Article interaction G x tabac - Hal-CEA
... unchanged results. Indeed, most of the mothers which smoked during pregnancy also continued to smoke during the early-childhood of their child. Analyses considering ETS ‘in-utero’ only were not possible here because of too small sample sizes. We finally also considered ETS in early childhood defined ...
... unchanged results. Indeed, most of the mothers which smoked during pregnancy also continued to smoke during the early-childhood of their child. Analyses considering ETS ‘in-utero’ only were not possible here because of too small sample sizes. We finally also considered ETS in early childhood defined ...
HLA imputation - BioMed Central
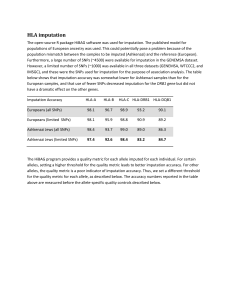
... populations of European ancestry was used. This could potentially pose a problem because of the population mismatch between the samples to be imputed (Ashkenazi) and the reference (European). Furthermore, a large number of SNPs (~4500) were available for imputation in the GENEMSA dataset. However, a ...
... populations of European ancestry was used. This could potentially pose a problem because of the population mismatch between the samples to be imputed (Ashkenazi) and the reference (European). Furthermore, a large number of SNPs (~4500) were available for imputation in the GENEMSA dataset. However, a ...
The Integrated Phenotype
... morphology and evolution of form (see Afterword by Chernoff and Magwene 1999 in Olson and Millers 1958; also see Cheverud 1982, 1996; Klingenberg 2010). From the early formal discussions of phenotypic integration, the joint importance of development, environment, and differentiation in patterns of i ...
... morphology and evolution of form (see Afterword by Chernoff and Magwene 1999 in Olson and Millers 1958; also see Cheverud 1982, 1996; Klingenberg 2010). From the early formal discussions of phenotypic integration, the joint importance of development, environment, and differentiation in patterns of i ...
Similar traits, different genes? Examining convergent evolution in
... is often also evident in agricultural weeds – highly competitive plants that repeatedly invade the disturbed cropland soils (Basu et al. 2004). Despite sometimes being unrelated, agricultural weeds often converge on similar adaptive traits such as rapid growth, high seed production, increased seed d ...
... is often also evident in agricultural weeds – highly competitive plants that repeatedly invade the disturbed cropland soils (Basu et al. 2004). Despite sometimes being unrelated, agricultural weeds often converge on similar adaptive traits such as rapid growth, high seed production, increased seed d ...
Hierarchical Nuclear and Cytoplasmic Genetic
... and repeated measures of size at different time intervals can be used to calculate growth rates. By measuring all growth descriptors and chemical defense phenotypes in the same experiment on the same individuals, we are able to reduce the amount of environmental variation that may differentially infl ...
... and repeated measures of size at different time intervals can be used to calculate growth rates. By measuring all growth descriptors and chemical defense phenotypes in the same experiment on the same individuals, we are able to reduce the amount of environmental variation that may differentially infl ...
SARS Outbreaks in Ontario, Hong Kong and Singapore: the role of
... Ott, J, 1991 Analysis of Human Genetic Linkage. The Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore and London ...
... Ott, J, 1991 Analysis of Human Genetic Linkage. The Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore and London ...
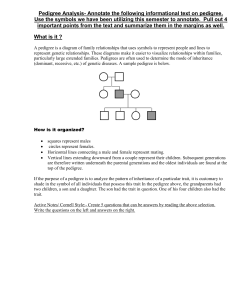
Pedigree Analysis
... In the pedigree above, the grandparents had two children, a son and a daughter. The son had the trait in question. One of his four children also had the trait. In the exercises below, assume that the trait in question is a genetic disease or abnormality. We will learn patterns of inheritance that ha ...
