File
... By the end of the lesson you should be able to: • Compare and contrast bryophytes and pteridophytes • Describe the life cycle of a pteridophyte • Give some examples of pteridophytes ...
... By the end of the lesson you should be able to: • Compare and contrast bryophytes and pteridophytes • Describe the life cycle of a pteridophyte • Give some examples of pteridophytes ...
Lecture 38 - Amino Acid Metabolism 1
... Nitrogen fixation takes place in bacteria and is the primary process by which atmospheric N2 gas is converted to ammonia (NH4+) and nitrogen oxides (NO2- and NO3-) in the biosphere. Nitrogen assimilation incorporates this ammonia into amino acids, primarily glutamate and glutamine. 2. What are the n ...
... Nitrogen fixation takes place in bacteria and is the primary process by which atmospheric N2 gas is converted to ammonia (NH4+) and nitrogen oxides (NO2- and NO3-) in the biosphere. Nitrogen assimilation incorporates this ammonia into amino acids, primarily glutamate and glutamine. 2. What are the n ...
Protecting Your Waterfront â Part 2 of 2: Plants for the Waterfront
... clumping flowering perennials that will grow from one foot to five feet tall in the water. They are hefty plant with leaves in the shape of an arrowhead growing on sturdy stalks. The flowers are white with a yellow central disk that flowers all year long. It grows in up to six inches of water and in ...
... clumping flowering perennials that will grow from one foot to five feet tall in the water. They are hefty plant with leaves in the shape of an arrowhead growing on sturdy stalks. The flowers are white with a yellow central disk that flowers all year long. It grows in up to six inches of water and in ...
Lavender Star Flower Care Sheet
... chlorotic easily; it is a good idea to supplement with chelated iron once a year to avoid problems. Pruning / Training: The Starflower can be cut back heavily as desired. Prune after flowering to promote new flowers, can be wired successfully. Lavender Star Flower is a vigorous grower. Prune the tip ...
... chlorotic easily; it is a good idea to supplement with chelated iron once a year to avoid problems. Pruning / Training: The Starflower can be cut back heavily as desired. Prune after flowering to promote new flowers, can be wired successfully. Lavender Star Flower is a vigorous grower. Prune the tip ...
PDF
... recurving, and occasionally climbing. Published literature (2) suggests that spines are found on older growth, although they were also observed on specimens with young growth from MICH specimens; as axillary spines, they are branch replacements (L.S.S. pers. obs.). The 2-3cm long leaves are simple, ...
... recurving, and occasionally climbing. Published literature (2) suggests that spines are found on older growth, although they were also observed on specimens with young growth from MICH specimens; as axillary spines, they are branch replacements (L.S.S. pers. obs.). The 2-3cm long leaves are simple, ...
Indoor Botanical Garden of Art
... Review from last session by having students share samples of plants they found that were examples of terms discussed. Tell the group that their next task is to begin work on an indoor garden that will be built along a wall of your meeting site or hallway. It will be a combination of a botanical gard ...
... Review from last session by having students share samples of plants they found that were examples of terms discussed. Tell the group that their next task is to begin work on an indoor garden that will be built along a wall of your meeting site or hallway. It will be a combination of a botanical gard ...
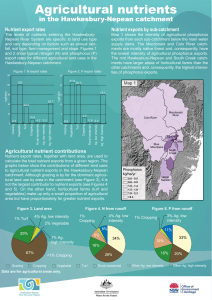
Agricultural nutrients in the Hawkesbury
... significantly reduced. Mechanical aeration can also increase delivery of water to the root zone improving the health of crops. Typically, by reducing runoff, aeration can reduce nutrient ...
... significantly reduced. Mechanical aeration can also increase delivery of water to the root zone improving the health of crops. Typically, by reducing runoff, aeration can reduce nutrient ...
Plants notes
... Plants use energy from sunlight to carry out photosynthesis. Photosynthetic organs such as leaves are broad and flat to maximize light absorption. Water and Minerals All cells require a constant supply of water. ...
