Heritability of the Second to Forth Digit Ratio (2d:4d) of a Japanese
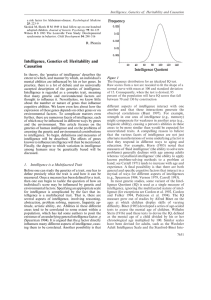
... Spector, 2006; van Anders, Vernon, & Wilbur, 2006; Voracek & Dressler, 2007). Those studies can be roughly classified into three types. Classic Twin Method The first type employs the classic twin method, which decomposes the covariance of twin traits into variances of three independent parameters: a ...
... Spector, 2006; van Anders, Vernon, & Wilbur, 2006; Voracek & Dressler, 2007). Those studies can be roughly classified into three types. Classic Twin Method The first type employs the classic twin method, which decomposes the covariance of twin traits into variances of three independent parameters: a ...
Genes Propose and Environments Dispose: Ecological Genomics
... colonized freshwater lakes from the ocean and represent one of the most common examples of adaptation from standing genetic variation. Yet, it is often assumed that the marine form of stickleback along the Pacific coast of North America constitute a single, large population. If true, then parallel e ...
... colonized freshwater lakes from the ocean and represent one of the most common examples of adaptation from standing genetic variation. Yet, it is often assumed that the marine form of stickleback along the Pacific coast of North America constitute a single, large population. If true, then parallel e ...
Patterns of Inheritance: Genetics Chapt. 10
... hemoglobin that they do not suffer as long as oxygen concentrations remain high, such as at sea-level. ...
... hemoglobin that they do not suffer as long as oxygen concentrations remain high, such as at sea-level. ...
Ch. 15 Chromosomal Inheritance
... diploid number of chromosomes, and is the most frequently observed type of cytogenetic abnormality. ...
... diploid number of chromosomes, and is the most frequently observed type of cytogenetic abnormality. ...
Intelligence, Genetics of: Heritability and Causation
... l VG\VP. This formulation assumes that the phenotype can be neatly partitioned into two parts and ignores genetic-by-environment interactions (GxE). All treatable genetic disorders, such as PKU, exhibit strong GxE, since symptoms depend on both predisposing mutations and insufficient treatment. Inte ...
... l VG\VP. This formulation assumes that the phenotype can be neatly partitioned into two parts and ignores genetic-by-environment interactions (GxE). All treatable genetic disorders, such as PKU, exhibit strong GxE, since symptoms depend on both predisposing mutations and insufficient treatment. Inte ...
Complex Genetics - mvhs
... the X chromosome • Colorblindness is caused by a recessive allele (mutation in the opsin gene) • Who is more likely to be color blind– men or women? – Men: only 1 X chromosome – if they have the recessive allele they don’t have another X to make up for it. ...
... the X chromosome • Colorblindness is caused by a recessive allele (mutation in the opsin gene) • Who is more likely to be color blind– men or women? – Men: only 1 X chromosome – if they have the recessive allele they don’t have another X to make up for it. ...
Course Competency Learning Outcomes
... Comparing and contrasting genes, chromosomes, and genomes. Explaining how genetics and the environment can influence gender determination. Describing gene linkage. Analyzing sex influence and linkage. Explaining genetic anomalies caused by changes in chromosome number. Summarizing genetic anomalies ...
... Comparing and contrasting genes, chromosomes, and genomes. Explaining how genetics and the environment can influence gender determination. Describing gene linkage. Analyzing sex influence and linkage. Explaining genetic anomalies caused by changes in chromosome number. Summarizing genetic anomalies ...
Lect 4 JF 12
... ‘A genetic map of the genes affecting adult height. Genetic linkage analysis was used for locating genes affecting stature. This method utilizes genetic markers known to show variation between individuals. The markers are evenly distributed across the entire genome and they are determined from DNA s ...
... ‘A genetic map of the genes affecting adult height. Genetic linkage analysis was used for locating genes affecting stature. This method utilizes genetic markers known to show variation between individuals. The markers are evenly distributed across the entire genome and they are determined from DNA s ...
