genetics study of how traits of characteristics are passed from parent
... inorganic soil amendments that are mined or manmade internal parasites parasites that spend part of their life cycle inside the animal’s body internodes segments on a stem between nodes ...
... inorganic soil amendments that are mined or manmade internal parasites parasites that spend part of their life cycle inside the animal’s body internodes segments on a stem between nodes ...
flowering plants
... PLANTS • eukaryotic • autotrophic (through photosynthesis) • cells have walls made of cellulose ...
... PLANTS • eukaryotic • autotrophic (through photosynthesis) • cells have walls made of cellulose ...
Worksheet 9.1 - contentextra
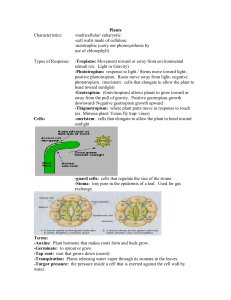
... Water moves into the root hairs of roots because they have a higher solute concentration and a lower water concentration than the surrounding soil. Once in the root hairs, water follows this pathway: epidermis → cortex → vascular cylinder. A protein pump may carry out chemiosmosis to transport miner ...
... Water moves into the root hairs of roots because they have a higher solute concentration and a lower water concentration than the surrounding soil. Once in the root hairs, water follows this pathway: epidermis → cortex → vascular cylinder. A protein pump may carry out chemiosmosis to transport miner ...
Interiorscaping
... Multi-colored leaves 4-6 feet tall Flowers are fuzzy spikes Euphorbiaceae family Native to South India ...
... Multi-colored leaves 4-6 feet tall Flowers are fuzzy spikes Euphorbiaceae family Native to South India ...
Poinsettias
... • Day temperature 5 to 10 degrees higher than night temperature. • Night temp should be 65 degrees with day temp being around 70-75 degrees. ...
... • Day temperature 5 to 10 degrees higher than night temperature. • Night temp should be 65 degrees with day temp being around 70-75 degrees. ...
CRSC 6 – Introduction to Precision Agriculture
... 1. List two tillage factors which could be varied with the assistance of GPS and soil sensor technology. ...
... 1. List two tillage factors which could be varied with the assistance of GPS and soil sensor technology. ...
Plantae - phsgirard.org
... Anchor the plant Absorb & transport nutrients & water Store food The Stem Produce & support new leaves, branches, and flowers Place them in positions where they can function most efficiently Transport materials to and from the roots Store food Carry on photosynthesis Reproduce new plants ...
... Anchor the plant Absorb & transport nutrients & water Store food The Stem Produce & support new leaves, branches, and flowers Place them in positions where they can function most efficiently Transport materials to and from the roots Store food Carry on photosynthesis Reproduce new plants ...
An increase in the Aplectrum hyemale population in Hougham
... flowers in spring as the leaf dies. It is found throughout the Midwest in relatively, undisturbed mesic woods,including Hougham Woods Biological Field Station in Johnson County, Indiana. The plant population biology of these orchids has been studied for three years. The population remained stable fo ...
... flowers in spring as the leaf dies. It is found throughout the Midwest in relatively, undisturbed mesic woods,including Hougham Woods Biological Field Station in Johnson County, Indiana. The plant population biology of these orchids has been studied for three years. The population remained stable fo ...
2 - Capital High School
... Plants keep stomata open just enough so that gas exchange can occur for photosynthesis but not so much that they lose too much water When water is ______________ water flows into the leaf. This increases water pressure in the guard cells and ____________ them. When water is __________________, ...
... Plants keep stomata open just enough so that gas exchange can occur for photosynthesis but not so much that they lose too much water When water is ______________ water flows into the leaf. This increases water pressure in the guard cells and ____________ them. When water is __________________, ...
Bundle 12 Ecology Gallery Walk Key 2
... 47. Example: nitrogen fixing bacteria on plant roots 48. Example: wolf and bunny 49. Example: bird in a tree 50. Example: humans and mosquitos 51. Change of a population over time (plants growing from small to big) 52. Breakdown of rock leads to soil which can help bigger plants grow 53. It increase ...
