Plants
... Most students will list poppy seeds and caraway seeds. In addition, some “multi-grain” breads contain millet and flax seeds. In addition to corn, what are some other seeds that are eaten as “vegetables”? Peas and all types of beans, such as lima beans, black beans, kidney beans, and so on What are s ...
... Most students will list poppy seeds and caraway seeds. In addition, some “multi-grain” breads contain millet and flax seeds. In addition to corn, what are some other seeds that are eaten as “vegetables”? Peas and all types of beans, such as lima beans, black beans, kidney beans, and so on What are s ...
Basic Plant ID - Minnesota Board of Water and Soil Resources
... flowers, with each flower subtended by a scalelike ...
... flowers, with each flower subtended by a scalelike ...
Digestion and Nutrition
... 4.Vitamins: assist your body in changing food to energy. Vitamins are either water soluble (not stored in the body) or fat soluble (stored in fatty tissues). Some essential vitamins are A, C, D, B1, B2, E and K. *Q – Find a source for each vitamin, its function, and what happens if there is a defici ...
... 4.Vitamins: assist your body in changing food to energy. Vitamins are either water soluble (not stored in the body) or fat soluble (stored in fatty tissues). Some essential vitamins are A, C, D, B1, B2, E and K. *Q – Find a source for each vitamin, its function, and what happens if there is a defici ...
Mistflower and Mexican devil
... Why mistflower and Mexican devil are pest plants Mistflower and Mexican devil grow densely, overtopping groundcovers and preventing native plant species from regenerating. Both plants can invade a wide range of habitats and are especially happy in riparian areas where they compete with vulnerable na ...
... Why mistflower and Mexican devil are pest plants Mistflower and Mexican devil grow densely, overtopping groundcovers and preventing native plant species from regenerating. Both plants can invade a wide range of habitats and are especially happy in riparian areas where they compete with vulnerable na ...
Document
... Organ and tissue systems interact to carry out vital functions*ALL 3 are necessary for a plant to survive • Transport • Reproduction • Response ...
... Organ and tissue systems interact to carry out vital functions*ALL 3 are necessary for a plant to survive • Transport • Reproduction • Response ...
Plant Unit: part 2
... Vascular cambium produces vascular tissue and increases the thickness of stems over time. Pericycle enables roots to grow thicker and makes it possible for roots to branch Secondary growth is the increase in diameter Most herbaceous monocots don’t experience secondary growth while all woody plants d ...
... Vascular cambium produces vascular tissue and increases the thickness of stems over time. Pericycle enables roots to grow thicker and makes it possible for roots to branch Secondary growth is the increase in diameter Most herbaceous monocots don’t experience secondary growth while all woody plants d ...
Plant a Drought-Tolerant Garden
... foliage is topped with bright yellow flowers from April into May. Cut plants back by a third after flowering to keep them neat for the remainder of the season. Iberis, or candytuft, is another good choice for the front of the border. It features glossy green, evergreen foliage and cheery white flowe ...
... foliage is topped with bright yellow flowers from April into May. Cut plants back by a third after flowering to keep them neat for the remainder of the season. Iberis, or candytuft, is another good choice for the front of the border. It features glossy green, evergreen foliage and cheery white flowe ...
Course - Georgia FFA
... 1. Identify acids and bases using pH scale 2. Describe importance of soil pH on crops 3. Select compounds that will change soil pH 4. List pH best suited for certain crops ...
... 1. Identify acids and bases using pH scale 2. Describe importance of soil pH on crops 3. Select compounds that will change soil pH 4. List pH best suited for certain crops ...
food nutrients - Queensland Science Teachers
... Long-chain molecules made of amino acids Contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and usually sulphur and phosphorus Used to repair and build body tissues, but can be used as a last source of energy Digestive enzymes break down proteins into amino acids There are over 30 amino acids. Plants can ma ...
... Long-chain molecules made of amino acids Contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and usually sulphur and phosphorus Used to repair and build body tissues, but can be used as a last source of energy Digestive enzymes break down proteins into amino acids There are over 30 amino acids. Plants can ma ...
Click here to the file.
