Difference Mechanisms - Philsci-Archive
... the phenomenon under investigation. For example, a question such as, How do rats form spatial memories of their environments?, is answered by elucidating the regular causal mechanisms responsible for the individual development of spatial memory in rats. But consider a slightly different question: Ho ...
... the phenomenon under investigation. For example, a question such as, How do rats form spatial memories of their environments?, is answered by elucidating the regular causal mechanisms responsible for the individual development of spatial memory in rats. But consider a slightly different question: Ho ...
How many lethal alleles? - University of Edinburgh
... population is important for our understanding of population genetics and evolution, and yet there have been few attempts to measure their number in wild populations. A new study has revealed unexpectedly low numbers of segregating lethal alleles in two species of fish. More experiments are needed, h ...
... population is important for our understanding of population genetics and evolution, and yet there have been few attempts to measure their number in wild populations. A new study has revealed unexpectedly low numbers of segregating lethal alleles in two species of fish. More experiments are needed, h ...
molecular approaches in natural resource conservation
... resource management strategies were determined by the collection and interpretation of basic field data. Today, as challenges to the sustainability and conservation of our natural resources arise, managers often need data that cannot be acquired using conventional methods. For example, a natural res ...
... resource management strategies were determined by the collection and interpretation of basic field data. Today, as challenges to the sustainability and conservation of our natural resources arise, managers often need data that cannot be acquired using conventional methods. For example, a natural res ...
Developing Conclusions About Different Modes of Inheritance
... The fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster is a very useful organism for genetic research and has probably been used to define more fundamental genetic principles than any other ulticellular eukaryote. One person responsible for development of D. melanogaster into a model genetic system was named Thomas ...
... The fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster is a very useful organism for genetic research and has probably been used to define more fundamental genetic principles than any other ulticellular eukaryote. One person responsible for development of D. melanogaster into a model genetic system was named Thomas ...
Section 2
... Punnett squares allow you to predict the genotype and phenotype combinations in genetic crosses using mathematical probability. ...
... Punnett squares allow you to predict the genotype and phenotype combinations in genetic crosses using mathematical probability. ...
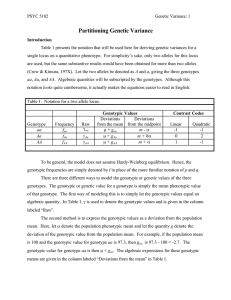
Introduction to Genetic Algorithms
... through the juxtaposition of short, low-order, highperformance schemata, called the building blocks ...
... through the juxtaposition of short, low-order, highperformance schemata, called the building blocks ...
Genotype Discrimination: The complex case for some legislative protection. Henry T. Greely. 149 U. Pa. L. Rev. 1483 (May 2001)
... Start with some definitions. People do not have "genes" for disease. As far as we know, all humans have the same set of genes, about 32,000 of them, n1 except for those few genes on the Y chromosome, found in men and not in women. n2 Those genes come in many variations; indeed, for the most part, t ...
... Start with some definitions. People do not have "genes" for disease. As far as we know, all humans have the same set of genes, about 32,000 of them, n1 except for those few genes on the Y chromosome, found in men and not in women. n2 Those genes come in many variations; indeed, for the most part, t ...
Patterns of Heredity and Human Genetics What You’ll Learn
... carriers is two in three for each because they can have only two possible genotypes—homozygous normal and heterozygous. The homozygous recessive genotype is not a possibility in these individuals because neither of them shows the affected phenotype. Because none of the children in generation III are ...
... carriers is two in three for each because they can have only two possible genotypes—homozygous normal and heterozygous. The homozygous recessive genotype is not a possibility in these individuals because neither of them shows the affected phenotype. Because none of the children in generation III are ...
Pedigrees
... genetic history. Pedigrees are used to find out the probability of a child having a disorder in a particular family. To begin to interpret a pedigree, determine if the disease or condition is autosomal or Xlinked and dominant or recessive. ...
... genetic history. Pedigrees are used to find out the probability of a child having a disorder in a particular family. To begin to interpret a pedigree, determine if the disease or condition is autosomal or Xlinked and dominant or recessive. ...