... 47. Example: nitrogen fixing bacteria on plant roots 48. Example: wolf and bunny 49. Example: bird in a tree 50. Example: humans and mosquitos 51. Change of a population over time (plants growing from small to big) 52. Breakdown of rock leads to soil which can help bigger plants grow 53. It increase ...
Spider Plant - Kansas State University
... Spider or Airplane Plants have either one of three leaf color patterns: solid green leaves, green edges with a white variegated stripe down the center of the leaf blade or leaves with white edges and a green stripe down the center. Basics: This easy to grow plant is more tolerant of extreme conditio ...
... Spider or Airplane Plants have either one of three leaf color patterns: solid green leaves, green edges with a white variegated stripe down the center of the leaf blade or leaves with white edges and a green stripe down the center. Basics: This easy to grow plant is more tolerant of extreme conditio ...
Plant Responses to Stimuli
... only flower if the night is short enough. They will flower in the late Spring early Summer. Short-day plants: Need a long night to flower. Day-neutral plants: These are sensitive to temperature ...
... only flower if the night is short enough. They will flower in the late Spring early Summer. Short-day plants: Need a long night to flower. Day-neutral plants: These are sensitive to temperature ...
plant packet_ans
... 12. What are the three basic types of plant cells? Parenchyma – loosely packed, used for photosynthesis, storage of water and nutrients and healing Collenchyma – thicker and uneven, provide support Sclerenchyma - thick and even, used for support and structure where growth is no longer occurrin ...
... 12. What are the three basic types of plant cells? Parenchyma – loosely packed, used for photosynthesis, storage of water and nutrients and healing Collenchyma – thicker and uneven, provide support Sclerenchyma - thick and even, used for support and structure where growth is no longer occurrin ...
Spider Plant - Market Blooms
... Spider Plant A very common houseplant, grown as such for more than two hundred years. Numerous plantlets, (babies) develop on mature plants. These are easily rooted to propagate new plants. Tiny white unscented flowers will develop at the ends of long stems before the baby plantlets begin to grow. A ...
... Spider Plant A very common houseplant, grown as such for more than two hundred years. Numerous plantlets, (babies) develop on mature plants. These are easily rooted to propagate new plants. Tiny white unscented flowers will develop at the ends of long stems before the baby plantlets begin to grow. A ...
Caring for Oxalis (Flowering Shamrock)
... The Oxalis is a great houseplant, easy to care for, and one of the few houseplants that actually blooms all year long. It has clover shaped leaves that fold up at night. The 5-petaled flowers appear on tall stems above the foliage and may be white, pink or red, depending on the species. They will gr ...
... The Oxalis is a great houseplant, easy to care for, and one of the few houseplants that actually blooms all year long. It has clover shaped leaves that fold up at night. The 5-petaled flowers appear on tall stems above the foliage and may be white, pink or red, depending on the species. They will gr ...
The Plant Kingdom - Modesto Junior College
... • 500,000 kinds of plants exist. • Many don’t fit well. • Recent trends based on evolutionary origins & Relationship. – Monera; the bacteria & blue green algae. – Protista; all other algae & the protozoans. – Mycota, fungi; such as mushrooms & molds – Plantae; mosses, ferns, seed plants & several mi ...
... • 500,000 kinds of plants exist. • Many don’t fit well. • Recent trends based on evolutionary origins & Relationship. – Monera; the bacteria & blue green algae. – Protista; all other algae & the protozoans. – Mycota, fungi; such as mushrooms & molds – Plantae; mosses, ferns, seed plants & several mi ...
Download/View
... nitrogen cycle. The fixation of nitrogen, in which the gaseous form dinitrogen, N2) is converted into forms usable by living organisms, occurs as a consequence of atmospheric processes such as lightning, but most fixation is carried out by free-living and symbiotic bacteria. Plants and bacteria part ...
... nitrogen cycle. The fixation of nitrogen, in which the gaseous form dinitrogen, N2) is converted into forms usable by living organisms, occurs as a consequence of atmospheric processes such as lightning, but most fixation is carried out by free-living and symbiotic bacteria. Plants and bacteria part ...