... effective. Burning removes above ground vegetation but does not kill the underground rhizomes, which will continue to sprout. In certain situations, tethered goats have been used to remove honeysuckle growth, but must be monitored to prevent their escape to the wild where they would become an added ...
... effective. Burning removes above ground vegetation but does not kill the underground rhizomes, which will continue to sprout. In certain situations, tethered goats have been used to remove honeysuckle growth, but must be monitored to prevent their escape to the wild where they would become an added ...
Plant Structures: Seeds - Colorado State University Extension
... dispersion. Adapting plants to a variety of hostile environments, nature programs a variety of germination blocks. The following are common types. Seed coat dormancy – When the seed coat is impermeable to water, and gases (oxygen). It requires action by weathering, microorganisms, passage through an ...
... dispersion. Adapting plants to a variety of hostile environments, nature programs a variety of germination blocks. The following are common types. Seed coat dormancy – When the seed coat is impermeable to water, and gases (oxygen). It requires action by weathering, microorganisms, passage through an ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 9. Agrobacterium mediated gene transfer is brought about by Ag plasmid. 10. Blue green algae is used as biofertilizer to fix atmospheric nitrogen. III. Complete the following:[5 x 1 = 5 Marks] 11. Sterilization is the process of ___________________. 12. Meristerm culture is advantageous because it p ...
... 9. Agrobacterium mediated gene transfer is brought about by Ag plasmid. 10. Blue green algae is used as biofertilizer to fix atmospheric nitrogen. III. Complete the following:[5 x 1 = 5 Marks] 11. Sterilization is the process of ___________________. 12. Meristerm culture is advantageous because it p ...
Greenhouse Tomato Growers` Glossary
... on the bottom or near the bottom of a tomato fruit; not from a disease; usually from lack of water or not enough calcium in the fruit. bullish: a plant with thick, leathery, dark-green leaves, little or no fruit, and very vegetative; may be caused by overfertilization with nitrogen or genetic off-ty ...
... on the bottom or near the bottom of a tomato fruit; not from a disease; usually from lack of water or not enough calcium in the fruit. bullish: a plant with thick, leathery, dark-green leaves, little or no fruit, and very vegetative; may be caused by overfertilization with nitrogen or genetic off-ty ...
Unit 12.1 web
... their own bodies. All of our minerals became part of the earth at its creation and enter our bodies only from the earth, directly through the plants we eat or indirectly from the animals that feed on plants. ...
... their own bodies. All of our minerals became part of the earth at its creation and enter our bodies only from the earth, directly through the plants we eat or indirectly from the animals that feed on plants. ...
Plant Adaptations - Science.kennesaw.edu
... dropping them as there is no way to get back any nutrients from them once they fall to the ground. To cut down on moisture loss, many epiphytes also have a specialized form of photosynthesis called C4 photosynthesis. All plants require carbon dioxide for photosynthesis. Most collect this during the ...
... dropping them as there is no way to get back any nutrients from them once they fall to the ground. To cut down on moisture loss, many epiphytes also have a specialized form of photosynthesis called C4 photosynthesis. All plants require carbon dioxide for photosynthesis. Most collect this during the ...
Propagating Plants Sexually
... What is the difference between stratification and scarification? Contrast viability and vigor. Describe how to indirectly seed a plant. What factors affect the direct seeding of a plant? ...
... What is the difference between stratification and scarification? Contrast viability and vigor. Describe how to indirectly seed a plant. What factors affect the direct seeding of a plant? ...
K,Mg,Ca,Na… 0,4%
... Passive (simple) diffusion Nutrients moving from a region of higher concentration to one of lower (influence of concentration gradient) – ions, glycerol, O2, CO2 – no energy consumption Osmosis Some solvent molecules and water move across membrane Isotonic – Hypotonic - Hypertonic Facilitated ...
... Passive (simple) diffusion Nutrients moving from a region of higher concentration to one of lower (influence of concentration gradient) – ions, glycerol, O2, CO2 – no energy consumption Osmosis Some solvent molecules and water move across membrane Isotonic – Hypotonic - Hypertonic Facilitated ...
