible process Q = TS and G = -W(other), so W(other) (Gi Gf ) Gf - Gi = -W (other) or The change in the Gibbs function gives the maximum energy that can be freed in an isothermal, isobaric process and made available for non-mechanical work. For this reas ...
Phys115 attend Epotentials sol
... f) Find a location (A-G) that is at a higher electrical potential than at D. There is not one. g) Find a location (A-G) where a positive test charge would have a higher electrical potential energy than at D. There is not one. 2. Charges are placed as indicated in diagram A. The electrical potential ...
... f) Find a location (A-G) that is at a higher electrical potential than at D. There is not one. g) Find a location (A-G) where a positive test charge would have a higher electrical potential energy than at D. There is not one. 2. Charges are placed as indicated in diagram A. The electrical potential ...
5.1 The Flow of Energy in Living Things
... 5.2 The Laws of Thermodynamics • Laws of thermodynamics govern the energy changes of the universe, including those involved with any activity of an organism • 1st Law of Thermodynamics the total amount of energy in the universe remains constant energy can change from one state to another but it ...
... 5.2 The Laws of Thermodynamics • Laws of thermodynamics govern the energy changes of the universe, including those involved with any activity of an organism • 1st Law of Thermodynamics the total amount of energy in the universe remains constant energy can change from one state to another but it ...
Entropy, free energy and equilibrium
... Consider graphite and diamond – two forms of carbon. Is it perhaps surprising that diamond is less stable than graphite? ΔG°f (diamond) = 2.9 kJ/mol Free energy change for conversion of diamond into CO2 is larger than for conversion of graphite into CO2 ...
... Consider graphite and diamond – two forms of carbon. Is it perhaps surprising that diamond is less stable than graphite? ΔG°f (diamond) = 2.9 kJ/mol Free energy change for conversion of diamond into CO2 is larger than for conversion of graphite into CO2 ...
Energy can be transferred - cms16-17
... the energy from one place to another · Electricity in a wire transfers the electrical energy · Sound energy is transferred from a musical instrument to the ear ...
... the energy from one place to another · Electricity in a wire transfers the electrical energy · Sound energy is transferred from a musical instrument to the ear ...
PHYSICS COURSE SYLLABUS Lucy C. Laney High School School
... a. Analyze, evaluate, and apply the principle of conservation of energy and measure the components of work-energy theorem by • describing total energy in a closed system. • identifying different types of potential energy. • calculating kinetic energy given mass and velocity. • relating transformatio ...
... a. Analyze, evaluate, and apply the principle of conservation of energy and measure the components of work-energy theorem by • describing total energy in a closed system. • identifying different types of potential energy. • calculating kinetic energy given mass and velocity. • relating transformatio ...
work and energy
... the potential energy at the top of the tall platform is 50 J, what is the potential energy at the other positions shown on the stair steps and the incline? ...
... the potential energy at the top of the tall platform is 50 J, what is the potential energy at the other positions shown on the stair steps and the incline? ...
A lever is used to lift a rock. Will the work done by the person on the
... Quiz: A sled and rider with a total mass of 40 kg are perched at the top of the hill shown. Suppose that 2000 J of work is done against friction as the sled travels from the top (at 40 m) to the second hump (at 30 m). Will the sled make it to the top of the second hump if no kinetic energy is given ...
... Quiz: A sled and rider with a total mass of 40 kg are perched at the top of the hill shown. Suppose that 2000 J of work is done against friction as the sled travels from the top (at 40 m) to the second hump (at 30 m). Will the sled make it to the top of the second hump if no kinetic energy is given ...
Thermodynamic Concep..
... solvent. Thus, in essentially all biochemical reactions, water is always at its standard state (which will mean we can ignore it in our thermodynamic calculations for the most part). You should also note that in biochemistry, unlike chemistry, the standard state of H+ is 10-7 M (pH 7.0) rather than ...
... solvent. Thus, in essentially all biochemical reactions, water is always at its standard state (which will mean we can ignore it in our thermodynamic calculations for the most part). You should also note that in biochemistry, unlike chemistry, the standard state of H+ is 10-7 M (pH 7.0) rather than ...
CHAP4
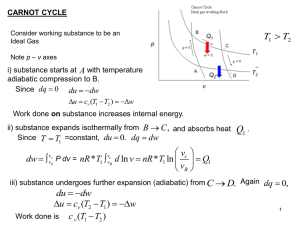
... The Carnot cycle may be one the the most popular examples used in the study of (general) Thermodynamics. Tsonis discusses it in disproportionate detail on pp. 49-56, and the student is encouraged to read this. The Carnot cycle illustrates several aspects of the Second Law, and also defines thermodyn ...
... The Carnot cycle may be one the the most popular examples used in the study of (general) Thermodynamics. Tsonis discusses it in disproportionate detail on pp. 49-56, and the student is encouraged to read this. The Carnot cycle illustrates several aspects of the Second Law, and also defines thermodyn ...
3.2 “Conserving” Energy
... • Energy causes change. • Some changes that occur in systems include: ...
... • Energy causes change. • Some changes that occur in systems include: ...
ENERGY
... of the earth’s surface (you in your seat) Chemical Energy – Energy stored in elements/compounds that will be released during a chemical reaction (batteries, food) Electromagnetic Energy - Energy in the form of wavelengths, usually light. ...
... of the earth’s surface (you in your seat) Chemical Energy – Energy stored in elements/compounds that will be released during a chemical reaction (batteries, food) Electromagnetic Energy - Energy in the form of wavelengths, usually light. ...