Chapter 21 - 22
... generates sugar which are the building blocks of other organic molecules Water – absorbed by plant – supplies the hydrogen for photosynthesis; solvent for transport of other molecules; makes up about 80-85% of a nonwoody plant’s mass Soil – source of inorganic nutrients (minerals) ...
... generates sugar which are the building blocks of other organic molecules Water – absorbed by plant – supplies the hydrogen for photosynthesis; solvent for transport of other molecules; makes up about 80-85% of a nonwoody plant’s mass Soil – source of inorganic nutrients (minerals) ...
Unit 8
... allows them to grow, but in case of drought the plants will die off quicker. List three cues that contribute to stomatal opening at dawn. light, potassium guard cells accumulate potassium Describe environmental stresses that can cause stomata to close during the daytime. Excessive potassium, flash o ...
... allows them to grow, but in case of drought the plants will die off quicker. List three cues that contribute to stomatal opening at dawn. light, potassium guard cells accumulate potassium Describe environmental stresses that can cause stomata to close during the daytime. Excessive potassium, flash o ...
notes
... incorporate into their tissues in relatively large amounts • The rest are micronutrients, required only in trace amounts ...
... incorporate into their tissues in relatively large amounts • The rest are micronutrients, required only in trace amounts ...
MOST COMMON NUTRIENT DEFICIENCIES IN VASCULAR PLANTS
... The first symptom in some plants is a white specking or freckling of the leaf blades. Cl excess impedes the uptake of K. K deficiency ...
... The first symptom in some plants is a white specking or freckling of the leaf blades. Cl excess impedes the uptake of K. K deficiency ...
Plants
... Xylem-a transport subsystem containing key cells called tracheids. This system carries water upward from the roots to every part of a plant. Tracheids are hollow cells with thick cell walls that resist pressure (example- drinking straw). Phloem-transports solutions of nutrients and carbohydrates pro ...
... Xylem-a transport subsystem containing key cells called tracheids. This system carries water upward from the roots to every part of a plant. Tracheids are hollow cells with thick cell walls that resist pressure (example- drinking straw). Phloem-transports solutions of nutrients and carbohydrates pro ...
Kingdom Plantae Introduction Questions
... 1. What is the cell wall of plants made of? (pg 551) 2. A spore producing plant is known as a _____________ (pg 552). 3. Name three examples of a bryophyte (pg 556). 4. Bryophytes lack true roots. Instead, they have _______, which are long a thin and help anchor them to the ground (pg 557). 5. Which ...
... 1. What is the cell wall of plants made of? (pg 551) 2. A spore producing plant is known as a _____________ (pg 552). 3. Name three examples of a bryophyte (pg 556). 4. Bryophytes lack true roots. Instead, they have _______, which are long a thin and help anchor them to the ground (pg 557). 5. Which ...
Plant nutrition
.jpg?width=300)
Plant nutrition is the study of the chemical elements and compounds that are necessary for plant growth, and also of their external supply and internal metabolism. In 1972, E. Epstein defined two criteria for an element to be essential for plant growth: in its absence the plant is unable to complete a normal life cycle; or that the element is part of some essential plant constituent or metabolite.This is in accordance with Liebig's law of the minimum. There are 14 essential plant nutrients. Carbon and oxygen are absorbed from the air, while other nutrients including water are typically obtained from the soil (exceptions include some parasitic or carnivorous plants).Plants must obtain the following mineral nutrients from the growing media: the primary macronutrients: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K) the three secondary macronutrients: calcium (Ca), sulfur (S), magnesium (Mg) the micronutrients/trace minerals: boron (B), chlorine (Cl), manganese (Mn), iron (Fe), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), molybdenum (Mo), nickel (Ni)The macronutrients are consumed in larger quantities and are present in plant tissue in quantities from 0.2% to 4.0% (on a dry matter weight basis). Micro nutrients are present in plant tissue in quantities measured in parts per million, ranging from 5 to 200 ppm, or less than 0.02% dry weight.Most soil conditions across the world can provide plants with adequate nutrition and do not require fertilizer for a complete life cycle. However, humans can artificially modify soil through the addition of fertilizer to promote vigorous growth and increase yield. The plants are able to obtain their required nutrients from the fertilizer added to the soil. A colloidal carbonaceous residue, known as humus, can serve as a