... In the pedigree above, the grandparents had two children, a son and a daughter. The son had the trait in question. One of his four children also had the trait. In the exercises below, assume that the trait in question is a genetic disease or abnormality. We will learn patterns of inheritance that ha ...
Pedigree Analysis - Westwind Alternate School
... the children of two parents that are not affected? 5. We will determine if the pedigree below can be for a trait that is autosomal recessive. a) Write the genotype of each individual next to the symbol. ...
... the children of two parents that are not affected? 5. We will determine if the pedigree below can be for a trait that is autosomal recessive. a) Write the genotype of each individual next to the symbol. ...
Genetic epidemiology of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis
... chromosomal location without any prior knowledge of the position or function of the gene. Positional cloning requires collection of families with multiple affected individuals so that linkage analysis can be performed. This can be done by one of two methods: constructing a model to explain the inher ...
... chromosomal location without any prior knowledge of the position or function of the gene. Positional cloning requires collection of families with multiple affected individuals so that linkage analysis can be performed. This can be done by one of two methods: constructing a model to explain the inher ...
Modest evidence for linkage and possible confirmation of
... The second approach uses the family based association test (FBAT) [Rabinowitz and Laird, 2000]. In addition to being able to use extended families, the FBAT also handles missing data appropriately, and so does not waste information. Association between a specific allele and schizophrenia is assessed ...
... The second approach uses the family based association test (FBAT) [Rabinowitz and Laird, 2000]. In addition to being able to use extended families, the FBAT also handles missing data appropriately, and so does not waste information. Association between a specific allele and schizophrenia is assessed ...
Entering the second century of maize quantitative genetics
... that read-depth variants (a surrogate for moderate (2–10 kb) insertions, duplications, and deletions) were enriched for significant associations with phenotypic differences, indicating that SNPs do not capture the entirety of genetic variation. Thus, how effective this sort of projection will prove ...
... that read-depth variants (a surrogate for moderate (2–10 kb) insertions, duplications, and deletions) were enriched for significant associations with phenotypic differences, indicating that SNPs do not capture the entirety of genetic variation. Thus, how effective this sort of projection will prove ...
Simple Algorithms to Calculate Asymptotic Null Distributions of
... on this finding, Yamada and Okada (2009) proposed an optimal dose-effect mode trend test where the genetic effect of the heterozygous genotype is restricted between two homozygous genotypes. The performance of the test of Yamada and Okada (2009) is similar to that of the CLRT. Another recent propose ...
... on this finding, Yamada and Okada (2009) proposed an optimal dose-effect mode trend test where the genetic effect of the heterozygous genotype is restricted between two homozygous genotypes. The performance of the test of Yamada and Okada (2009) is similar to that of the CLRT. Another recent propose ...
Alleles of a reelin CGG repeat do not convey
... Our findings agree with those recently published by Krebs et al. [2002], who analyzed a sample of 117 simplex and 50 multiplex families. The estimated allele distribution from our families is quite similar to that estimated by both the Persico and Krebs studies, showing two common alleles with 8 and ...
... Our findings agree with those recently published by Krebs et al. [2002], who analyzed a sample of 117 simplex and 50 multiplex families. The estimated allele distribution from our families is quite similar to that estimated by both the Persico and Krebs studies, showing two common alleles with 8 and ...
Safety Administration Implementation Regulation on Agricultural
... environment, as well as its impact produced via the occurrence of genetic information exchange with other organisms. People involved in genetic engineering work must make precise evaluation on genetic manipulation, including gene transfer methods, characteristics of vectors, and the source,. functio ...
... environment, as well as its impact produced via the occurrence of genetic information exchange with other organisms. People involved in genetic engineering work must make precise evaluation on genetic manipulation, including gene transfer methods, characteristics of vectors, and the source,. functio ...
Application of Pedigree Analysis
... 1. The pedigree below is for a genetic disease or abnormality. We do not yet know if it is dominant or recessive. We will determine if it is possible that the trait is autosomal dominant. If the trait were dominant, we would use the following designations: A = the trait (a genetic disease or abnorma ...
