How are plants adapted for transport?
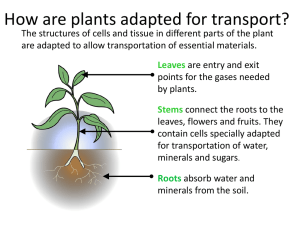
... Stems connect the roots to the leaves, flowers and fruits. They contain cells specially adapted for transportation of water, minerals and sugars. Roots absorb water and minerals from the soil. ...
... Stems connect the roots to the leaves, flowers and fruits. They contain cells specially adapted for transportation of water, minerals and sugars. Roots absorb water and minerals from the soil. ...
Flower Structure
... Not all plants have flowers, and there was a time in history when no plants at all had flowers. Conifers for example have cones, which produce pollen or seeds, they function as structures for sexual reproduction but they are not flowers. About 125 million years ago, primitive flowers appeared in the ...
... Not all plants have flowers, and there was a time in history when no plants at all had flowers. Conifers for example have cones, which produce pollen or seeds, they function as structures for sexual reproduction but they are not flowers. About 125 million years ago, primitive flowers appeared in the ...
Crazy Cuphea - Santa Rosa County Extension
... UF/IFAS Santa Rosa County Crazy Cupheas Looking for a plant that will bloom non-stop all summer long? Then you might want to take a look at the Cupheas. Cuphea (coo-fee’ah) is a large genus of plants belonging to the Loosestrife family, which makes them related to the Crape Myrtles. Cupheas originat ...
... UF/IFAS Santa Rosa County Crazy Cupheas Looking for a plant that will bloom non-stop all summer long? Then you might want to take a look at the Cupheas. Cuphea (coo-fee’ah) is a large genus of plants belonging to the Loosestrife family, which makes them related to the Crape Myrtles. Cupheas originat ...
NCERT Solutions Question 1: Name the parts of an angiosperm
... develops genetic incompatibility between individuals of the same species or between individuals of different species. The plants which exhibit this phenomenon have the ability to prevent germination of pollen grains and thus, prevent the growth of the pollen tube on the stigma of the flower. This pr ...
... develops genetic incompatibility between individuals of the same species or between individuals of different species. The plants which exhibit this phenomenon have the ability to prevent germination of pollen grains and thus, prevent the growth of the pollen tube on the stigma of the flower. This pr ...
PowerPoint
... Reproductive cells, sperm and egg cells, have a single set of chromosomes and are said to be haploid. When fertilization occurs, the single sets of chromosomes are combined into the double set, one from each parent, resulting in traits from each parent being passed on to the offspring. ...
... Reproductive cells, sperm and egg cells, have a single set of chromosomes and are said to be haploid. When fertilization occurs, the single sets of chromosomes are combined into the double set, one from each parent, resulting in traits from each parent being passed on to the offspring. ...
PLANT STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
... Food storage tissue that nourishes the embryo – Embryo – New plant developed after fertilization ...
... Food storage tissue that nourishes the embryo – Embryo – New plant developed after fertilization ...
key stage 2 year group : t - Aldingbourne Primary School
... Collect plants from the school grounds. Observe features. 2 ½ hours occurring plants to groups Show children a simple key and how to use it using a key Introduce Venn diagrams as a way of organising the information Ask children to locate data and answers questions about information in Venn d ...
... Collect plants from the school grounds. Observe features. 2 ½ hours occurring plants to groups Show children a simple key and how to use it using a key Introduce Venn diagrams as a way of organising the information Ask children to locate data and answers questions about information in Venn d ...
Plant Life Cycles
... Instead of producing sperm or egg directly, meiosis in plants in the diploid sporophyte stage produces spores. These are single cells which can be male or female and can divide. When these spores divide by mitosis, they make haploid gametophytes. It is the gametophytes that produce sperm or eggs. Sp ...
