Review Questions for Exam 2
... 3. Why are the Charophyceans considered to be more closely related to land plants than other green algae (what traits do they share)? 4. What benefits could be gained by the ancestors of plants from moving from water to land? 5. What were four big problems the ancestors of plants faced when moving f ...
... 3. Why are the Charophyceans considered to be more closely related to land plants than other green algae (what traits do they share)? 4. What benefits could be gained by the ancestors of plants from moving from water to land? 5. What were four big problems the ancestors of plants faced when moving f ...
Biology 3 Plants Ch 12
... Male cones release pollen grains that are dispersed by the wind to ovules found beneath the scales of female cones. ...
... Male cones release pollen grains that are dispersed by the wind to ovules found beneath the scales of female cones. ...
exam 4 practice questions
... 11. Non-vascular plants have a dominant ____________ stage of their life cycle where photosynthesis can be carried out: a. Gametophyte (n) b. Gametophyte (2n) c. Sporophyte (n) d. Sporophyte (2n) 12. All bryophytes have stomata. a. True b. False 13. In non-vascular sexual reproduction, the “seta” ac ...
... 11. Non-vascular plants have a dominant ____________ stage of their life cycle where photosynthesis can be carried out: a. Gametophyte (n) b. Gametophyte (2n) c. Sporophyte (n) d. Sporophyte (2n) 12. All bryophytes have stomata. a. True b. False 13. In non-vascular sexual reproduction, the “seta” ac ...
The Seed Plants - FacultyWeb Support Center
... Pollen released from the pollen sacs may be carried by wind, water and animals (insects, bats, humans and birds) to the stigma of the same or neighboring flower. The transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma is pollination. Once pollination has occurred, the pollen grain germinates with the t ...
... Pollen released from the pollen sacs may be carried by wind, water and animals (insects, bats, humans and birds) to the stigma of the same or neighboring flower. The transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma is pollination. Once pollination has occurred, the pollen grain germinates with the t ...
Chapter 13
... structure (stigma, style and ovary that contains the ovules). If a pollen grain from an anther lands on the stigma, a pollen tube forms down through the style. The sperm cells travel down the pollen tube and enter the ovary. Inside the ovary, there are the ovules that contain the eggs. The sperm tra ...
... structure (stigma, style and ovary that contains the ovules). If a pollen grain from an anther lands on the stigma, a pollen tube forms down through the style. The sperm cells travel down the pollen tube and enter the ovary. Inside the ovary, there are the ovules that contain the eggs. The sperm tra ...
Test yourself: Biology Chapter - How Do Organisms Reproduce Class...
... fertilization the ovary develops into fruit and protect the seeds, these seeds are actually fertilized ovule. But, carpels and petals do not have any role after fertilization so they fall off. After fertilization, the outer layers of the ovule become ...
... fertilization the ovary develops into fruit and protect the seeds, these seeds are actually fertilized ovule. But, carpels and petals do not have any role after fertilization so they fall off. After fertilization, the outer layers of the ovule become ...
Sexual Asexual Reproduction
... • An insect or the wind carries pollen grains from the anther of another flower. • The pollen grains land on the stigma and a pollen tube grows down through the style to the ovary. • The nucleus of the pollen grain passes down the tube. It fertilizes the egg cell inside the ovule. • The fertilized e ...
... • An insect or the wind carries pollen grains from the anther of another flower. • The pollen grains land on the stigma and a pollen tube grows down through the style to the ovary. • The nucleus of the pollen grain passes down the tube. It fertilizes the egg cell inside the ovule. • The fertilized e ...
Angiosperm Reproduction
... • Humans have devised various methods for asexual propagation of angiosperms • Many kinds of plants are asexually reproduced from plant ...
... • Humans have devised various methods for asexual propagation of angiosperms • Many kinds of plants are asexually reproduced from plant ...
Section 24–1 Reproduction With Cones and - Parkway C-2
... a. They produce pollen grains. b. They produce female gametophytes. c. They have two ovules at the base of each scale. d. They are generally much larger than pollen cones. 9. Is the following sentence true or false? Each mature female gametophyte contains hundreds of egg cells ready for fertilizatio ...
... a. They produce pollen grains. b. They produce female gametophytes. c. They have two ovules at the base of each scale. d. They are generally much larger than pollen cones. 9. Is the following sentence true or false? Each mature female gametophyte contains hundreds of egg cells ready for fertilizatio ...
Plants as Living Organisms
... Flowering Plants All major crops are flowering plants 2 classes of flowering plants – Monocots - Long, narrow blades w/ parallel veins • Flower parts in multiples of 3 • Contain 1 cotyledon ...
... Flowering Plants All major crops are flowering plants 2 classes of flowering plants – Monocots - Long, narrow blades w/ parallel veins • Flower parts in multiples of 3 • Contain 1 cotyledon ...