... 1. The pedigree below is for a genetic disease or abnormality. We do not yet know if it is dominant or recessive. We will determine if it is possible that the trait is autosomal dominant. If the trait were dominant, we would use the following designations: A = the trait (a genetic disease or abnorma ...
How and When Selection Experiments Might Actually be
... for maintaining particular patterns of variation observed in nature. The comparative approach can identify the possible selective agents but will not often be conclusive because phenotypic variation is usually associated with correlated variation in several environmental factors. Laboratory natural ...
... for maintaining particular patterns of variation observed in nature. The comparative approach can identify the possible selective agents but will not often be conclusive because phenotypic variation is usually associated with correlated variation in several environmental factors. Laboratory natural ...
QTXNetwork Manual.pdf
... On the right side of the equation symbol is the code for the marker type. The marker code should always be a single character (a number or a letter). The symbol dot “.” is used to represent missing marker data or trait value. It is not necessary to specify codes for all possible marker types except ...
... On the right side of the equation symbol is the code for the marker type. The marker code should always be a single character (a number or a letter). The symbol dot “.” is used to represent missing marker data or trait value. It is not necessary to specify codes for all possible marker types except ...
Mending Mendelism
... terms? Most people are surprised to learn that there is none. This reveals one of three major conceptions needing realignment (at least, among non-geneticists). Textbooks rarely address this matter. In the virtual silence, two conceptions typically emerge—both mistaken. First, some conceive dominanc ...
... terms? Most people are surprised to learn that there is none. This reveals one of three major conceptions needing realignment (at least, among non-geneticists). Textbooks rarely address this matter. In the virtual silence, two conceptions typically emerge—both mistaken. First, some conceive dominanc ...
Integration of QTL Information with Traditional Animal Breeding
... evidence of the power of quantitative genetic approaches to selection. The success of quantitative genetic approaches does, however, not mean that genetic progress could not be enhanced if we could gain insight into the black box of quantitative traits. By being able to study the genetic make-up of ...
... evidence of the power of quantitative genetic approaches to selection. The success of quantitative genetic approaches does, however, not mean that genetic progress could not be enhanced if we could gain insight into the black box of quantitative traits. By being able to study the genetic make-up of ...
Twin study

Twin studies reveal the absolute and relative importance of environmental and genetic influences on individuals in a sample. Twin research is considered a key tool in behavioral genetics and in content fields, from biology to psychology. Twin studies are part of the methods used in behavior genetics, which includes all data that are genetically informative – siblings, adoptees, pedigree data etc.Twins are a valuable source for observation because they allow the study of varying family environments (across pairs) and widely differing genetic makeup: ""identical"" or monozygotic (MZ) twins share nearly 100% of their genes, which means that most differences between the twins (such as height, susceptibility to boredom, intelligence, depression, etc.) is due to experiences that one twin has but not the other twin. ""Fraternal"" or dizygotic (DZ) twins share only about 50% of their genes. Thus powerful tests of the effects of genes can be made. Twins share many aspects of their environment (e.g., uterine environment, parenting style, education, wealth, culture, community) by virtue of being born in the same time and place. The presence of a given genetic trait in only one member of a pair of identical twins (called discordance) provides a powerful window into environmental effects.The classical twin design compares the similarity of monozygotic (identical) and dizygotic (fraternal) twins. If identical twins are considerably more similar than fraternal twins (which is found for most traits), this implicates that genes play an important role in these traits. By comparing many hundreds of families of twins, researchers can then understand more about the roles of genetic effects, shared environment, and unique environment in shaping behavior.Modern twin studies have shown that almost all traits are in part influenced by genetic differences, with some characteristics showing a strong influence (e.g. height), others an intermediate level (e.g. personality traits) and some more complex heritabilities, with evidence for different genes affecting different aspects of the trait — as in the case of autism.