... Instead of producing sperm or egg directly, meiosis in plants in the diploid sporophyte stage produces spores. These are single cells which can be male or female and can divide. When these spores divide by mitosis, they make haploid gametophytes. It is the gametophytes that produce sperm or eggs. Sp ...
Acc_Bio_Ch_23_ws
... In the space provided, write which of the following gymnosperms—conifers, cycads, ginkgo, or gnetophytes—is being described. 26. ____________________ only one living species; has fan-shaped leaves 27. ____________________ has short stems and palmlike leaves 28. ____________________ trees and shrubs ...
... In the space provided, write which of the following gymnosperms—conifers, cycads, ginkgo, or gnetophytes—is being described. 26. ____________________ only one living species; has fan-shaped leaves 27. ____________________ has short stems and palmlike leaves 28. ____________________ trees and shrubs ...
document
... and is carried by air to the female part of the plant, where it enters the ovary and fertilizes the ovule. This develops into the seed. In angiosperms, the seed is surrounded by the developed ovary, which becomes the fruit. • .How does this represent an advantage over the Bryophytes and Seedless Vas ...
... and is carried by air to the female part of the plant, where it enters the ovary and fertilizes the ovule. This develops into the seed. In angiosperms, the seed is surrounded by the developed ovary, which becomes the fruit. • .How does this represent an advantage over the Bryophytes and Seedless Vas ...
Seed plants
... • Club mosses are the earliest vascular plants – They lack seeds – Superficially resemble true mosses but they are not related – Homosporous or heterosporous ...
... • Club mosses are the earliest vascular plants – They lack seeds – Superficially resemble true mosses but they are not related – Homosporous or heterosporous ...
seeds - Cloudfront.net
... • THIS ENDOSPERM UNDERGOES CYTOKINESIS TO FORM MEMBRANES AND CELL WALLS BETWEEN THE NUCLEI, THUS BECOMING MULTICELLULAR – ENDOSPERM IS RICH IN NUTRIENTS, WHICH IT PROVIDES TO THE DEVELOPING EMBRYO – IN MOST MONOCOTS, THE ENDOSPERM STOCKS NUTRIENTS THAT CAN BE USED BY THE SEEDLING AFTER GERMINATION – ...
... • THIS ENDOSPERM UNDERGOES CYTOKINESIS TO FORM MEMBRANES AND CELL WALLS BETWEEN THE NUCLEI, THUS BECOMING MULTICELLULAR – ENDOSPERM IS RICH IN NUTRIENTS, WHICH IT PROVIDES TO THE DEVELOPING EMBRYO – IN MOST MONOCOTS, THE ENDOSPERM STOCKS NUTRIENTS THAT CAN BE USED BY THE SEEDLING AFTER GERMINATION – ...
Evol of Seed Plants
... 350-290 mya. Extensive coal deposits in sediments from about 350 to 290 mya. Coal is a carbon-rich rock packed with fossil spores, branches, leaves and tree-trunks. These fossils are frequently derived from platns called lycopods. Because coal formation is thought to start only in the presence of wa ...
... 350-290 mya. Extensive coal deposits in sediments from about 350 to 290 mya. Coal is a carbon-rich rock packed with fossil spores, branches, leaves and tree-trunks. These fossils are frequently derived from platns called lycopods. Because coal formation is thought to start only in the presence of wa ...
Seedless Vascular Plants
... Vein – contains xylem & phloem Stomata-mouth like openings on the underside of a leaf allow the exchange of CO2 and O2 gases with the air water vapor can be lost through open stomata Guard cells ...
... Vein – contains xylem & phloem Stomata-mouth like openings on the underside of a leaf allow the exchange of CO2 and O2 gases with the air water vapor can be lost through open stomata Guard cells ...
Many plants reproduce with flowers and fruit.
... Reproduction in many types of flowering plants includes interactions between plants and animals. The plants are a source of food for the animal. The animals provide a way to transport pollen and seeds. As they eat, animals move pollen from flower to flower and seeds from place to place. Have you eve ...
