Light-Regulated, Tissue-Specific, and Cell Differentiation
... of iron in response to distinctive developmental cues. ...
... of iron in response to distinctive developmental cues. ...
1 Introduction
... handles protein, the muscle’s main constituent. Unlike body fat, a highly efficient form of fuel storage, body protein cannot be stored but makes up functional or structural tissues. As a consequence, protein tissue is constantly being broken down and resynthesized, be it into muscle tissue, clottin ...
... handles protein, the muscle’s main constituent. Unlike body fat, a highly efficient form of fuel storage, body protein cannot be stored but makes up functional or structural tissues. As a consequence, protein tissue is constantly being broken down and resynthesized, be it into muscle tissue, clottin ...
Pink Profusion Phlox
... snow cover before exploding into flowering and new vegetative growth the following spring. ...
... snow cover before exploding into flowering and new vegetative growth the following spring. ...
Written Transcript of this video lesson (Word format)
... if giraffes are pollinators for the acacia tree. Another way a flower can be pollinated is by the wind. Wind-pollinated plants are usually duller to look at because they do not invest in resources that attract pollinating organisms such as showy flowers, nectars, or scent. A breeze or gust of wind m ...
... if giraffes are pollinators for the acacia tree. Another way a flower can be pollinated is by the wind. Wind-pollinated plants are usually duller to look at because they do not invest in resources that attract pollinating organisms such as showy flowers, nectars, or scent. A breeze or gust of wind m ...
Unit I – Grasslands and Grassland Plants
... terminal bud scars shows one year’s growth. Lenticels are breathing pores found scattered on the stem. A leaf scar is found where a leaf was attached to the stem. See Figure 3.19 for an illustration of the different parts of a woody plant stem. ...
... terminal bud scars shows one year’s growth. Lenticels are breathing pores found scattered on the stem. A leaf scar is found where a leaf was attached to the stem. See Figure 3.19 for an illustration of the different parts of a woody plant stem. ...
Discoveries in Plant Biology 1998 Hatch
... relating to sugar cane research. As a result we were aware of the work reported in the Annual Reports on the labelling of compounds from photoassimilated 14C02, and had often discussed the possible implications of this observation. Oddly, it was not until 1965 that this Hawaiian work was published i ...
... relating to sugar cane research. As a result we were aware of the work reported in the Annual Reports on the labelling of compounds from photoassimilated 14C02, and had often discussed the possible implications of this observation. Oddly, it was not until 1965 that this Hawaiian work was published i ...
Plant Profiles - Oklahoma Proven
... Toad lilies are known for their very unique flowers. Flowers are pale lilac with dark purple spots that appear on upright arching stems late summer to early fall when many other plants are beginning to wind down. The flowers are small, so place toad lily in a spot where they can be appreciated up cl ...
... Toad lilies are known for their very unique flowers. Flowers are pale lilac with dark purple spots that appear on upright arching stems late summer to early fall when many other plants are beginning to wind down. The flowers are small, so place toad lily in a spot where they can be appreciated up cl ...
Bacillus thuringiensis var kurstaki
... • Use a bacterium, fungus lines or protozoan as an active ingredient • Control many different pests • Bacillus thuringiensis – commonly used microbial pesticide – kills various species of mosquitoes, fungus gnats and blackflies – has no negative effect on non-target organisms ...
... • Use a bacterium, fungus lines or protozoan as an active ingredient • Control many different pests • Bacillus thuringiensis – commonly used microbial pesticide – kills various species of mosquitoes, fungus gnats and blackflies – has no negative effect on non-target organisms ...
Growing the Hallucinogens â Hudson Grubber
... reduce the area exposed to air and so prevent wilting. The cuttings should have some leaves, though, as this will help them to root faster. They should be shaded and have gentle bottom heat. Many herbaceous plants may be rooted in water. When rooting this way, never place the cuttings in more than 2 ...
... reduce the area exposed to air and so prevent wilting. The cuttings should have some leaves, though, as this will help them to root faster. They should be shaded and have gentle bottom heat. Many herbaceous plants may be rooted in water. When rooting this way, never place the cuttings in more than 2 ...
Sum and Substance - Niagara College Greenhouse and Nursery
... lavender or pale-lilac, bell-shaped, fragrant flowers on 3- to 4-foot-long stalks. Unfortunately, these will tend to droop with time. Seed pods eventually form. Culture While most hostas are shade lovers, ‘Sum and Substance’ can be planted in full sun (where it will receive five to six hours of sun ...