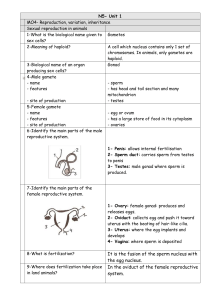
N5- Unit 1 MO4- Reproduction, variation, inheritance Sexual
... female reproductive system. 1- Ovary: female gonad: produces and releases eggs. 2- Oviduct: collects egg and push it toward uterus with the beating of hair-like cilia. 3- Uterus: where the egg implants and ...
... female reproductive system. 1- Ovary: female gonad: produces and releases eggs. 2- Oviduct: collects egg and push it toward uterus with the beating of hair-like cilia. 3- Uterus: where the egg implants and ...
The Functions of Plant Parts/ Plant Life Cycles
... stamen makes pollen that is collected by the pistil, which forms the ___. Seeds form when the stamen makes pollen that is collected by the pistil, which forms the seed. ...
... stamen makes pollen that is collected by the pistil, which forms the ___. Seeds form when the stamen makes pollen that is collected by the pistil, which forms the seed. ...
Flowering of plants
... asexual reproduction, since it does not involve the sexual organs of the plants, that is to say, the flowers. The new asexually generated plant will be genetically identical to its “mother”. Just like humans, plants also reproduce sexually to generate the next generation. Flowering plants, also call ...
... asexual reproduction, since it does not involve the sexual organs of the plants, that is to say, the flowers. The new asexually generated plant will be genetically identical to its “mother”. Just like humans, plants also reproduce sexually to generate the next generation. Flowering plants, also call ...
class : xii - Gitarattan Jindal Public School
... Q5.Which nuclei fuse to give rise to endosperm? Q6.What is double fertilisation? Q7.What is shield shaped single cotyledon of monocots called? Q8.Who discovered double fertilisation in angiosperms? Q9.Name a triploid tissue in the seed. Q10.Name a plant where dichogamy is found. Q11.Name a plant whi ...
... Q5.Which nuclei fuse to give rise to endosperm? Q6.What is double fertilisation? Q7.What is shield shaped single cotyledon of monocots called? Q8.Who discovered double fertilisation in angiosperms? Q9.Name a triploid tissue in the seed. Q10.Name a plant where dichogamy is found. Q11.Name a plant whi ...
Australian National Botanic Gardens
... anthers yellow. Each trumpet-shaped flower is held on a long, thin pedicel and is about 2 cm long. The plant makes an ideal rockery subject, taking up very little space but extending its flowering stem high enough to become obvious. lt may also be used in tight rows in more formal situations as the ...
... anthers yellow. Each trumpet-shaped flower is held on a long, thin pedicel and is about 2 cm long. The plant makes an ideal rockery subject, taking up very little space but extending its flowering stem high enough to become obvious. lt may also be used in tight rows in more formal situations as the ...
Chapter 1-Plants in Our World Formation of earth-4.5
... with nutritive tissue, providing for the early survival of the embryo. ...
... with nutritive tissue, providing for the early survival of the embryo. ...
SOL Study Book
... Dormancy can help a plant to survive unfavorable conditions, as in annual plants that pass the cold winter season as dormant seeds. Adaptations help the seeds survive in different types of environments, increasing the chances that they’ll germinate when conditions are right for growth. Some seeds ...
... Dormancy can help a plant to survive unfavorable conditions, as in annual plants that pass the cold winter season as dormant seeds. Adaptations help the seeds survive in different types of environments, increasing the chances that they’ll germinate when conditions are right for growth. Some seeds ...
Plant Cells
... Low growing plants, found in moist, shaded areas where water is in regular supply • Include “groundcover” plants, like moss • Lack vascular tissue (xylem and phloem). Draw up water by osmosis and transfer it by cell to cell contact • Needs water for reproduction • Can live in many different environm ...
... Low growing plants, found in moist, shaded areas where water is in regular supply • Include “groundcover” plants, like moss • Lack vascular tissue (xylem and phloem). Draw up water by osmosis and transfer it by cell to cell contact • Needs water for reproduction • Can live in many different environm ...
Who first discovered cells and what did he use? Robert Hooke
... Who first discovered cells and what did he use? ...
... Who first discovered cells and what did he use? ...
Chapter 23: Plant Evolution
... Pollen grain germinates and grows a tubular structure It grows slowly through the ovule’s tissue for about a year Penetrates the female gametophyte and sperm reaches egg and fertilization occurs ...
... Pollen grain germinates and grows a tubular structure It grows slowly through the ovule’s tissue for about a year Penetrates the female gametophyte and sperm reaches egg and fertilization occurs ...
Flowering plant

The flowering plants (angiosperms), also known as Angiospermae or Magnoliophyta, are the most diverse group of land plants. Angiosperms are seed-producing plants like the gymnosperms and can be distinguished from the gymnosperms by characteristics including flowers, endosperm within the seeds, and the production of fruits that contain the seeds. Etymologically, angiosperm means a plant that produces seeds within an enclosure, in other words, a fruiting plant.The ancestors of flowering plants diverged from gymnosperms around 245–202 million years ago, and the first flowering plants known to exist are from 160 million years ago. They diversified enormously during the Lower Cretaceous and became widespread around 120 million years ago, but replaced conifers as the dominant trees only around 60–100 million years ago.