rtf - Synod Resource Center
... At the base of the plant there is a large corm with roots coming from it. New corms can grow off of it and eventually produce new plants. A large corm with much stored food can produce two leaves and a female flower the following year. Smaller corms may produce only one leaf or a plant with a male f ...
... At the base of the plant there is a large corm with roots coming from it. New corms can grow off of it and eventually produce new plants. A large corm with much stored food can produce two leaves and a female flower the following year. Smaller corms may produce only one leaf or a plant with a male f ...
Jack-in-the-Pulpit (Arisaema triphyllum)
... Seeds fall to the ground nearby and animals disperse others. It takes four years for a seed to grow and mature into a flower-bearing plant. ...
... Seeds fall to the ground nearby and animals disperse others. It takes four years for a seed to grow and mature into a flower-bearing plant. ...
12 Top Lawn &
... Maintain turf density and health through proper culture; avoid spring cultivation, short mowing, summer fertilization, and light, frequent irrigation. Crabgrass can be hand pulled or mechanically removed. Apply preemergence herbicides before germination when soil temperatures stabilize at 55°F for s ...
... Maintain turf density and health through proper culture; avoid spring cultivation, short mowing, summer fertilization, and light, frequent irrigation. Crabgrass can be hand pulled or mechanically removed. Apply preemergence herbicides before germination when soil temperatures stabilize at 55°F for s ...
The Pepper-bark Tree - The Botanical Society
... This is the eleventh in a series of articles on indigenous plants that have traditionally been used by humans in southern Africa for food, medicine, crafts, and charms. Some of these plants are now threatened while others that once formed an important part of our diet have been forgotten. It is hope ...
... This is the eleventh in a series of articles on indigenous plants that have traditionally been used by humans in southern Africa for food, medicine, crafts, and charms. Some of these plants are now threatened while others that once formed an important part of our diet have been forgotten. It is hope ...
Chestnut School of Herbal Medicine
... the dust, succumbing to fungal diseases, whereas the modestly hairy plants have the edge against such diseases and survive, furthering the species. In both scenarios, one trait gives some individuals an edge over other individuals; this diversity creates resiliency for the entire group. Diversity al ...
... the dust, succumbing to fungal diseases, whereas the modestly hairy plants have the edge against such diseases and survive, furthering the species. In both scenarios, one trait gives some individuals an edge over other individuals; this diversity creates resiliency for the entire group. Diversity al ...
Easy Dwarf Shrubs - Alpine Garden Society
... losing its gloss, wilting, leaf edges browning or shriveling). It is better to give a thorough watering occasionally than to apply a little water at frequent intervals. Especially in the first year after planting, a shrub may occasionally form a long shoot. It is best to pinch out any such growth be ...
... losing its gloss, wilting, leaf edges browning or shriveling). It is better to give a thorough watering occasionally than to apply a little water at frequent intervals. Especially in the first year after planting, a shrub may occasionally form a long shoot. It is best to pinch out any such growth be ...
Insect pollinated flowers - GZ @ Science Class Online
... The role that stomata have in the process of transpiration (extension) Leaves are the main site of photosynthesis. They make food from carbon dioxide and water in the presence of light. As stomata open in the presence of light, carbon dioxide will diffuse into the leaf and at the same time, water v ...
... The role that stomata have in the process of transpiration (extension) Leaves are the main site of photosynthesis. They make food from carbon dioxide and water in the presence of light. As stomata open in the presence of light, carbon dioxide will diffuse into the leaf and at the same time, water v ...
Growing a Chocolate Tree at Home or in an Office
... day, although there may be periods of relatively less rain. This makes the humidity quite high, usually greater than 70%. However, the soil often contains large amounts of organic and sandy materials and these provide nutrients and help it drain rapidly. The soil is usually a bit acidic, averaging a ...
... day, although there may be periods of relatively less rain. This makes the humidity quite high, usually greater than 70%. However, the soil often contains large amounts of organic and sandy materials and these provide nutrients and help it drain rapidly. The soil is usually a bit acidic, averaging a ...
Cultural Requirements for Poha (Cape
... family. It has been introduced and commercially cultivated in various tropical, subtropical and temperate areas around the world. It can be eaten fresh; made into jams, jellies, or canned; dipped into chocolate; used in sauces or even as a flavoring for ice cream. Culture: The Poha is usually found ...
... family. It has been introduced and commercially cultivated in various tropical, subtropical and temperate areas around the world. It can be eaten fresh; made into jams, jellies, or canned; dipped into chocolate; used in sauces or even as a flavoring for ice cream. Culture: The Poha is usually found ...
Asarum caudatum species sheet (1
... morning sun. They do well planted with rhododendrons, ferns, cedars, and other shade and moisture loving plants. It has a strong smell of ginger when crushed. It should be used more often as a ground cover instead of some of the more rampant ornamentals. Availability: The eastern variety Asarum cana ...