... lavender or pale-lilac, bell-shaped, fragrant flowers on 3- to 4-foot-long stalks. Unfortunately, these will tend to droop with time. Seed pods eventually form. Culture While most hostas are shade lovers, ‘Sum and Substance’ can be planted in full sun (where it will receive five to six hours of sun ...
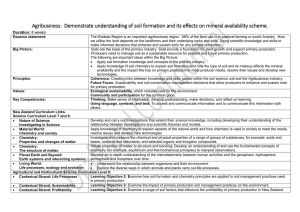
Demonstrate understanding of soil formation and its effects on
... formation affect the primary industry? use is in pastoral farming or exotic How does the knowledge of soil forestry. How we utilise the land chemistry explain soil formation? depends on the landforms and their How is soil chemistry used in primary underlying rocks and soils. production to meet p ...
... formation affect the primary industry? use is in pastoral farming or exotic How does the knowledge of soil forestry. How we utilise the land chemistry explain soil formation? depends on the landforms and their How is soil chemistry used in primary underlying rocks and soils. production to meet p ...
increased production in organic pecans
... Pecans from the Gebert orchard generally sell for about $2.00 per pound wholesale. Using the average yield for the conventional management system of 25 pounds per tree and roughly 35 trees per acre, sale of the crop generates about $1,750 per acre (25x35x$2). But the ARS bestmanagement organic syste ...
... Pecans from the Gebert orchard generally sell for about $2.00 per pound wholesale. Using the average yield for the conventional management system of 25 pounds per tree and roughly 35 trees per acre, sale of the crop generates about $1,750 per acre (25x35x$2). But the ARS bestmanagement organic syste ...
plant Identikit - The Great Plant Hunt
... When studying habitats and the wildlife in them, children and adults are encouraged to consider and discuss appropriate ways of behaving. Drawing up a code of conduct is a useful class exercise before undertaking an activity. It is not normally acceptable to pick or remove wild flowers from their ha ...
... When studying habitats and the wildlife in them, children and adults are encouraged to consider and discuss appropriate ways of behaving. Drawing up a code of conduct is a useful class exercise before undertaking an activity. It is not normally acceptable to pick or remove wild flowers from their ha ...
Azoles and Barbiturates
... SAR of Azole antifungals: • They are characterized by presence of a weekly basic imidazole / 1,2,4-triazole nucleus for antifungal activity. • The amidine ‘N’ atom at 3rd position of imidazole and 4th position of triazole are responsible for decreased concentration of heme iron due to complexation d ...
... SAR of Azole antifungals: • They are characterized by presence of a weekly basic imidazole / 1,2,4-triazole nucleus for antifungal activity. • The amidine ‘N’ atom at 3rd position of imidazole and 4th position of triazole are responsible for decreased concentration of heme iron due to complexation d ...
Ponds and Bogs with NW Native Plants
... Whichever style you select, the first requirement for a water garden is some way to hold water. You can use a bowl or a bucket or an old child’s wading pool. I’ve seen water gardens made out of the discarded tub of a washing machine, a plastic wine barrel liner, a wheelbarrow. I thought about making ...
... Whichever style you select, the first requirement for a water garden is some way to hold water. You can use a bowl or a bucket or an old child’s wading pool. I’ve seen water gardens made out of the discarded tub of a washing machine, a plastic wine barrel liner, a wheelbarrow. I thought about making ...
Poisonous Plants
... of the organ system affected, for example, cardiac. A more specific description of compounds may not be available (e.g., a resin), or the biochemical mechanism of a particular poisonous component in causing toxicity may not be known, although the organ system affected may be known. In some cases, a ...
... of the organ system affected, for example, cardiac. A more specific description of compounds may not be available (e.g., a resin), or the biochemical mechanism of a particular poisonous component in causing toxicity may not be known, although the organ system affected may be known. In some cases, a ...
IdentIfIcatIon of WInter annual Weeds
... Winter annual weeds typically emerge in late summer and fall, survive through the winter by growing into small rosettes, then resume their growth and produce seeds in late spring or early summer of the following year. Low atmospheric temperature, along with undisturbed soils with sufficient moisture ...
