Plant Parts and Their Functions
... CELLULAR RESPIRATION Food Energy Cellular Respiration: The process by which plants release stored energy from food to carry on life’s processes. ...
... CELLULAR RESPIRATION Food Energy Cellular Respiration: The process by which plants release stored energy from food to carry on life’s processes. ...
Plantinforpackt
... plants to make their food. Carpel: The part of a flower that grows into a fruit and in which the seeds develop Germinate: when a seed starts to grow and produce a new plant Oxygen: a gas in the air: plants and animals use this gas for breathing Petal: the part of a flower that is often brightly colo ...
... plants to make their food. Carpel: The part of a flower that grows into a fruit and in which the seeds develop Germinate: when a seed starts to grow and produce a new plant Oxygen: a gas in the air: plants and animals use this gas for breathing Petal: the part of a flower that is often brightly colo ...
Anticipated Problem: What are the main parts of a plant?
... There are six main parts of a plant. Each part is important to the plant’s survival. ...
... There are six main parts of a plant. Each part is important to the plant’s survival. ...
Plant Kingdom
... ovules occur in the ovary (bulging base of the carpel) stalk called the style rises from the ovary and ends with a sticky tip called a stigma the stigma receives pollen ...
... ovules occur in the ovary (bulging base of the carpel) stalk called the style rises from the ovary and ends with a sticky tip called a stigma the stigma receives pollen ...
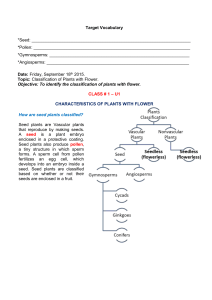
Target Vocabulary *Seed: *Pollen: *Gymnosperms: *Angiosperms
... forms. A sperm cell from pollen fertilizes an egg cell, which develops into an embryo inside a seed. Seed plants are classified based on whether or not their seeds are enclosed in a fruit. ...
... forms. A sperm cell from pollen fertilizes an egg cell, which develops into an embryo inside a seed. Seed plants are classified based on whether or not their seeds are enclosed in a fruit. ...
Ecology of plant–animal interactions: pollination, seed dispersal and
... have tremendous direct practical applications in the areas of crop production and food security, crop protection, forest management and conservation. Our knowledge on the fundamental aspects of bioresources in India is poor, despite having a huge biodiversity protected in the three global biodiversi ...
... have tremendous direct practical applications in the areas of crop production and food security, crop protection, forest management and conservation. Our knowledge on the fundamental aspects of bioresources in India is poor, despite having a huge biodiversity protected in the three global biodiversi ...
SECTION 2 - Florida Union Free School District
... Use spores to reproduce In sporophyte stage, sex cells are produced in spore cases Spores are released and spread by wind, water, and animals becoming new plants Can be from vascular or nonvascular plants ...
... Use spores to reproduce In sporophyte stage, sex cells are produced in spore cases Spores are released and spread by wind, water, and animals becoming new plants Can be from vascular or nonvascular plants ...
PLANTS IN PLAYSPACES - what works, what doesn’t and how to
... •Get the staff, families and children involved •Site security •Community garden networks •Do what’s best for your site – don’t try to duplicate what another centre has done – the conditions will be completely different! ...
... •Get the staff, families and children involved •Site security •Community garden networks •Do what’s best for your site – don’t try to duplicate what another centre has done – the conditions will be completely different! ...
plant_Kingdom
... Ferns, club mosses and horsetails need moist surroundings so spores will survive and grow into gametophytes. When the gametophytes produce egg and sperm cells, there must be enough water nearby for fertilization to occur. Most club mosses and horsetails have become extinct … ...
... Ferns, club mosses and horsetails need moist surroundings so spores will survive and grow into gametophytes. When the gametophytes produce egg and sperm cells, there must be enough water nearby for fertilization to occur. Most club mosses and horsetails have become extinct … ...
flowers - mitchelltechblitz2010
... The small shoot then begins to develop leaves that contain chlorophyll. Chlorophyll contains pigments that take in energy from the sun and convert it to carbon dioxide and water into sugars—the process of photosynthesis. Photosynthesis allows the plant to feed itself and continue to grow. The plant ...
... The small shoot then begins to develop leaves that contain chlorophyll. Chlorophyll contains pigments that take in energy from the sun and convert it to carbon dioxide and water into sugars—the process of photosynthesis. Photosynthesis allows the plant to feed itself and continue to grow. The plant ...
Facts for Consumers - Physicians and Scientists for Global
... species to another, usually between closely related species. This is known as horizontal gene transfer. HGT between species from different kingdoms is extremely rare in nature, even on an evolutionary timescale. Genetic engineering has now become the main cause of HGT in the biosphere. Novel genes i ...
... species to another, usually between closely related species. This is known as horizontal gene transfer. HGT between species from different kingdoms is extremely rare in nature, even on an evolutionary timescale. Genetic engineering has now become the main cause of HGT in the biosphere. Novel genes i ...
Plants Part 4
... brightness and floral form of the vining types, but its growth habit is bushy and contained. The plant produces a profusion of fragrant, bright yellow flowers from early spring to late fall. ‘Golden Butterfly’ loves full sun, and it needs a period of dryness between waterings to keep its roots healt ...