... morning sun. They do well planted with rhododendrons, ferns, cedars, and other shade and moisture loving plants. It has a strong smell of ginger when crushed. It should be used more often as a ground cover instead of some of the more rampant ornamentals. Availability: The eastern variety Asarum cana ...
Slide 1
... • “Non-Rooting Room” forcing – Primary difference to “standard forcing” is that rooting takes place in the greenhouse – For some, flower initiation and development also take place in the greenhouse phase (Easter Lilies and Dutch Iris) – “Non-Rooting” does not mean no cold treatment – There are two t ...
... • “Non-Rooting Room” forcing – Primary difference to “standard forcing” is that rooting takes place in the greenhouse – For some, flower initiation and development also take place in the greenhouse phase (Easter Lilies and Dutch Iris) – “Non-Rooting” does not mean no cold treatment – There are two t ...
The Aizoaceae
... on the tops of their leaves. These windows usually appear as darker spots or lines. Sunlight can penetrate into these windows down to chlorophyll-containing cells lining the inner portion of the stem. There are many succulent plants that have these translucent “windows” – they are often called “wind ...
... on the tops of their leaves. These windows usually appear as darker spots or lines. Sunlight can penetrate into these windows down to chlorophyll-containing cells lining the inner portion of the stem. There are many succulent plants that have these translucent “windows” – they are often called “wind ...
013368718X_CH24_377-392.indd
... The Angiosperm Life Cycle The life cycle involves alternation of generations. Meiosis in stamens and carpels produces haploid cells (spores) that develop into gametophytes. The haploid cells in a stamen’s anther undergo mitosis and form pollen grains, the male gametophytes, that contain 2 sperm nucl ...
... The Angiosperm Life Cycle The life cycle involves alternation of generations. Meiosis in stamens and carpels produces haploid cells (spores) that develop into gametophytes. The haploid cells in a stamen’s anther undergo mitosis and form pollen grains, the male gametophytes, that contain 2 sperm nucl ...
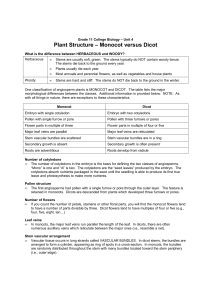
Unit 4 - Lesson 6 - Monocot and Dicot
... Root development • In most dicots, the root develops from the lower end of the embryo from a region called the RADICLE. The radicle gives rise to the APICAL MERISTEM which produces new root tissue throughout the plant’s life. In monocots, the radicle stops growing and new roots grow ADVENTIOUSLY fr ...
... Root development • In most dicots, the root develops from the lower end of the embryo from a region called the RADICLE. The radicle gives rise to the APICAL MERISTEM which produces new root tissue throughout the plant’s life. In monocots, the radicle stops growing and new roots grow ADVENTIOUSLY fr ...
Need and Importance of Conservation of Endangered
... consumed raw, roasted, boiled, fried, cooked, or they are used in the form of oil, spices, jams or pickles. The indigenous communities use some medicinal plant species as a source of food, fodder, timber as well as various other ethnobotanical purposes [Dhyaniand Dhar 1994]. Approximately 81 species ...
... consumed raw, roasted, boiled, fried, cooked, or they are used in the form of oil, spices, jams or pickles. The indigenous communities use some medicinal plant species as a source of food, fodder, timber as well as various other ethnobotanical purposes [Dhyaniand Dhar 1994]. Approximately 81 species ...
Roselle Culture Hibiscus sabdariffa
... levels but too much nitrogen will delay flowering until too late in the season. Keep plants unmulched, evenly moist and well weeded until they are 1 ½ to 2 ft high. At that point we mulch the plants and have few weeds for the rest of the season. Early tip pruning and the formation of more flowering ...
... levels but too much nitrogen will delay flowering until too late in the season. Keep plants unmulched, evenly moist and well weeded until they are 1 ½ to 2 ft high. At that point we mulch the plants and have few weeds for the rest of the season. Early tip pruning and the formation of more flowering ...
Papyrus, Cyperus papyrus
... African species hardy in zones 9-12. It is native throughout the wetter parts of Africa, Madagascar and around the southern Mediterranean where it occurs in vast stands in swamps, shallow lakes, and along stream banks throughout the wetter parts of Africa. The large, dense populations often line bod ...
... African species hardy in zones 9-12. It is native throughout the wetter parts of Africa, Madagascar and around the southern Mediterranean where it occurs in vast stands in swamps, shallow lakes, and along stream banks throughout the wetter parts of Africa. The large, dense populations often line bod ...