Unit 04 Part III - Madeira City Schools
... • Pedigrees are family trees that explain your genetic history. • Pedigrees are used to find out the probability of a child having a disorder in a particular family. • To begin to interpret a pedigree, determine if the disease or condition is autosomal or X-linked and dominant or recessive. ...
... • Pedigrees are family trees that explain your genetic history. • Pedigrees are used to find out the probability of a child having a disorder in a particular family. • To begin to interpret a pedigree, determine if the disease or condition is autosomal or X-linked and dominant or recessive. ...
Inheritance (heredity): The transmission of genes from parents to
... * Alleles IA & IB are dominant over i & are fally expressed when they present together (codominance). Mating between AB & AB can produce A,AB & B with a ratio of 1 : 2 : 1 respectively. * Type AB is known as universal acceptor & type O is known as universal donor, why? Rh factor: is inherited separa ...
... * Alleles IA & IB are dominant over i & are fally expressed when they present together (codominance). Mating between AB & AB can produce A,AB & B with a ratio of 1 : 2 : 1 respectively. * Type AB is known as universal acceptor & type O is known as universal donor, why? Rh factor: is inherited separa ...
Exploring the association between the 2
... the 2-repeat allele, in comparison with 3-repeat and 4-repeat alleles, had the lowest level of promoter activity. The results of the study by Guo et al. suggest that pooling together the 2-repeat and 3-repeat alleles may be incorrect and that the 2-repeat allele should be examined in isolation becau ...
... the 2-repeat allele, in comparison with 3-repeat and 4-repeat alleles, had the lowest level of promoter activity. The results of the study by Guo et al. suggest that pooling together the 2-repeat and 3-repeat alleles may be incorrect and that the 2-repeat allele should be examined in isolation becau ...
Informed Consent for Prenatal Diagnosis by
... 1) I understand that I may feel some discomfort during the amniocentesis as the needle passes into and out of my uterus. 2) I understand that there is a chance for needle damage to me and to the fetus. This risk is thought to be small as the needle is very thin, and the ultrasound is used to find a ...
... 1) I understand that I may feel some discomfort during the amniocentesis as the needle passes into and out of my uterus. 2) I understand that there is a chance for needle damage to me and to the fetus. This risk is thought to be small as the needle is very thin, and the ultrasound is used to find a ...
Chapter 1
... • The behavioural similarity of identical twins is compared with the behavioural similarity of fraternal twins. • Identical twins (monzygotic twins) develop from a single fertilized egg that splits into two genetically identical replicas, each of which becomes a person. • Fraternal twins (dizigotic ...
... • The behavioural similarity of identical twins is compared with the behavioural similarity of fraternal twins. • Identical twins (monzygotic twins) develop from a single fertilized egg that splits into two genetically identical replicas, each of which becomes a person. • Fraternal twins (dizigotic ...
Genetic tradeâ•`offs and conditional neutrality
... antagonistic pleiotropy and conditional neutrality requires large field studies that explicitly consider the fitness effects of alleles in their native habitats (Anderson et al. 2011b). To investigate the genomic basis of local adaptation, we develop a novel permutation analysis of allele frequency ...
... antagonistic pleiotropy and conditional neutrality requires large field studies that explicitly consider the fitness effects of alleles in their native habitats (Anderson et al. 2011b). To investigate the genomic basis of local adaptation, we develop a novel permutation analysis of allele frequency ...
Title: Genetic architecture of contemporary adaptation to biotic
... 2013). These insects exploit a broad variety of host plants from the family Sapindaceae (CARROLL 2007). In North America and Australia different species of soapberry bug show ongoing rapid evolution of their mouthparts (stylets or “beaks”) to better match the seed defense structures of newly introdu ...
... 2013). These insects exploit a broad variety of host plants from the family Sapindaceae (CARROLL 2007). In North America and Australia different species of soapberry bug show ongoing rapid evolution of their mouthparts (stylets or “beaks”) to better match the seed defense structures of newly introdu ...
behavior and neurobiology
... changes in the density of neurotransmitter receptor proteins, synthesis of neurotransmitters, and/or the structure or quantity of signaling molecules or transcription factors downstream of receptors might underlie evolutionary changes in behavior. Alternatively, changes in the development or connect ...
