01463-02.1 Classify Plants
... 2. Horticultural Classification of Plants A. Evergreen - a plant that retains green leaves/needles year round. Ex. Burford Holly B. Deciduous - a plant that drops its leaves in winter. Ex. Sugar Maple C. Woody - producing woody growth. Ex. Savannah Holly D. Herbaceous - not producing wood growth. Ex ...
... 2. Horticultural Classification of Plants A. Evergreen - a plant that retains green leaves/needles year round. Ex. Burford Holly B. Deciduous - a plant that drops its leaves in winter. Ex. Sugar Maple C. Woody - producing woody growth. Ex. Savannah Holly D. Herbaceous - not producing wood growth. Ex ...
Draft Orbea variegata fsheet
... bright sun. Leaves: represented by conical teeth along the stems. Flowers: five-lobed, shaped like starfish, 5-7 cm across with creamy yellowish-green background covered in purple to purplish-brown splotches. Flowering time - late summer to autumn. Fruit: A pair of cylindrical pods from each flower, ...
... bright sun. Leaves: represented by conical teeth along the stems. Flowers: five-lobed, shaped like starfish, 5-7 cm across with creamy yellowish-green background covered in purple to purplish-brown splotches. Flowering time - late summer to autumn. Fruit: A pair of cylindrical pods from each flower, ...
Investigative study of angiosperms morphology - Bij Javia
... plants. Though they are seed producing plants like gymnosperms, angiosperms produced enclosed seeds. These are flowering plants and produce fruits containing seeds. Some prominent characteristics of angiosperms are : flowers, which are the reproductive organs of the plant and also most distinguishin ...
... plants. Though they are seed producing plants like gymnosperms, angiosperms produced enclosed seeds. These are flowering plants and produce fruits containing seeds. Some prominent characteristics of angiosperms are : flowers, which are the reproductive organs of the plant and also most distinguishin ...
Drosera capensis
... hours with good sunlight. The flowers can be pollinated by insects, but are usually self-pollinated. •When the seeds are ripe, their capsules open to release the fine, light-weight seeds which fall out and are dispersed near the parent plants. ...
... hours with good sunlight. The flowers can be pollinated by insects, but are usually self-pollinated. •When the seeds are ripe, their capsules open to release the fine, light-weight seeds which fall out and are dispersed near the parent plants. ...
Year 5 Living things and their Habitats planning
... Ask children to think, pair, share the names of as many part of a flower, and the functions of each of these, as they can from the previous lesson Explain that plants can reproduce in two different ways: sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction Explain that asexual reproduction does not involve ...
... Ask children to think, pair, share the names of as many part of a flower, and the functions of each of these, as they can from the previous lesson Explain that plants can reproduce in two different ways: sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction Explain that asexual reproduction does not involve ...
Modified Structures - 1 We observed earlier several types of
... A bulb is a dormant shoot system, with a compact, below ground, fleshy set of leaves (Technically bud scales), surrounding the shoot meristem. There is little nutrient stem storage in a bulb; nutrients are found in the fleshy leaves. Bulbs propagate by forming bulblets, which are buds that originate ...
... A bulb is a dormant shoot system, with a compact, below ground, fleshy set of leaves (Technically bud scales), surrounding the shoot meristem. There is little nutrient stem storage in a bulb; nutrients are found in the fleshy leaves. Bulbs propagate by forming bulblets, which are buds that originate ...
Plants I
... structures to draw water up from the soil would have been able to live out of water on the shore. This ancestral plant would also have had to nourish and protect the zygote and developing embryo from drying out; it might have done this by retaining the embryo within its body. Such a plant may have g ...
... structures to draw water up from the soil would have been able to live out of water on the shore. This ancestral plant would also have had to nourish and protect the zygote and developing embryo from drying out; it might have done this by retaining the embryo within its body. Such a plant may have g ...
Lab 5 Plants 1
... structures to draw water up from the soil would have been able to live out of water on the shore. This ancestral plant would also have had to nourish and protect the zygote and developing embryo from drying out; it might have done this by retaining the embryo within its body. Such a plant may have g ...
... structures to draw water up from the soil would have been able to live out of water on the shore. This ancestral plant would also have had to nourish and protect the zygote and developing embryo from drying out; it might have done this by retaining the embryo within its body. Such a plant may have g ...