PDF - SAGE Journals
... Pettersson, & Horn, 2014). The original Three Laws summarized results from studies of twins, adoptees, and other kinships. These research designs have many valuable uses, but they cannot discover particular genomic regions or specific variants that are causally responsible for downstream phenotypic ...
... Pettersson, & Horn, 2014). The original Three Laws summarized results from studies of twins, adoptees, and other kinships. These research designs have many valuable uses, but they cannot discover particular genomic regions or specific variants that are causally responsible for downstream phenotypic ...
Chapter 10 Mendelian Genetics - An
... gamete formation (based on independent assortment of nonhomologous chromosomes at meiosis). ...
... gamete formation (based on independent assortment of nonhomologous chromosomes at meiosis). ...
PowerPoint to accompany - Home Page of Ken Jones
... • different alleles are both expressed • ABO blood type is an example • three alleles of ABO blood typing are IA, IB, I • a person with type A may have the genotype IA i or IA IA • a person with type B may have the genotype IB i or IB IB • a person with type AB must have the genotype IA IB • a perso ...
... • different alleles are both expressed • ABO blood type is an example • three alleles of ABO blood typing are IA, IB, I • a person with type A may have the genotype IA i or IA IA • a person with type B may have the genotype IB i or IB IB • a person with type AB must have the genotype IA IB • a perso ...
New
... have a good understanding of Phenotypes, Genotypes, Dominant, Recessive, etc. I allow the student to create their own Alien Babies. They are given a list of criteria and a sheet that tells them that the parents are Heterozygous for all of the traits and they have to flip a coin to figure out ea ...
... have a good understanding of Phenotypes, Genotypes, Dominant, Recessive, etc. I allow the student to create their own Alien Babies. They are given a list of criteria and a sheet that tells them that the parents are Heterozygous for all of the traits and they have to flip a coin to figure out ea ...
file
... Heredity – passing of characteristics from parents to offspring Gametes –male and female sex cells Fertilization – process where male and female sex cells unite ...
... Heredity – passing of characteristics from parents to offspring Gametes –male and female sex cells Fertilization – process where male and female sex cells unite ...
Gregor Mendel “The Father of Genetics”
... Ex: Gene: height Alleles: tall, dwarf Genes are inherited in pairs, one allele from each parent Homozygous: identical alleles Heterozygous: different alleles In a hybrid, only the dominant allele (T) will be expressed (or seen). The other allele is recessive (t). Alleles segregate (separate) from ea ...
... Ex: Gene: height Alleles: tall, dwarf Genes are inherited in pairs, one allele from each parent Homozygous: identical alleles Heterozygous: different alleles In a hybrid, only the dominant allele (T) will be expressed (or seen). The other allele is recessive (t). Alleles segregate (separate) from ea ...
genetics
... • The F1 generation always displayed one trait (he later called this the dominant trait) • The F1 generation must have within it the trait from the original parents - the white trait • The F2 generation displayed the “hidden” trait, 1/4 of the F2 generation had it (he later called this hidden trait ...
... • The F1 generation always displayed one trait (he later called this the dominant trait) • The F1 generation must have within it the trait from the original parents - the white trait • The F2 generation displayed the “hidden” trait, 1/4 of the F2 generation had it (he later called this hidden trait ...
Mendelian Genetics
... » BI3. A multicellular organism develops from a single zygote, and its phenotype depends on its genotype, which is established at fertilization. As a basis for understanding this concept: » BI2. d. Students know new combinations of alleles may be generated in a zygote through the fusion of male and ...
... » BI3. A multicellular organism develops from a single zygote, and its phenotype depends on its genotype, which is established at fertilization. As a basis for understanding this concept: » BI2. d. Students know new combinations of alleles may be generated in a zygote through the fusion of male and ...
Heredity Chpt 11
... up, both parents may have the hidden recessive gene but not shown in one or either parent Cystic fibrosis is homozygous recessive disorder Disorder produces thick mucus in lungs that make it hard to breath ...