... changes in the density of neurotransmitter receptor proteins, synthesis of neurotransmitters, and/or the structure or quantity of signaling molecules or transcription factors downstream of receptors might underlie evolutionary changes in behavior. Alternatively, changes in the development or connect ...
Genetic Crosses
... Four alleles allows for 16 possible combinations of alleles. (16 box Punnett square) Four combinations of alleles can be determined by using the “foil” method of distribution. YyTt First pair of alleles = YT (dominant ) Outer pair of alleles = Yt (heterozygous) Inner pair of alleles = yT (hete ...
... Four alleles allows for 16 possible combinations of alleles. (16 box Punnett square) Four combinations of alleles can be determined by using the “foil” method of distribution. YyTt First pair of alleles = YT (dominant ) Outer pair of alleles = Yt (heterozygous) Inner pair of alleles = yT (hete ...
1 Sequential elimination of major-effect contributors
... Several quantitative trait loci (QTL) mapping strategies have successfully identified major-effect loci based on their strong association with the phenotype in segregating populations. Although mapping strategies have been designed to detect minor-effect loci, many of these strategies have had poor ...
... Several quantitative trait loci (QTL) mapping strategies have successfully identified major-effect loci based on their strong association with the phenotype in segregating populations. Although mapping strategies have been designed to detect minor-effect loci, many of these strategies have had poor ...
apbio ch 14 study guide
... o Offspring of a cross between heterozygotes show three phenotypes: each parental phenotype and the heterozygous phenotype. o The phenotypic and genotypic ratios are identical: 1:2:1. ...
... o Offspring of a cross between heterozygotes show three phenotypes: each parental phenotype and the heterozygous phenotype. o The phenotypic and genotypic ratios are identical: 1:2:1. ...
De Jong`s Sphere Model Test for A Social
... in selecting parents. In choosing two individuals to mate together there are no constraints [36]. Many studies have been done to tackle this problem trying to overcome it, and trying to design structured population with some control on how individuals interact [36]. ...
... in selecting parents. In choosing two individuals to mate together there are no constraints [36]. Many studies have been done to tackle this problem trying to overcome it, and trying to design structured population with some control on how individuals interact [36]. ...
Twin study

Twin studies reveal the absolute and relative importance of environmental and genetic influences on individuals in a sample. Twin research is considered a key tool in behavioral genetics and in content fields, from biology to psychology. Twin studies are part of the methods used in behavior genetics, which includes all data that are genetically informative – siblings, adoptees, pedigree data etc.Twins are a valuable source for observation because they allow the study of varying family environments (across pairs) and widely differing genetic makeup: ""identical"" or monozygotic (MZ) twins share nearly 100% of their genes, which means that most differences between the twins (such as height, susceptibility to boredom, intelligence, depression, etc.) is due to experiences that one twin has but not the other twin. ""Fraternal"" or dizygotic (DZ) twins share only about 50% of their genes. Thus powerful tests of the effects of genes can be made. Twins share many aspects of their environment (e.g., uterine environment, parenting style, education, wealth, culture, community) by virtue of being born in the same time and place. The presence of a given genetic trait in only one member of a pair of identical twins (called discordance) provides a powerful window into environmental effects.The classical twin design compares the similarity of monozygotic (identical) and dizygotic (fraternal) twins. If identical twins are considerably more similar than fraternal twins (which is found for most traits), this implicates that genes play an important role in these traits. By comparing many hundreds of families of twins, researchers can then understand more about the roles of genetic effects, shared environment, and unique environment in shaping behavior.Modern twin studies have shown that almost all traits are in part influenced by genetic differences, with some characteristics showing a strong influence (e.g. height), others an intermediate level (e.g. personality traits) and some more complex heritabilities, with evidence for different genes affecting different aspects of the trait — as in the case of autism.