Sandy seeds notes
... to be able to make a fair comparison (same amount of watering/light etc) but the focus should be on making observations over time (see slide 2). The children should plant several seeds in each pot. Show slide 3 to encourage children to make and explain a prediction about their experiment. Ask the ch ...
... to be able to make a fair comparison (same amount of watering/light etc) but the focus should be on making observations over time (see slide 2). The children should plant several seeds in each pot. Show slide 3 to encourage children to make and explain a prediction about their experiment. Ask the ch ...
Aster Callistephus Meteor Series
... Aster Callistephus are an old time favorite that have never gone out of style. They were introduced in the Ball Company by George Ball himself in the early nineteen hundreds. The Aster Callistephus family is a big one , and has flowers that come in many bright colors and different sizes. Very versat ...
... Aster Callistephus are an old time favorite that have never gone out of style. They were introduced in the Ball Company by George Ball himself in the early nineteen hundreds. The Aster Callistephus family is a big one , and has flowers that come in many bright colors and different sizes. Very versat ...
BIOL 201 - Queen`s Biology
... Learning Objectives The goals of Biology 201 are to provide students with the background knowledge and interpretive skills needed to recognize and study the diversity of life as a product of Darwinian evolution, based largely on the process of natural selection. Students will be able to: • Describe ...
... Learning Objectives The goals of Biology 201 are to provide students with the background knowledge and interpretive skills needed to recognize and study the diversity of life as a product of Darwinian evolution, based largely on the process of natural selection. Students will be able to: • Describe ...
Crown - of - Thorns (Euphorbia milii)
... The Thai hybrids. For the past 20 -30 years growers in Thailand have developed an array of hybrids with much larger flowers (i.e. the cyathophylls) than found in previous cultivars, with a seemingly infinite variety of color combinations. These range from all shades of red and pink to cream and yell ...
... The Thai hybrids. For the past 20 -30 years growers in Thailand have developed an array of hybrids with much larger flowers (i.e. the cyathophylls) than found in previous cultivars, with a seemingly infinite variety of color combinations. These range from all shades of red and pink to cream and yell ...
outline () - Queen`s Biology Department
... Learning Objectives The goals of Biology 201 are to provide students with the background knowledge and interpretive skills needed to recognize and study the diversity of life as a product of Darwinian evolution, based largely on the process of natural selection. Students will be able to: • Describe ...
... Learning Objectives The goals of Biology 201 are to provide students with the background knowledge and interpretive skills needed to recognize and study the diversity of life as a product of Darwinian evolution, based largely on the process of natural selection. Students will be able to: • Describe ...
Botany

Botany, also called plant science(s) or plant biology, is the science of plant life and a branch of biology. A botanist or plant scientist is a scientist who specializes in this field of study. The term ""botany"" comes from the Ancient Greek word βοτάνη (botanē) meaning ""pasture"", ""grass"", or ""fodder""; βοτάνη is in turn derived from βόσκειν (boskein), ""to feed"" or ""to graze"". Traditionally, botany has also included the study of fungi and algae by mycologists and phycologists respectively, with the study of these three groups of organisms remaining within the sphere of interest of the International Botanical Congress. Nowadays, botanists study approximately 400,000 species of living organisms of which some 260,000 species are vascular plants and about 248,000 are flowering plants.Botany originated in prehistory as herbalism with the efforts of early humans to identify – and later cultivate – edible, medicinal and poisonous plants, making it one of the oldest branches of science. Medieval physic gardens, often attached to monasteries, contained plants of medical importance. They were forerunners of the first botanical gardens attached to universities, founded from the 1540s onwards. One of the earliest was the Padua botanical garden. These gardens facilitated the academic study of plants. Efforts to catalogue and describe their collections were the beginnings of plant taxonomy, and led in 1753 to the binomial system of Carl Linnaeus that remains in use to this day.In the 19th and 20th centuries, new techniques were developed for the study of plants, including methods of optical microscopy and live cell imaging, electron microscopy, analysis of chromosome number, plant chemistry and the structure and function of enzymes and other proteins. In the last two decades of the 20th century, botanists exploited the techniques of molecular genetic analysis, including genomics and proteomics and DNA sequences to classify plants more accurately.Modern botany is a broad, multidisciplinary subject with inputs from most other areas of science and technology. Research topics include the study of plant structure, growth and differentiation, reproduction, biochemistry and primary metabolism, chemical products, development, diseases, evolutionary relationships, systematics, and plant taxonomy. Dominant themes in 21st century plant science are molecular genetics and epigenetics, which are the mechanisms and control of gene expression during differentiation of plant cells and tissues. Botanical research has diverse applications in providing staple foods and textiles, in modern horticulture, agriculture and forestry, plant propagation, breeding and genetic modification, in the synthesis of chemicals and raw materials for construction and energy production, in environmental management, and the maintenance of biodiversity.