4.4
... Using Graphic organizer: students will label the parts of a seed producing plant and explain the functions of the roots, stems, leaves, and flowers. Students will analyze foods we eat and identify them as a root, stem, leaf, etc. use “ What part of the plant do we eat” students will describe their f ...
... Using Graphic organizer: students will label the parts of a seed producing plant and explain the functions of the roots, stems, leaves, and flowers. Students will analyze foods we eat and identify them as a root, stem, leaf, etc. use “ What part of the plant do we eat” students will describe their f ...
Pacific Coast Native Iris - California Native Plant Society
... needles, or peat moss are all good soil amendments for improving the acid condition of the soil. They do well with only occasional feeding. They do not need frequent dividing like the bearded iris, and may be left in the ground to slowly increase over the years. If you want to divide or move th ...
... needles, or peat moss are all good soil amendments for improving the acid condition of the soil. They do well with only occasional feeding. They do not need frequent dividing like the bearded iris, and may be left in the ground to slowly increase over the years. If you want to divide or move th ...
plant parts 1
... –Outer covering of the flower bud –Protects the stamens and pistills when flower is in bud stage ...
... –Outer covering of the flower bud –Protects the stamens and pistills when flower is in bud stage ...
Lesson 7 Organisms Reproduce
... The top surface of the leaf is smooth, covered with a waxy cuticle. The bottom surface is rough and has many openings called stomata through which gas exchange occurs. The plant can adjust the size of the openings, making them larger on cool days and smaller or closed altogether on hot days. 6. Each ...
... The top surface of the leaf is smooth, covered with a waxy cuticle. The bottom surface is rough and has many openings called stomata through which gas exchange occurs. The plant can adjust the size of the openings, making them larger on cool days and smaller or closed altogether on hot days. 6. Each ...
Family Grossulariaceae By: Noah Berglund
... palmate venation • Flowers - 6-15 in drooping clusters; reddish or greenish purple; petals about 1 mm long • Fruit - bright red to purplish, smooth berries, about 6 mm ...
... palmate venation • Flowers - 6-15 in drooping clusters; reddish or greenish purple; petals about 1 mm long • Fruit - bright red to purplish, smooth berries, about 6 mm ...
Course: 01.469 Fruit and Vegetable Production Unit 3, Lesson 3
... John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, 1997 ...
... John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, 1997 ...
Sweet pittosporum - Cardinia Shire Council
... beyond its natural range. Plants can readily colonise large area of natural bush. A fast growing plant, it produces large numbers of seeds in early spring, contributing to its invasiveness. This plant is drought and shade tolerant, with seedlings germinating and establishing underneath tree canopies ...
... beyond its natural range. Plants can readily colonise large area of natural bush. A fast growing plant, it produces large numbers of seeds in early spring, contributing to its invasiveness. This plant is drought and shade tolerant, with seedlings germinating and establishing underneath tree canopies ...
Class: VI Subject: Biology Topic: Getting to know plants
... Part of plant that produces food is leaves. It contains chlorophyll that traps the solar energy of sun. Chlorophyll is present inside the chloroplast. This process is called photosynthesis. ...
... Part of plant that produces food is leaves. It contains chlorophyll that traps the solar energy of sun. Chlorophyll is present inside the chloroplast. This process is called photosynthesis. ...
Lesson 1 How Does a Seed Become a Plant?
... whether or not all three kinds of seeds will sprout at the same time, and whether or not all the seeds of one kind (e.g., sunflowers) will sprout simultaneously. Decide how often students will record their observations of plant growth on graph paper or on Activity Sheet 1B-1. An interval of two or t ...
... whether or not all three kinds of seeds will sprout at the same time, and whether or not all the seeds of one kind (e.g., sunflowers) will sprout simultaneously. Decide how often students will record their observations of plant growth on graph paper or on Activity Sheet 1B-1. An interval of two or t ...
ch8
... They function in the development of the floral pattern, e. g. sepals form the first whorl, petals the next whorl, then anthers, etc. We know that there are three classes of organ identity genes that control formation of sepals, petals, stamens, and carpels. In many angiosperms, the flowers are arran ...