... Winter annual weeds typically emerge in late summer and fall, survive through the winter by growing into small rosettes, then resume their growth and produce seeds in late spring or early summer of the following year. Low atmospheric temperature, along with undisturbed soils with sufficient moisture ...
Production guideline
... The nutritional requirements of soya beans are moderately high in comparison with other grains. Soya beans consume more phosphorus, potassium, magnesium and calcium than maize crops do. The soya bean plant has a strong tap-root system and is able to use nutrients in the subsoil very effectively. Rot ...
... The nutritional requirements of soya beans are moderately high in comparison with other grains. Soya beans consume more phosphorus, potassium, magnesium and calcium than maize crops do. The soya bean plant has a strong tap-root system and is able to use nutrients in the subsoil very effectively. Rot ...
Identification of genes involved in the response of Arabidopsis
... This work was funded by the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council. Present address of Nicky Atkinson: The Roslin Institute, The University of Edinburgh, Easter ...
... This work was funded by the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council. Present address of Nicky Atkinson: The Roslin Institute, The University of Edinburgh, Easter ...
English
... should have high viability of over a 75 percent germination rate. Vigor is the ability of seeds to germinate under different conditions and still produce healthy seedlings. Commercial seed is often graded according to size to aid in planting. B. Seed production is an important link in insuring qual ...
... should have high viability of over a 75 percent germination rate. Vigor is the ability of seeds to germinate under different conditions and still produce healthy seedlings. Commercial seed is often graded according to size to aid in planting. B. Seed production is an important link in insuring qual ...
Effects of Calotropis procera (Ait.) R.Br. leaves on the
... The inhibitory substances (allelochemicals) are released to the environment where they affect the growth and development of neighbouring plants. The allelochemicals are found in plant parts such as leaves, flowers, roots, fruits, stem, rhizomes and seeds( Sisodia and Siddiqui, 2010) from where they ...
... The inhibitory substances (allelochemicals) are released to the environment where they affect the growth and development of neighbouring plants. The allelochemicals are found in plant parts such as leaves, flowers, roots, fruits, stem, rhizomes and seeds( Sisodia and Siddiqui, 2010) from where they ...
The Rop GTPase Switch Controls Multiple Developmental
... G proteins are universal molecular switches in eukaryotic signal transduction. The Arabidopsis genome sequence reveals no RAS small GTPase and only one or a few heterotrimeric G proteins, two predominant classes of signaling G proteins found in animals. In contrast, Arabidopsis possesses a unique fa ...
... G proteins are universal molecular switches in eukaryotic signal transduction. The Arabidopsis genome sequence reveals no RAS small GTPase and only one or a few heterotrimeric G proteins, two predominant classes of signaling G proteins found in animals. In contrast, Arabidopsis possesses a unique fa ...
Morphological evolution in land plants
... period, was partially achieved through the recruitment of genes and genetic mechanisms that had previously evolved and functioned in the gametophyte generation of charophytes and early land plants. Some genes also have ancient functions that are restricted to the diploid phase of the life cycle (zyg ...
... period, was partially achieved through the recruitment of genes and genetic mechanisms that had previously evolved and functioned in the gametophyte generation of charophytes and early land plants. Some genes also have ancient functions that are restricted to the diploid phase of the life cycle (zyg ...