nutrient reservoir. Even with adequate water and sunshine, nutrient deficiency can limit growth.Nutrient uptake from the soil is achieved by cation exchange, where root hairs pump hydrogen ions (H+) into the soil through proton pumps. These hydrogen ions displace cations attached to negatively charged soil particles so that the cations are available for uptake by the root.Plant nutrition is a difficult subject to understand completely, partly because of the variation between different plants and even between different species or individuals of a given clone. An element present at a low level may cause deficiency symptoms, while the same element at a higher level may cause toxicity. Further, deficiency of one element may present as symptoms of toxicity from another element. An abundance of one nutrient may cause a deficiency of another nutrient. For example, lower availability of a given nutrient such as SO42− can affect the uptake of another nutrient, such as NO3−. As another example, K+ uptake can be influenced by the amount of NH4+ available.The root, especially the root hair, is the most essential organ for the uptake of nutrients. The structure and architecture of the root can alter the rate of nutrient uptake. Nutrient ions are transported to the center of the root, the stele in order for the nutrients to reach the conducting tissues, xylem and phloem. The Casparian strip, a cell wall outside the stele but within the root, prevents passive flow of water and nutrients, helping to regulate the uptake of nutrients and water. Xylem moves water and inorganic molecules within the plant and phloem accounts for organic molecule transportation. Water potential plays a key role in a plants nutrient uptake. If the water potential is more negative within the plant than the surrounding soils, the nutrients will move from the region of higher solute concentration—in the soil—to the area of lower solute concentration: in the plant.There are three fundamental ways plants uptake nutrients through the root: simple diffusion, occurs when a nonpolar molecule, such as O2, CO2, and NH3 follows a concentration gradient, moving passively through the cell lipid bilayer membrane without the use of transport proteins. facilitated diffusion, is the rapid movement of solutes or ions following a concentration gradient, facilitated by transport proteins. Active transport, is the uptake by cells of ions or molecules against a concentration gradient; this requires an energy source, usually ATP, to power molecular pumps that move the ions or molecules through the membrane. Nutrients are moved inside a plant to where they are most needed. For example, a plant will try to supply more nutrients to its younger leaves than to its older ones. When nutrients are mobile, symptoms of any deficiency become apparent first on the older leaves. However, not all nutrients are equally mobile. Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are mobile nutrients, while the others have varying degrees of mobility. When a less mobile nutrient is deficient, the younger leaves suffer because the nutrient does not move up to them but stays in the older leaves. This phenomenon is helpful in determining which nutrients a plant may be lacking.Many plants engage in symbiosis with microorganisms. Two important types of these relationship are with bacteria such as rhizobia, that carry out biological nitrogen fixation, in which atmospheric nitrogen (N2) is converted into ammonium (NH4); and with mycorrhizal fungi, which through their association with the plant roots help to create a larger effective root surface area. Both of these mutualistic relationships enhance nutrient uptake. Though nitrogen is plentiful in the Earth's atmosphere, relatively few plants harbor nitrogen fixing bacteria, so most plants rely on nitrogen compounds present in the soil to support their growth. These can be supplied by mineralization of soil organic matter or added plant residues, nitrogen fixing bacteria, animal waste, or through the application of fertilizers.Hydroponics, is a method for growing plants in a water-nutrient solution without the use of nutrient-rich soil. It allows researchers and home gardeners to grow their plants in a controlled environment. The most common solution, is the Hoagland solution, developed by D. R. Hoagland in 1933, the solution consists of all the essential nutrients in the correct proportions necessary for most plant growth. An aerator is used to prevent an anoxic event or hypoxia. Hypoxia can affect nutrient uptake of a plant because without oxygen present, respiration becomes inhibited within the root cells. The Nutrient film technique is a variation of hydroponic technique. The roots are not fully submerged, which allows for adequate aeration of the roots, while a ""film"" thin layer of nutrient rich water is pumped through the system to provide nutrients and water to the plant.