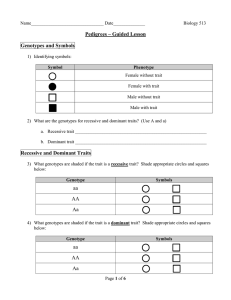
X-linked Recessive Traits
... 14) (a) In an X-linked recessive trait, which gender is more likely to show the trait and thus be shaded more often in the pedigree? (b) What would this individual’s symbol look like? Draw it. (c) How often would you see this symbol appear in a pedigree compared to other symbols? ...
... 14) (a) In an X-linked recessive trait, which gender is more likely to show the trait and thus be shaded more often in the pedigree? (b) What would this individual’s symbol look like? Draw it. (c) How often would you see this symbol appear in a pedigree compared to other symbols? ...
Gene affecting stature and body size in mammalian species
... within population variation in body size. In the study of Valdar et al. [26] QTL ...
... within population variation in body size. In the study of Valdar et al. [26] QTL ...
Chapter 3
... • Actual approaches for detecting aggregation depend on the nature of the phenotype, but the common factor in existing approaches is that they are taken without any specific genetic model in mind. • The basic design of familial aggregation studies typically involves sampling families • In most place ...
... • Actual approaches for detecting aggregation depend on the nature of the phenotype, but the common factor in existing approaches is that they are taken without any specific genetic model in mind. • The basic design of familial aggregation studies typically involves sampling families • In most place ...
FREE Sample Here - test bank and solution manual for
... characteristics frequently associated with race (e.g., skin color, eye shape, hair color and texture), these traits do not occur as “either–or” features; rather, they are distributed continuously throughout the human population. 2.14. Dr. Johnson corrects a student who talks about “genetic racial di ...
... characteristics frequently associated with race (e.g., skin color, eye shape, hair color and texture), these traits do not occur as “either–or” features; rather, they are distributed continuously throughout the human population. 2.14. Dr. Johnson corrects a student who talks about “genetic racial di ...
The Experiments of Gregor Mendel
... determined by factors that are passed from one parental generation to the next. Scientists call the factors that are passed from parent to offspring genes. ...
... determined by factors that are passed from one parental generation to the next. Scientists call the factors that are passed from parent to offspring genes. ...
Curt Stern on Somatic Crossing Over
... distinct; and that, as for meiosis, somatic crossing over in inversion heterozygotes led to defective products. In later years, the use of Minute heterozygotes to expand the size of homozygous normal sectors became a powerful technique to understand developmental patterns of Drosophila. Though somat ...
... distinct; and that, as for meiosis, somatic crossing over in inversion heterozygotes led to defective products. In later years, the use of Minute heterozygotes to expand the size of homozygous normal sectors became a powerful technique to understand developmental patterns of Drosophila. Though somat ...
Heredity - PellitoScience
... What did Gregor Mendel discover about heredity? • The seven different characteristics Mendel studied were plant height, flower and pod position, seed shape, seed color, pod shape, pod color, and flower color. • Each characteristic had two different forms. These different forms are called traits. ...
... What did Gregor Mendel discover about heredity? • The seven different characteristics Mendel studied were plant height, flower and pod position, seed shape, seed color, pod shape, pod color, and flower color. • Each characteristic had two different forms. These different forms are called traits. ...
Understanding-Human-Development-2nd-Edition
... Rationale: Meiosis is the process of cell division that yields sperm and ova, each including one half of a full set of chromosomes. In males, meiosis occurs in the texts. 2.33. Suppose that a human female is accidentally exposed to a poison at one of four different points in development. If the effe ...
... Rationale: Meiosis is the process of cell division that yields sperm and ova, each including one half of a full set of chromosomes. In males, meiosis occurs in the texts. 2.33. Suppose that a human female is accidentally exposed to a poison at one of four different points in development. If the effe ...
tutorial in biostatistics genetic mapping of complex traits
... Simple genetic models are derived from Mendelian laws of inheritance. Each individual has two sets of 23 chromosomes, one maternal and one paternal in origin. One of the 23 pairs of chromosomes are the sex chromosomes, and we shall concern ourselves with the remaining 22 pairs of autosomal chromosom ...