... They function in the development of the floral pattern, e. g. sepals form the first whorl, petals the next whorl, then anthers, etc. We know that there are three classes of organ identity genes that control formation of sepals, petals, stamens, and carpels. In many angiosperms, the flowers are arran ...
Native vs. Introduced Plants
... Does not need lots of fertiliser to eat Does not need lots of attention Native plants are suited to the Australian ...
... Does not need lots of fertiliser to eat Does not need lots of attention Native plants are suited to the Australian ...
Types of Rangeland Plants
... The forage value of a plant refers to how well it provides nutrients to grazing animals. The forage value of a plant varies depending on which animal is eating it because nutritional needs and dietary preferences differ by species for grazing animals. For example, a plant could have excellent forage ...
... The forage value of a plant refers to how well it provides nutrients to grazing animals. The forage value of a plant varies depending on which animal is eating it because nutritional needs and dietary preferences differ by species for grazing animals. For example, a plant could have excellent forage ...
evolution and diversity of woody and seed plants
... shrubs or trees with tall overstory canopies (e.g., Figure 5.2), a significant ecological adaptation. Cork produced by the cork cambium functions as a thick layer of cells that protects the delicate vascular cambium and secondary phloem from mechanical damage, predation, and desiccation. Wood anatom ...
... shrubs or trees with tall overstory canopies (e.g., Figure 5.2), a significant ecological adaptation. Cork produced by the cork cambium functions as a thick layer of cells that protects the delicate vascular cambium and secondary phloem from mechanical damage, predation, and desiccation. Wood anatom ...
Hopea odorata1
... even a small decrease in moisture content will lead to a decrease in germination. A recent trial showed that when seeds were dried down to 44% mc, germination went from 100 to 86%, at 31% mc germination was 74% and at 23% mc all seeds were dead. After 16 weeks of storage germination was down to 50% ...
... even a small decrease in moisture content will lead to a decrease in germination. A recent trial showed that when seeds were dried down to 44% mc, germination went from 100 to 86%, at 31% mc germination was 74% and at 23% mc all seeds were dead. After 16 weeks of storage germination was down to 50% ...
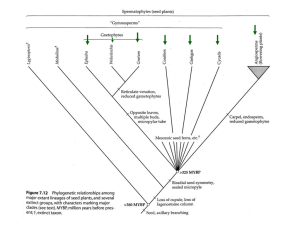
topic #11: gymnosperms
... (both of which have flagellated sperm), the presence of external liquid water is not required. In algae generally and in bryophytes, liquid water is required for gamete transfer. In the ferns and their allies, the sperm are flagellated, but archegonia and antheridia are at or below ground level and ...
... (both of which have flagellated sperm), the presence of external liquid water is not required. In algae generally and in bryophytes, liquid water is required for gamete transfer. In the ferns and their allies, the sperm are flagellated, but archegonia and antheridia are at or below ground level and ...
Tap Root
... – Outer covering of the flower bud – Protects the stamens and pistills when flower is in bud stage ...
... – Outer covering of the flower bud – Protects the stamens and pistills when flower is in bud stage ...
Evolution of the Seed
... Coconut Fruit (a drupe=a fleshy indehiscent fruit with a seed enclosed in a stony endocarp) with its single seed in the center. Peaches and cherries are also drupes. www.botany.hawaii.edu/faculty/webb/BOT410/Angiosperm/CoconutDrawFruitsLab.jpg&imgrefurl=http://www.botany.hawaii.edu/faculty/we ...
... Coconut Fruit (a drupe=a fleshy indehiscent fruit with a seed enclosed in a stony endocarp) with its single seed in the center. Peaches and cherries are also drupes. www.botany.hawaii.edu/faculty/webb/BOT410/Angiosperm/CoconutDrawFruitsLab.jpg&imgrefurl=http://www.botany.hawaii.edu/faculty/we ...
Quiz Ten (9:30-9:35 AM) - University of South Alabama
... A bit more info on prokaryotic evolution is needed • The first prokaryotes were heterotrophs (they simply digested carbon from other organisms; “consumers in the food chain”). By the way, all animals are heterotrophs. ...
... A bit more info on prokaryotic evolution is needed • The first prokaryotes were heterotrophs (they simply digested carbon from other organisms; “consumers in the food chain”). By the way, all animals are heterotrophs. ...