American beautyberry - Okaloosa County Extension
... even as a specimen plant. But avoid using it where it will require regular shearing as the flowers and fruit are produced on new growth. Thinning out old or low growing branches is a better method of pruning this plant. American beautyberry may self seed but I have not seen this to be a bothersome p ...
... even as a specimen plant. But avoid using it where it will require regular shearing as the flowers and fruit are produced on new growth. Thinning out old or low growing branches is a better method of pruning this plant. American beautyberry may self seed but I have not seen this to be a bothersome p ...
Actinomycetes:
... was the result of this work. Streptomycin is still used, but in combination with other drugs, in the battle against ...
... was the result of this work. Streptomycin is still used, but in combination with other drugs, in the battle against ...
Golgi- Packages and transports proteins outside the cell
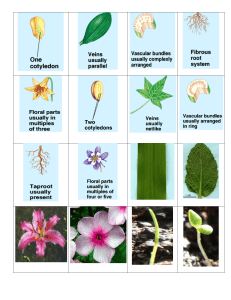
... The big difference that most people note about monocots and dicots is the formation of the plants’ veins on leaves. ...
... The big difference that most people note about monocots and dicots is the formation of the plants’ veins on leaves. ...
flowering plants - VCE
... Adapted to live in either partially or fully submerged in water. Thin cuticle Stomata mainly on upper surface particularly if water lilly… Large air spaces in spongy mesophyll allow storage of gases and make leaf lighter. ...
... Adapted to live in either partially or fully submerged in water. Thin cuticle Stomata mainly on upper surface particularly if water lilly… Large air spaces in spongy mesophyll allow storage of gases and make leaf lighter. ...
Photosynthesis - Jan. 28.
... plants – it takes 5 ATP to fix one molecule of CO2 in C4 but only 3 ATP in C3 • For all C3 plants photosynthesis is always accompanied by photorespiration which consumes and releases CO2 in the presence of light - it wastes carbon fixed by photosynthesis - up to 50% of carbon fixed in photosynthesis ...
... plants – it takes 5 ATP to fix one molecule of CO2 in C4 but only 3 ATP in C3 • For all C3 plants photosynthesis is always accompanied by photorespiration which consumes and releases CO2 in the presence of light - it wastes carbon fixed by photosynthesis - up to 50% of carbon fixed in photosynthesis ...
General Botany I - Conservatory of Flowers
... absorb light. For most plants, light is life. It is the essential kick start for photosynthesis, the fascinating internal process by which plants trap the energy of light to make their own food. So, to keep leaves dry and epiphytes off, many rainforest plants have smooth or waxy leaves. These slick ...
... absorb light. For most plants, light is life. It is the essential kick start for photosynthesis, the fascinating internal process by which plants trap the energy of light to make their own food. So, to keep leaves dry and epiphytes off, many rainforest plants have smooth or waxy leaves. These slick ...
Plant nutrition
.jpg?width=300)
Plant nutrition is the study of the chemical elements and compounds that are necessary for plant growth, and also of their external supply and internal metabolism. In 1972, E. Epstein defined two criteria for an element to be essential for plant growth: in its absence the plant is unable to complete a normal life cycle; or that the element is part of some essential plant constituent or metabolite.This is in accordance with Liebig's law of the minimum. There are 14 essential plant nutrients. Carbon and oxygen are absorbed from the air, while other nutrients including water are typically obtained from the soil (exceptions include some parasitic or carnivorous plants).Plants must obtain the following mineral nutrients from the growing media: the primary macronutrients: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K) the three secondary macronutrients: calcium (Ca), sulfur (S), magnesium (Mg) the micronutrients/trace minerals: boron (B), chlorine (Cl), manganese (Mn), iron (Fe), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), molybdenum (Mo), nickel (Ni)The macronutrients are consumed in larger quantities and are present in plant tissue in quantities from 0.2% to 4.0% (on a dry matter weight basis). Micro nutrients are present in plant tissue in quantities measured in parts per million, ranging from 5 to 200 ppm, or less than 0.02% dry weight.Most soil conditions across the world can provide plants with adequate nutrition and do not require fertilizer for a complete life cycle. However, humans can artificially modify soil through the addition of fertilizer to promote vigorous growth and increase yield. The plants are able to obtain their required nutrients from the fertilizer added to the soil. A colloidal carbonaceous residue, known as humus, can serve as a nutrient reservoir. Even