... Simple genetic models are derived from Mendelian laws of inheritance. Each individual has two sets of 23 chromosomes, one maternal and one paternal in origin. One of the 23 pairs of chromosomes are the sex chromosomes, and we shall concern ourselves with the remaining 22 pairs of autosomal chromosom ...
Overview: Alcohol and Nicotine Use and Dependence: Common
... Individuals at high genetic risk of alcohol dependence are on average also at increased genetic risk of becoming regular smokers, an outcome that usually precedes the onset of alcohol dependence. ...
... Individuals at high genetic risk of alcohol dependence are on average also at increased genetic risk of becoming regular smokers, an outcome that usually precedes the onset of alcohol dependence. ...
Means (*) and standard deviation (s) of quantitative
... Individuals at high genetic risk of alcohol dependence are on average also at increased genetic risk of becoming regular smokers, an outcome that usually precedes the onset of alcohol dependence. ...
... Individuals at high genetic risk of alcohol dependence are on average also at increased genetic risk of becoming regular smokers, an outcome that usually precedes the onset of alcohol dependence. ...
Biology CLIL lesson Mendel`s work
... The F1 generation showed only one character that was present in P1. The other character reappeared in the F2. Mendel concluded that the F1 plants must contain 2 distinct factors, one for each character. The character that was seen in the F1 is called DOMINANT. The character that was not seen in the ...
... The F1 generation showed only one character that was present in P1. The other character reappeared in the F2. Mendel concluded that the F1 plants must contain 2 distinct factors, one for each character. The character that was seen in the F1 is called DOMINANT. The character that was not seen in the ...
Fun With Mendelian Genetics Introduction Charles Darwin`s and
... 8. What is the probability that Debbie and her partner could have a child who is heterozygous for hand-clasping? _____________________________ Mendel’s Fourth Discovery The way in which the paired alleles for one trait are segregated is TOTALLY INDEPENDENT of the way in which paired alleles for a ...
... 8. What is the probability that Debbie and her partner could have a child who is heterozygous for hand-clasping? _____________________________ Mendel’s Fourth Discovery The way in which the paired alleles for one trait are segregated is TOTALLY INDEPENDENT of the way in which paired alleles for a ...
Mendelian Genetics and Chromosomes PPT
... also contains Rh factor, + or – with standard Mendelian rules ...
... also contains Rh factor, + or – with standard Mendelian rules ...
A SAS/IML® Program for Mapping QTL in Line Crosses
... QTL. This design involves four inbred lines and allows simultaneous estimation and test of several QTL effects. If one effect is significant, the QTL is declared as significant. Therefore, the power of QTL detection can be increased. In addition, the method can detect more QTL because it simultaneou ...
... QTL. This design involves four inbred lines and allows simultaneous estimation and test of several QTL effects. If one effect is significant, the QTL is declared as significant. Therefore, the power of QTL detection can be increased. In addition, the method can detect more QTL because it simultaneou ...
The Evolution of Genetic Architecture
... by Cheverud & Routman (1995), who developed an explicit model of “physiological” epistasis defined without regard to allele frequencies and showed how this physiological epistasis differed from the Fisherian notion of statistical epistasis and even contributed to the additive genetic variance. The Fi ...
... by Cheverud & Routman (1995), who developed an explicit model of “physiological” epistasis defined without regard to allele frequencies and showed how this physiological epistasis differed from the Fisherian notion of statistical epistasis and even contributed to the additive genetic variance. The Fi ...
How to obtain and recognize partial-diploid strains that are duplicated... chromosome segments.
... information on individual duplication-generating rearrangements, see Perkins (1997). For a listing of rearrangement strains that generate duplications, see Part V E in the FGSC Catalog. Because segmental duplications are unstable, duplication strains are usually not carried in stock, but are obtaine ...
... information on individual duplication-generating rearrangements, see Perkins (1997). For a listing of rearrangement strains that generate duplications, see Part V E in the FGSC Catalog. Because segmental duplications are unstable, duplication strains are usually not carried in stock, but are obtaine ...