MELASTOMATACEAE
... ROSIDAE CHARACTERS: petals separate, stamens twice the petals in number MYRTALES CHARACTERS: connate carpels, stamens at least twice the petals, tendency to flower parts in fours, internal phloem, hypanthium or inferior ovary APG MYRTALES RECOGNITION CHARACTERS: Myrtales may be recognised by their o ...
... ROSIDAE CHARACTERS: petals separate, stamens twice the petals in number MYRTALES CHARACTERS: connate carpels, stamens at least twice the petals, tendency to flower parts in fours, internal phloem, hypanthium or inferior ovary APG MYRTALES RECOGNITION CHARACTERS: Myrtales may be recognised by their o ...
aquatic plants of texas - AgriLife Extension County Offices
... Distinctive yellow, star-shaped flowers provides basis for it’s common name. ARROWHEAD (Sagittaria spp.) Perennial, generally emergent plants growing from a rhizome with large leaves. Leaf shape can vary from blade to the broad lancelot form. Some underwater rosettes of leaves can be produced. White ...
... Distinctive yellow, star-shaped flowers provides basis for it’s common name. ARROWHEAD (Sagittaria spp.) Perennial, generally emergent plants growing from a rhizome with large leaves. Leaf shape can vary from blade to the broad lancelot form. Some underwater rosettes of leaves can be produced. White ...
concepts-of-biology
... plants. Of these, about 260,000 are plants that produce seeds. Mosses, ferns, conifers, and flowering plants are all members of the plant kingdom. The plant kingdom contains mostly photosynthetic organisms; a few parasitic forms have lost the ability to photosynthesize. The process of photosynthesis ...
... plants. Of these, about 260,000 are plants that produce seeds. Mosses, ferns, conifers, and flowering plants are all members of the plant kingdom. The plant kingdom contains mostly photosynthetic organisms; a few parasitic forms have lost the ability to photosynthesize. The process of photosynthesis ...
full text pdf
... microspores. When the microspores are released from the tetrads, microgametogenesis starts and after subsequent divisions, complete male gametophytes are formed. Our studies concern the events and changes that occur during microsporogenesis and microgametogenesis that lead to formation of mature pol ...
... microspores. When the microspores are released from the tetrads, microgametogenesis starts and after subsequent divisions, complete male gametophytes are formed. Our studies concern the events and changes that occur during microsporogenesis and microgametogenesis that lead to formation of mature pol ...
Early Plant Development
... entiate into two kinds of cells: trichoblasts which form hairbearing epidermal cells, and atrichoblasts which form hairless epidermal cells. The positioning of trichoblasts among atrichoblasts determines the pattern of root hairs on the developing root. When researchers looked very carefully at the ...
... entiate into two kinds of cells: trichoblasts which form hairbearing epidermal cells, and atrichoblasts which form hairless epidermal cells. The positioning of trichoblasts among atrichoblasts determines the pattern of root hairs on the developing root. When researchers looked very carefully at the ...
Mother of Millions - Narrabri Shire Council
... in colour with dark green patches and a shallow groove on the upper surface. There are up to 7 projections at the tip of each leaf which when broken off can develop into new plants. Stem: Pinkish-brown or grey in colour. Underground Structures: Confusing Species: In NSW there are two less common Bry ...
... in colour with dark green patches and a shallow groove on the upper surface. There are up to 7 projections at the tip of each leaf which when broken off can develop into new plants. Stem: Pinkish-brown or grey in colour. Underground Structures: Confusing Species: In NSW there are two less common Bry ...
Flowering plant

The flowering plants (angiosperms), also known as Angiospermae or Magnoliophyta, are the most diverse group of land plants. Angiosperms are seed-producing plants like the gymnosperms and can be distinguished from the gymnosperms by characteristics including flowers, endosperm within the seeds, and the production of fruits that contain the seeds. Etymologically, angiosperm means a plant that produces seeds within an enclosure, in other words, a fruiting plant.The ancestors of flowering plants diverged from gymnosperms around 245–202 million years ago, and the first flowering plants known to exist are from 160 million years ago. They diversified enormously during the Lower Cretaceous and became widespread around 120 million years ago, but replaced conifers as the dominant trees only around 60–100 million years ago.