... Plants use energy from sunlight to carry out photosynthesis. Photosynthetic organs such as leaves are broad and flat to maximize light absorption. Water and Minerals All cells require a constant supply of water. ...
Effects of Drought on Plant Growth
... Because of the potential seriousness of a drought whenever and wherever it occurs, landowners and managers need to be aware of the effects of drought on forage growth. Obviously, lack of soil moisture restricts plant growth, both in terms of the total quantity of tissue produced and the time that th ...
... Because of the potential seriousness of a drought whenever and wherever it occurs, landowners and managers need to be aware of the effects of drought on forage growth. Obviously, lack of soil moisture restricts plant growth, both in terms of the total quantity of tissue produced and the time that th ...
Insect pests of tomato
... • The green peach aphid has piercing sucking mouthparts, and feeds by inserting these mouthparts into plant tissue and sucking out the sap. • The aphids injures plants in three ways. • First, feeding interferes with proper nutrient transfer in the plant. • Second, the green peach aphid can transmit ...
... • The green peach aphid has piercing sucking mouthparts, and feeds by inserting these mouthparts into plant tissue and sucking out the sap. • The aphids injures plants in three ways. • First, feeding interferes with proper nutrient transfer in the plant. • Second, the green peach aphid can transmit ...
Hybrid hazelnuts: wildlife cover and feed
... cumulative of 70 plus years of research on hazelnut plants. During those research years we have noticed what tremendous wildlife plants hazelnuts are. Their catkins are often eaten by animals in the winter for a food source, they provide tremendous cover, and the nuts are extremely high in protein a ...
... cumulative of 70 plus years of research on hazelnut plants. During those research years we have noticed what tremendous wildlife plants hazelnuts are. Their catkins are often eaten by animals in the winter for a food source, they provide tremendous cover, and the nuts are extremely high in protein a ...
In The Name Of God**
... *This plant is adored by slugs and is therefore very difficult to grow in the open garden where slugs are common[187]. Phillips. R. & Rix. M *A very ornamental plant [1], F. Chittendon ...
... *This plant is adored by slugs and is therefore very difficult to grow in the open garden where slugs are common[187]. Phillips. R. & Rix. M *A very ornamental plant [1], F. Chittendon ...
Bedding Plant Production
... When Transplanting • Plants are fragile so be very careful. • Transplants should be watered in immediately after being placed in the plug tray. • As a general rule, while growing, plants should be watered with 100ppm Nitrogen and Phosphorous once per week. ...
... When Transplanting • Plants are fragile so be very careful. • Transplants should be watered in immediately after being placed in the plug tray. • As a general rule, while growing, plants should be watered with 100ppm Nitrogen and Phosphorous once per week. ...
Horse netttle Solanum carolinense
... its 5 stamens have bright yellow elongated anthers that unite at the tip to form a central cone, and it has 1 pistil. All parts are attached to the base of the ovary. These flowers are unscented and are pollinated by Bumblebees (Genus Bombus). Flowering season is April to October. Fruit: Its fruit i ...
... its 5 stamens have bright yellow elongated anthers that unite at the tip to form a central cone, and it has 1 pistil. All parts are attached to the base of the ovary. These flowers are unscented and are pollinated by Bumblebees (Genus Bombus). Flowering season is April to October. Fruit: Its fruit i ...
cbse class – x science solutions
... The small intestine produces intestinal juice from the glands present in its wall, which helps in further digestion of food. Small intestine also obtains digestive juices from liver and pancreas that helps in mixing of food and complete digestion of food. The liver produces bile juice which causes e ...
... The small intestine produces intestinal juice from the glands present in its wall, which helps in further digestion of food. Small intestine also obtains digestive juices from liver and pancreas that helps in mixing of food and complete digestion of food. The liver produces bile juice which causes e ...