The quantitative genetic theory of parental effects
... in parents. In the first section I give a detailed exposition of the Kirkpatrick–Lande model (hence forth the K–L model; Kirkpatrick and Lande 1989, 1992; Lande and Kirkpatrick 1990), a model that generalized a great deal of previous theory in which the phenotype and fitness of an individual was influe ...
... in parents. In the first section I give a detailed exposition of the Kirkpatrick–Lande model (hence forth the K–L model; Kirkpatrick and Lande 1989, 1992; Lande and Kirkpatrick 1990), a model that generalized a great deal of previous theory in which the phenotype and fitness of an individual was influe ...
Vorms final version + images
... fascinating case of interdisciplinary research. The laying and consolidation of its essential components, in the 1910’s and 1920’s, resulted to a large extent from the integration of two modes of analysis, corresponding to two different disciplines: the Mendelian study of heredity (Mendelism), and c ...
... fascinating case of interdisciplinary research. The laying and consolidation of its essential components, in the 1910’s and 1920’s, resulted to a large extent from the integration of two modes of analysis, corresponding to two different disciplines: the Mendelian study of heredity (Mendelism), and c ...
Slide 1
... • 2655 tag SNPs from roughly 200 selected candidate genes for cardiovascular disease • 820 individuals • Non-genetic covariates: gender, smoking status, age ...
... • 2655 tag SNPs from roughly 200 selected candidate genes for cardiovascular disease • 820 individuals • Non-genetic covariates: gender, smoking status, age ...
Database of cattle candidate genes and genetic markers for
... of key drivers related to complex traits needs a more holistic approach, based on integration of gene-to-gene interactions with DNA variation data. This approach has recently been developed to elucidate the complexity of common human diseases by intersecting genotypic, molecular profiling and clinic ...
... of key drivers related to complex traits needs a more holistic approach, based on integration of gene-to-gene interactions with DNA variation data. This approach has recently been developed to elucidate the complexity of common human diseases by intersecting genotypic, molecular profiling and clinic ...
Schizophrenia genetics: emerging themes for a complex disorder
... Using histone acetylation markers from various sources including the ENCODE project32 to define enhancer elements, if not unsurprisingly, then reassuringly, the PGC group found associations were enriched in enhancers that were relatively brainspecific. However, they also found associations were enrich ...
... Using histone acetylation markers from various sources including the ENCODE project32 to define enhancer elements, if not unsurprisingly, then reassuringly, the PGC group found associations were enriched in enhancers that were relatively brainspecific. However, they also found associations were enrich ...
Twin study

Twin studies reveal the absolute and relative importance of environmental and genetic influences on individuals in a sample. Twin research is considered a key tool in behavioral genetics and in content fields, from biology to psychology. Twin studies are part of the methods used in behavior genetics, which includes all data that are genetically informative – siblings, adoptees, pedigree data etc.Twins are a valuable source for observation because they allow the study of varying family environments (across pairs) and widely differing genetic makeup: ""identical"" or monozygotic (MZ) twins share nearly 100% of their genes, which means that most differences between the twins (such as height, susceptibility to boredom, intelligence, depression, etc.) is due to experiences that one twin has but not the other twin. ""Fraternal"" or dizygotic (DZ) twins share only about 50% of their genes. Thus powerful tests of the effects of genes can be made. Twins share many aspects of their environment (e.g., uterine environment, parenting style, education, wealth, culture, community) by virtue of being born in the same time and place. The presence of a given genetic trait in only one member of a pair of identical twins (called discordance) provides a powerful window into environmental effects.The classical twin design compares the similarity of monozygotic (identical) and dizygotic (fraternal) twins. If identical twins are considerably more similar than fraternal twins (which is found for most traits), this implicates that genes play an important role in these traits. By comparing many hundreds of families of twins, researchers can then understand more about the roles of genetic effects, shared environment, and unique environment in shaping behavior.Modern twin studies have shown that almost all traits are in part influenced by genetic differences, with some characteristics showing a strong influence (e.g. height), others an intermediate level (e.g. personality traits) and some more complex heritabilities, with evidence for different genes affecting different aspects of the trait — as in the case of autism.