... Reproduction in many types of flowering plants includes interactions between plants and animals. The plants are a source of food for the animal. The animals provide a way to transport pollen and seeds. As they eat, animals move pollen from flower to flower and seeds from place to place. Have you eve ...
View Teacher`s Guide PDF (F.P.O.)
... a) Seeds: Most plants begin as seeds. The outside part of the seed is called the seed coat; it is a sheath that protects the seed. Inside the seed coat, there is an embryo and a food source. The embryo, a tiny plant, is made up of a small root, a small stem, and very tiny leaves. The food source pro ...
... a) Seeds: Most plants begin as seeds. The outside part of the seed is called the seed coat; it is a sheath that protects the seed. Inside the seed coat, there is an embryo and a food source. The embryo, a tiny plant, is made up of a small root, a small stem, and very tiny leaves. The food source pro ...
Name: Unit Two: Flowers and Plant Life Cycles Review Worksheet
... 4. Why are petals also considered sterile leaves? ...
... 4. Why are petals also considered sterile leaves? ...
Angelonia angustifolia
... Angelonia are heat-loving plants that will grow most vigorously and bloom best when the heat is on, perfect to bring a touch of color to any garden. Angelonia will tolerate wet feet and a fair amount of drought. The plants are easy care with no deadheading needed. A bit of fertilizer or some compost ...
... Angelonia are heat-loving plants that will grow most vigorously and bloom best when the heat is on, perfect to bring a touch of color to any garden. Angelonia will tolerate wet feet and a fair amount of drought. The plants are easy care with no deadheading needed. A bit of fertilizer or some compost ...
Interiorscaping
... Codiaeum variegatum Multi-colored leaves 4-6 feet tall Flowers are fuzzy spikes Euphorbiaceae family Native to South India ...
... Codiaeum variegatum Multi-colored leaves 4-6 feet tall Flowers are fuzzy spikes Euphorbiaceae family Native to South India ...
Article
... the touch, and hairs often have swollen dark bases that form noticeable flecks. Leaves become progressively smaller as they approach the top of the plant. Although large infestations make a pretty photograph, this plant can spread quickly by producing healthy seeds that are easily distributed. A sin ...
... the touch, and hairs often have swollen dark bases that form noticeable flecks. Leaves become progressively smaller as they approach the top of the plant. Although large infestations make a pretty photograph, this plant can spread quickly by producing healthy seeds that are easily distributed. A sin ...
Chapter 8 `Plants` C8S1 `The Plant Kingdom` What is a Plant
... ii. The sperm fertilizes the egg and develops into an embryo c. Seed Development i. As the seeds develop, the female cone increase in size ii. It can take 2 years for the seeds to be ready d. Seed Dispersal i. After the seeds mature, the scales open 1. Wind helps to shake the seeds out of the cone 2 ...
... ii. The sperm fertilizes the egg and develops into an embryo c. Seed Development i. As the seeds develop, the female cone increase in size ii. It can take 2 years for the seeds to be ready d. Seed Dispersal i. After the seeds mature, the scales open 1. Wind helps to shake the seeds out of the cone 2 ...
Flowering plant

The flowering plants (angiosperms), also known as Angiospermae or Magnoliophyta, are the most diverse group of land plants. Angiosperms are seed-producing plants like the gymnosperms and can be distinguished from the gymnosperms by characteristics including flowers, endosperm within the seeds, and the production of fruits that contain the seeds. Etymologically, angiosperm means a plant that produces seeds within an enclosure, in other words, a fruiting plant.The ancestors of flowering plants diverged from gymnosperms around 245–202 million years ago, and the first flowering plants known to exist are from 160 million years ago. They diversified enormously during the Lower Cretaceous and became widespread around 120 million years ago, but replaced conifers as the dominant trees only around 60–100 million years ago.