Unit C 4-10 Basic Principles of Agricultural/Horticultural Science
... Simple layering - branches are bent to the ground and portions of branches are covered with soil. The terminal ends are left exposed. The covered portion must have a bud or buds and must be injured - roots should form in this area. ...
... Simple layering - branches are bent to the ground and portions of branches are covered with soil. The terminal ends are left exposed. The covered portion must have a bud or buds and must be injured - roots should form in this area. ...
Invasive species in pollination networks
... animals that pollinate flowers are mostly generalists, while flowers are more specialised. For example, some plants have flowers that are specialised for pollination by hawkmoths (the functional group in this case), but the hawkmoths themselves may visit dozens of different plant species. There are ...
... animals that pollinate flowers are mostly generalists, while flowers are more specialised. For example, some plants have flowers that are specialised for pollination by hawkmoths (the functional group in this case), but the hawkmoths themselves may visit dozens of different plant species. There are ...
Life Cycle of a Plant
... Once a seed is watered and warmed, it germinates. The root pushes through the seed coat. The roots of the seedling grow down into the soil and the leaves and stem push out of the ground. The stem and its leaves grow toward the sunlight. The leaves make the plant’s food. The flowers form and bloom. N ...
... Once a seed is watered and warmed, it germinates. The root pushes through the seed coat. The roots of the seedling grow down into the soil and the leaves and stem push out of the ground. The stem and its leaves grow toward the sunlight. The leaves make the plant’s food. The flowers form and bloom. N ...
PPT as PDF
... Temperatures 19 - 27 °C are suitable for growing most cultivars. Temperature extremes can result in reduced growth. Temperatures greater than 32° C can cause buds and flowers to drop. Rain during flowering can also cause flowers to drop. Growth and development stop when temperatures ...
... Temperatures 19 - 27 °C are suitable for growing most cultivars. Temperature extremes can result in reduced growth. Temperatures greater than 32° C can cause buds and flowers to drop. Rain during flowering can also cause flowers to drop. Growth and development stop when temperatures ...
Horehound - University of Arizona
... Reproduction: From seeds and spreading roots Weedy characteristics: Can form dense monoculture stands over large areas, reducing native plant diversity. Seeds can remain viable up to 5 years. ...
... Reproduction: From seeds and spreading roots Weedy characteristics: Can form dense monoculture stands over large areas, reducing native plant diversity. Seeds can remain viable up to 5 years. ...
Topic 10: Ferns and Fern Allies
... bryophytes (some mosses and hornworts; in both taxa, stomata are sometimes not functional). Stomata are lacking on bryophyte gametophytes—but, (nonadjustable) pores are found on the liverwort thallus, and some fossil gametophytes appear to have functional stomata. These plants—unlike living plants— ...
... bryophytes (some mosses and hornworts; in both taxa, stomata are sometimes not functional). Stomata are lacking on bryophyte gametophytes—but, (nonadjustable) pores are found on the liverwort thallus, and some fossil gametophytes appear to have functional stomata. These plants—unlike living plants— ...
Shrubs and Small Trees - Missouri Botanical Garden
... small to medium native woody shrubs can be found growing in our state. While this doesn’t include several of the small trees, some are species we might think of as small trees rather than as shrubs. There is a fine line distinguishing between small trees and shrubs—in general, trees have single trun ...
... small to medium native woody shrubs can be found growing in our state. While this doesn’t include several of the small trees, some are species we might think of as small trees rather than as shrubs. There is a fine line distinguishing between small trees and shrubs—in general, trees have single trun ...
Plant parts and functions ppt
... cells that transport water, nutrients, and minerals to all parts of the plant Image found at: www.bio.psu.edu ...
... cells that transport water, nutrients, and minerals to all parts of the plant Image found at: www.bio.psu.edu ...
Spirea - Texas ASLA
... having the appearance of a fountain when in full bloom. The leaves remain on the plant all year and in the fall, they may turn a reddish color. Give this spirea plenty of room because it grows to a height of about six feet tall in full sun or some shade to develop its cascade-like structure. If it r ...
... having the appearance of a fountain when in full bloom. The leaves remain on the plant all year and in the fall, they may turn a reddish color. Give this spirea plenty of room because it grows to a height of about six feet tall in full sun or some shade to develop its cascade-like structure. If it r ...