Plant nutrition
.jpg?width=300)
Plant nutrition is the study of the chemical elements and compounds that are necessary for plant growth, and also of their external supply and internal metabolism. In 1972, E. Epstein defined two criteria for an element to be essential for plant growth: in its absence the plant is unable to complete a normal life cycle; or that the element is part of some essential plant constituent or metabolite.This is in accordance with Liebig's law of the minimum. There are 14 essential plant nutrients. Carbon and oxygen are absorbed from the air, while other nutrients including water are typically obtained from the soil (exceptions include some parasitic or carnivorous plants).Plants must obtain the following mineral nutrients from the growing media: the primary macronutrients: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K) the three secondary macronutrients: calcium (Ca), sulfur (S), magnesium (Mg) the micronutrients/trace minerals: boron (B), chlorine (Cl), manganese (Mn), iron (Fe), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), molybdenum (Mo), nickel (Ni)The macronutrients are consumed in larger quantities and are present in plant tissue in quantities from 0.2% to 4.0% (on a dry matter weight basis). Micro nutrients are present in plant tissue in quantities measured in parts per million, ranging from 5 to 200 ppm, or less than 0.02% dry weight.Most soil conditions across the world can provide plants with adequate nutrition and do not require fertilizer for a complete life cycle. However, humans can artificially modify soil through the addition of fertilizer to promote vigorous growth and increase yield. The plants are able to obtain their required nutrients from the fertilizer added to the soil. A colloidal carbonaceous residue, known as humus, can serve as a nutrient reservoir. Even with adequate water and sunshine, nutrient deficiency can limit growth.Nutrient uptake from the soil is achieved by cation exchange, where root hairs pump hydrogen ions (H+) into the soil through proton pumps. These hydrogen ions displace cations attached to negatively charged soil particles so that the cations are available for uptake by the root.Plant nutrition is a difficult subject to understand completely, partly because of the variation between different plants and even between different species or individuals of a given clone. An element present at a low level may cause deficiency symptoms, while the same element at a higher level may cause toxicity. Further, deficiency of one element may present as symptoms of toxicity from another element. An abundance of one nutrient may cause a deficiency of another nutrient. For example, lower availability of a given nutrient such as SO42− can affect the uptake of another nutrient, such as NO3−. As another example, K+ uptake can be influenced by the amount of NH4+ available.The root, especially the root hair, is the most essential organ for the uptake of nutrients. The structure and architecture of the root can alter the rate of nutrient uptake. Nutrient ions are transported to the center of the root, the stele in order for the nutrients to reach the conducting tissues, xylem and phloem. The Casparian strip, a cell wall outside the stele but within the root, prevents passive flow of water and nutrients, helping to regulate the uptake of nutrients and water. Xylem moves water and inorganic molecules within the plant and phloem accounts for organic molecule transportation. Water potential plays a key role in a plants nutrient uptake. If the water potential is more negative within the plant than the surrounding soils, the nutrients will move from the region of higher solute concentration—in the soil—to the area of lower solute concentration: in the plant.There are three fundamental ways plants uptake nutrients through the root: simple diffusion, occurs when a nonpolar molecule, such as O2, CO2, and NH3 follows a concentration gradient, moving passively through the cell lipid bilayer membrane without the use of transport proteins. facilitated diffusion, is the rapid movement of solutes or ions following a concentration gradient, facilitated by transport proteins. Active transport, is the uptake by cells of ions or molecules against a concentration gradient; this requires an energy source, usually ATP, to power molecular pumps that move the ions or molecules through the membrane. Nutrients are moved inside a plant to where they are most needed. For example, a plant will try to supply more nutrients to its younger leaves than to its older ones. When nutrients are mobile, symptoms of any deficiency become apparent first on the older leaves. However, not all nutrients are equally mobile. Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are mobile nutrients, while the others have varying degrees of mobility. When a less mobile nutrient is deficient, the younger leaves suffer because the nutrient does not move up to them but stays in the older leaves. This phenomenon is helpful in determining which nutrients a plant may be lacking.Many plants engage in symbiosis with microorganisms. Two important types of these relationship are with bacteria such as rhizobia, that carry out biological nitrogen fixation, in which atmospheric nitrogen (N2) is converted into ammonium (NH4); and with mycorrhizal fungi, which through their association with the plant roots help to create a larger effective root surface area. Both of these mutualistic relationships enhance nutrient uptake. Though nitrogen is plentiful in the Earth's atmosphere, relatively few plants harbor nitrogen fixing bacteria, so most plants rely on nitrogen compounds present in the soil to support their growth. These can be supplied by mineralization of soil organic matter or added plant residues, nitrogen fixing bacteria, animal waste, or through the application of fertilizers.Hydroponics, is a method for growing plants in a water-nutrient solution without the use of nutrient-rich soil. It allows researchers and home gardeners to grow their plants in a controlled environment. The most common solution, is the Hoagland solution, developed by D. R. Hoagland in 1933, the solution consists of all the essential nutrients in the correct proportions necessary for most plant growth. An aerator is used to prevent an anoxic event or hypoxia. Hypoxia can affect nutrient uptake of a plant because without oxygen present, respiration becomes inhibited within the root cells. The Nutrient film technique is a variation of hydroponic technique. The roots are not fully submerged, which allows for adequate aeration of the roots, while a ""film"" thin layer of nutrient rich water is pumped through the system to provide nutrients and water to the plant.