with adequate water and sunshine, nutrient deficiency can limit growth.Nutrient uptake from the soil is achieved by cation exchange, where root hairs pump hydrogen ions (H+) into the soil through proton pumps. These hydrogen ions displace cations attached to negatively charged soil particles so that the cations are available for uptake by the root.Plant nutrition is a difficult subject to understand completely, partly because of the variation between different plants and even between different species or individuals of a given clone. An element present at a low level may cause deficiency symptoms, while the same element at a higher level may cause toxicity. Further, deficiency of one element may present as symptoms of toxicity from another element. An abundance of one nutrient may cause a deficiency of another nutrient. For example, lower availability of a given nutrient such as SO42− can affect the uptake of another nutrient, such as NO3−. As another example, K+ uptake can be influenced by the amount of NH4+ available.The root, especially the root hair, is the most essential organ for the uptake of nutrients. The structure and architecture of the root can alter the rate of nutrient uptake. Nutrient ions are transported to the center of the root, the stele in order for the nutrients to reach the conducting tissues, xylem and phloem. The Casparian strip, a cell wall outside the stele but within the root, prevents passive flow of water and nutrients, helping to regulate the uptake of nutrients and water. Xylem moves water and inorganic molecules within the plant and phloem accounts for organic molecule transportation. Water potential plays a key role in a plants nutrient uptake. If the water potential is more negative within the plant than the surrounding soils, the nutrients will move from the region of higher solute concentration—in the soil—to the area of lower solute concentration: in the plant.There are three fundamental ways plants uptake nutrients through the root: simple diffusion, occurs when a nonpolar molecule, such as O2, CO2, and NH3 follows a concentration gradient, moving passively through the cell lipid bilayer membrane without the use of transport proteins. facilitated diffusion, is the rapid movement of solutes or ions following a concentration gradient, facilitated by transport proteins. Active transport, is the uptake by cells of ions or molecules against a concentration gradient; this requires an energy source, usually ATP, to power molecular pumps that move the ions or molecules through the membrane. Nutrients are moved inside a plant to where they are most needed. For example, a plant will try to supply more nutrients to its younger leaves than to its older ones. When nutrients are mobile, symptoms of any deficiency become apparent first on the older leaves. However, not all nutrients are equally mobile. Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are mobile nutrients, while the others have varying degrees of mobility. When a less mobile nutrient is deficient, the younger leaves suffer because the nutrient does not move up to them but stays in the older leaves. This phenomenon is helpful in determining which nutrients a plant may be lacking.Many plants engage in symbiosis with microorganisms. Two important types of these relationship are with bacteria such as rhizobia, that carry out biological nitrogen fixation, in which atmospheric nitrogen (N2) is converted into ammonium (NH4); and with mycorrhizal fungi, which through their association with the plant roots help to create a larger effective root surface area. Both of these mutualistic relationships enhance nutrient uptake. Though nitrogen is plentiful in the Earth's atmosphere, relatively few plants harbor nitrogen fixing bacteria, so most plants rely on nitrogen compounds present in the soil to support their growth. These can be supplied by mineralization of soil organic matter or added plant residues, nitrogen fixing bacteria, animal waste, or through the application of fertilizers.Hydroponics, is a method for growing plants in a water-nutrient solution without the use of nutrient-rich soil. It allows researchers and home gardeners to grow their plants in a controlled environment. The most common solution, is the Hoagland solution, developed by D. R. Hoagland in 1933, the solution consists of all the essential nutrients in the correct proportions necessary for most plant growth. An aerator is used to prevent an anoxic event or hypoxia. Hypoxia can affect nutrient uptake of a plant because without oxygen present, respiration becomes inhibited within the root cells. The Nutrient film technique is a variation of hydroponic technique. The roots are not fully submerged, which allows for adequate aeration of the roots, while a ""film"" thin layer of nutrient rich water is pumped through the system to provide nutrients and water to the plant.