... brightness and floral form of the vining types, but its growth habit is bushy and contained. The plant produces a profusion of fragrant, bright yellow flowers from early spring to late fall. ‘Golden Butterfly’ loves full sun, and it needs a period of dryness between waterings to keep its roots healt ...
Purple Loosestrife (Lythrum salicaria)
... Flowers: Flowers in long, dense, ver"cal clusters (or terminal racemes) with leaves. Showy flowers with 4 to 8 wrinkled petals. Sepals have 8, 10 or 12 prominent green veins. Leaves and Stems: Opposite leaves without stalks, some"mes in spirals (or whorls) around the stem. Lance-shaped, slightly hair ...
... Flowers: Flowers in long, dense, ver"cal clusters (or terminal racemes) with leaves. Showy flowers with 4 to 8 wrinkled petals. Sepals have 8, 10 or 12 prominent green veins. Leaves and Stems: Opposite leaves without stalks, some"mes in spirals (or whorls) around the stem. Lance-shaped, slightly hair ...
Primary root disappear giving rise to fibrous root system
... advance over most algae by the development of archegonia, multicellular antheridia and a distinct alternation of generation. The sporophyte is dependent on the gametophyte in the Bryophyets. The gametophytic plant body is either thaloid (flattened) as in ...
... advance over most algae by the development of archegonia, multicellular antheridia and a distinct alternation of generation. The sporophyte is dependent on the gametophyte in the Bryophyets. The gametophytic plant body is either thaloid (flattened) as in ...
Purple false brome (Brachypodium distachyon), a potential model
... Model organisms are species that share many essential biological properties with organisms of specific interest and have advantageous characteristics such as small size, short generation time, large number of progeny or compact genome. For the past few decades Arabidopsis thaliana, a member of the m ...
... Model organisms are species that share many essential biological properties with organisms of specific interest and have advantageous characteristics such as small size, short generation time, large number of progeny or compact genome. For the past few decades Arabidopsis thaliana, a member of the m ...
File - Biology with Ms. Murillo
... 1. Pollen grain lands on the stigma. 2. The pollen tube cell grows a tube to the ovary. 3. The two sperm cells move through the tube into the ovule. •One sperm joins with the egg in the ovule. •The other joins with the central cell (2N) to form the endosperm (3N) •The process is called double fertil ...
... 1. Pollen grain lands on the stigma. 2. The pollen tube cell grows a tube to the ovary. 3. The two sperm cells move through the tube into the ovule. •One sperm joins with the egg in the ovule. •The other joins with the central cell (2N) to form the endosperm (3N) •The process is called double fertil ...
Genetics-study of heredity Heredity- transmission of - OG
... 3. Pollination-movement of pollen from stamen to pistil a. Self-pollination -same flower b. Cross-pollination - different plants ...
... 3. Pollination-movement of pollen from stamen to pistil a. Self-pollination -same flower b. Cross-pollination - different plants ...
2009 Plants of the Year
... female plants give clusters of bluish‐black fruit in late summer. Its thick, leathery leaves turn a striking yellow in autumn, against its smooth, gray bark. It prefers full sun to partial shade, and deep, fertile soil. However, it is pH adaptable. It is best planted ...
... female plants give clusters of bluish‐black fruit in late summer. Its thick, leathery leaves turn a striking yellow in autumn, against its smooth, gray bark. It prefers full sun to partial shade, and deep, fertile soil. However, it is pH adaptable. It is best planted ...
Document
... • SC.3.N.3.2 Recognize that scientists use models to help understand and explain how things work. • SC.3.N.3.3 Recognize that all models are approximations of natural phenomena; as such, they do not perfectly account for all observations. • SC.3.L.14.1 Describe structures in plants and their roles i ...
... • SC.3.N.3.2 Recognize that scientists use models to help understand and explain how things work. • SC.3.N.3.3 Recognize that all models are approximations of natural phenomena; as such, they do not perfectly account for all observations. • SC.3.L.14.1 Describe structures in plants and their roles i ...
Plant Evolution - Cloudfront.net
... Vascular tissue consists of what’s called xylem (ZY-LUM)and phloem (FLO-M), that’s what the first picture on the left shows. The picture on the ...
... Vascular tissue consists of what’s called xylem (ZY-LUM)and phloem (FLO-M), that’s what the first picture on the left shows. The picture on the ...
Media release
... The breeding of new varieties to rival box plant, the traditional choice for a hedge, is a challenge this new gardenia meets head on. O So Fine™ gardenia is a form of Gardenia augusta ‘Radicans’ ...
... The breeding of new varieties to rival box plant, the traditional choice for a hedge, is a challenge this new gardenia meets head on. O So Fine™ gardenia is a form of Gardenia augusta ‘Radicans’ ...
Plant breeding

Plant breeding is the art and science of changing the traits of plants in order to produce desired characteristics. Plant breeding can be accomplished through many different techniques ranging from simply selecting plants with desirable characteristics for propagation, to more complex molecular techniques (see cultigen and cultivar).Plant breeding has been practiced for thousands of years, since near the beginning of human civilization. It is practiced worldwide by individuals such as gardeners and farmers, or by professional plant breeders employed by organizations such as government institutions, universities, crop-specific industry associations or research centers.International development agencies believe that breeding new crops is important for ensuring food security by developing new varieties that are higher-yielding, resistant to pests and diseases, drought-resistant or regionally adapted to different environments and growing conditions.