Long-day plants
... It is thought that plants evolved from aquatic, single-celled organisms called green algae. Today, the dominant terrestrial plants are the angiospermophytes (flowering plants). Fossil records indicate that the angiosperms took over about 100 mya. Angiosperms, or flowering plants, produce seeds enclo ...
... It is thought that plants evolved from aquatic, single-celled organisms called green algae. Today, the dominant terrestrial plants are the angiospermophytes (flowering plants). Fossil records indicate that the angiosperms took over about 100 mya. Angiosperms, or flowering plants, produce seeds enclo ...
chap-4 c
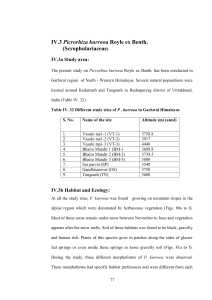
... IV. 34). Flowers bracteate, with a small pedicel, complete, zygomorphic, pentamerous, hermaphrodite and hypogynous (Figs. 87a to c). Bract 1, ovate with dentate margins and acute apex, twisted along the length. Calyx lobes 5, unequal, smaller lobe anterior. Sepals ovate, have dentitions in some of ...
... IV. 34). Flowers bracteate, with a small pedicel, complete, zygomorphic, pentamerous, hermaphrodite and hypogynous (Figs. 87a to c). Bract 1, ovate with dentate margins and acute apex, twisted along the length. Calyx lobes 5, unequal, smaller lobe anterior. Sepals ovate, have dentitions in some of ...
Lab Manual - UBC Blogs
... Double fertilization. unique to angiosperms, then occurs. One sperm fuses with the egg to form the zygote, and the other unites with the polar nuclei to initiate endosperm development (the nutritive tissue for the growing embryo). Following fertilization, the ovules become seeds and the ovary (plus ...
... Double fertilization. unique to angiosperms, then occurs. One sperm fuses with the egg to form the zygote, and the other unites with the polar nuclei to initiate endosperm development (the nutritive tissue for the growing embryo). Following fertilization, the ovules become seeds and the ovary (plus ...
Nerve activates contraction
... Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
PDF - Zebra TechnoSys
... physiology, yet their sexual mode of reproduction is similar in pattern. All organisms reach a certain stage of growth and maturity in their life before they can reproduce sexually. This period is called the juvenile phase and in plants it is known as vegetative phase. After attaining maturity, al ...
... physiology, yet their sexual mode of reproduction is similar in pattern. All organisms reach a certain stage of growth and maturity in their life before they can reproduce sexually. This period is called the juvenile phase and in plants it is known as vegetative phase. After attaining maturity, al ...
reproduction
... physiology, yet their sexual mode of reproduction is similar in pattern. All organisms reach a certain stage of growth and maturity in their life before they can reproduce sexually. This period is called the juvenile phase and in plants it is known as vegetative phase. After attaining maturity, al ...
... physiology, yet their sexual mode of reproduction is similar in pattern. All organisms reach a certain stage of growth and maturity in their life before they can reproduce sexually. This period is called the juvenile phase and in plants it is known as vegetative phase. After attaining maturity, al ...
Plant Growth, Reproduction, and Response
... of a flower is made up of sepals. Sepals are modified leaves that protect the developing flower. They are often green but can also be brightly colored. The layer just inside the sepals is made up of petals, which are also modified leaves. Their bright colors often help attract animal pollinators. Mo ...
... of a flower is made up of sepals. Sepals are modified leaves that protect the developing flower. They are often green but can also be brightly colored. The layer just inside the sepals is made up of petals, which are also modified leaves. Their bright colors often help attract animal pollinators. Mo ...
Flowering plant

The flowering plants (angiosperms), also known as Angiospermae or Magnoliophyta, are the most diverse group of land plants. Angiosperms are seed-producing plants like the gymnosperms and can be distinguished from the gymnosperms by characteristics including flowers, endosperm within the seeds, and the production of fruits that contain the seeds. Etymologically, angiosperm means a plant that produces seeds within an enclosure, in other words, a fruiting plant.The ancestors of flowering plants diverged from gymnosperms around 245–202 million years ago, and the first flowering plants known to exist are from 160 million years ago. They diversified enormously during the Lower Cretaceous and became widespread around 120 million years ago, but replaced conifers as the dominant trees only around 60–100 million years ago.