... up, both parents may have the hidden recessive gene but not shown in one or either parent Cystic fibrosis is homozygous recessive disorder Disorder produces thick mucus in lungs that make it hard to breath ...
Biology Passage 2 - HCC Learning Web
... 1. Test Cross uses mating as a genetic tool to experimentally determine genotypes by observing the phenotypes of filial progeny (F) from a cross of parents (P) follows Mendelian Hereditary Law (Great – we can predict outcome!) 2. Punnett Squares theoretically predict the results of a cross between t ...
... 1. Test Cross uses mating as a genetic tool to experimentally determine genotypes by observing the phenotypes of filial progeny (F) from a cross of parents (P) follows Mendelian Hereditary Law (Great – we can predict outcome!) 2. Punnett Squares theoretically predict the results of a cross between t ...
Study Guide
... genotype ratio: phenotypes: phenotype ratio: 2. Draw a Punnett square for a trait that has incomplete dominance showing a cross between two heterozygous parents. trait: genotypes: genotype ratio: phenotypes: phenotype ratio: 3. Draw a Punnett square for a trait that has codominance showing a cross b ...
... genotype ratio: phenotypes: phenotype ratio: 2. Draw a Punnett square for a trait that has incomplete dominance showing a cross between two heterozygous parents. trait: genotypes: genotype ratio: phenotypes: phenotype ratio: 3. Draw a Punnett square for a trait that has codominance showing a cross b ...
Mendelian Inheritance
... had been raised as a farmer and who studied mathematics in Vienna • Considered the “Father of Genetics” ...
... had been raised as a farmer and who studied mathematics in Vienna • Considered the “Father of Genetics” ...
Document
... Regardless of the trait, results were the same and could be predicted in future generations…Mendel developed his first law of genetics; The Law of Dominance ...
... Regardless of the trait, results were the same and could be predicted in future generations…Mendel developed his first law of genetics; The Law of Dominance ...
b, wt - Cytoscape Wiki
... Fine Mapping: Due to the spacing of genetic markers and/or linkage disequilibrium, several genes can reside near each SNP marker. Typically, only one of these genes is responsible for the observed expression phenotype. Identifying the true causative gene requires additional data, since all genes at ...
... Fine Mapping: Due to the spacing of genetic markers and/or linkage disequilibrium, several genes can reside near each SNP marker. Typically, only one of these genes is responsible for the observed expression phenotype. Identifying the true causative gene requires additional data, since all genes at ...
Twin study

Twin studies reveal the absolute and relative importance of environmental and genetic influences on individuals in a sample. Twin research is considered a key tool in behavioral genetics and in content fields, from biology to psychology. Twin studies are part of the methods used in behavior genetics, which includes all data that are genetically informative – siblings, adoptees, pedigree data etc.Twins are a valuable source for observation because they allow the study of varying family environments (across pairs) and widely differing genetic makeup: ""identical"" or monozygotic (MZ) twins share nearly 100% of their genes, which means that most differences between the twins (such as height, susceptibility to boredom, intelligence, depression, etc.) is due to experiences that one twin has but not the other twin. ""Fraternal"" or dizygotic (DZ) twins share only about 50% of their genes. Thus powerful tests of the effects of genes can be made. Twins share many aspects of their environment (e.g., uterine environment, parenting style, education, wealth, culture, community) by virtue of being born in the same time and place. The presence of a given genetic trait in only one member of a pair of identical twins (called discordance) provides a powerful window into environmental effects.The classical twin design compares the similarity of monozygotic (identical) and dizygotic (fraternal) twins. If identical twins are considerably more similar than fraternal twins (which is found for most traits), this implicates that genes play an important role in these traits. By comparing many hundreds of families of twins, researchers can then understand more about the roles of genetic effects, shared environment, and unique environment in shaping behavior.Modern twin studies have shown that almost all traits are in part influenced by genetic differences, with some characteristics showing a strong influence (e.g. height), others an intermediate level (e.g. personality traits) and some more complex heritabilities, with evidence for different genes affecting different aspects of the trait — as in the case of autism.