Chapter 1 - Charleville Gardens
... Living organisms including: plants and plant roots bacteria & fungi worms, insects, etc. dead/decomposing organisms ...
... Living organisms including: plants and plant roots bacteria & fungi worms, insects, etc. dead/decomposing organisms ...
1-2
... It is essential for students to know that plants require air, water, nutrients, space, and light. A distinct environment is a special surrounding that supports the life of different plants. Plants can survive only in environments in which their needs can be met. The world has many different distinct ...
... It is essential for students to know that plants require air, water, nutrients, space, and light. A distinct environment is a special surrounding that supports the life of different plants. Plants can survive only in environments in which their needs can be met. The world has many different distinct ...
Soil Nutrients and Fertilizers
... have a large budget for this. Should she use an organic or inorganic fertilizer? – Case Study 2: In order for the horticulture department to have its vegetable garden it needs to increase its field’s phosphorus levels. Although the nitrogen level does not need to change. We will buy a bag of N-P-K f ...
... have a large budget for this. Should she use an organic or inorganic fertilizer? – Case Study 2: In order for the horticulture department to have its vegetable garden it needs to increase its field’s phosphorus levels. Although the nitrogen level does not need to change. We will buy a bag of N-P-K f ...
NPH_3820_sm_FigS1-S7-TableS1
... PstDC3000 in wild-type and two additional rADS1 lines at 0 (hatched bar), 3 (white bar) and 5 (black bar) dpi. Data points are the average of three technical replicates (±SD). Student’s t test confirmed significant differences at p = 0.05 between bacterial growth in the rADS1 lines relative to WT pl ...
... PstDC3000 in wild-type and two additional rADS1 lines at 0 (hatched bar), 3 (white bar) and 5 (black bar) dpi. Data points are the average of three technical replicates (±SD). Student’s t test confirmed significant differences at p = 0.05 between bacterial growth in the rADS1 lines relative to WT pl ...
B3 lesson 5 Transport in Plants B3.2.3 Transport systems in plants
... B3.2.3 Transport systems in plants Flowering plants have separate transport systems: xylem transports water and mineral ions from roots to stem and leaves movement of water from roots to leaves is the transpiration stream phloem carries dissolved sugars from leaves to the rest of the plant. ...
... B3.2.3 Transport systems in plants Flowering plants have separate transport systems: xylem transports water and mineral ions from roots to stem and leaves movement of water from roots to leaves is the transpiration stream phloem carries dissolved sugars from leaves to the rest of the plant. ...
UMAXX® StAbilized NitrogeN
... can significantly impact the efficiency of nitrogen fertilizer and ultimately compromise performance. UMAXX® stabilized nitrogen helps make the most of the nitrogen investment by controlling these types of losses. The product is formulated with a urease inhibitor that helps minimize nitrogen loss in ...
... can significantly impact the efficiency of nitrogen fertilizer and ultimately compromise performance. UMAXX® stabilized nitrogen helps make the most of the nitrogen investment by controlling these types of losses. The product is formulated with a urease inhibitor that helps minimize nitrogen loss in ...
Culture of Dendrobium kingianum
... Dendrobium kingianum grows normally down to 35F (will tolerate temps down to 29F), so I put mine outside in April (Boston area), in full east sun; and it comes back inside in Nov. After blooming, all keikis are removed, as well as old flower spikes, and the new developing keikis are left on as they ...
... Dendrobium kingianum grows normally down to 35F (will tolerate temps down to 29F), so I put mine outside in April (Boston area), in full east sun; and it comes back inside in Nov. After blooming, all keikis are removed, as well as old flower spikes, and the new developing keikis are left on as they ...
Plant Hormones - U of L Class Index
... •Ethylene causes chlorophyll to break down and other pigments to form (e.g., the change in apple skin color with ripening). •It also causes fruit softening by causing the production of the enzymes cellulase and pectinase, which break down cellulose and pectin, structural components of the cell wall. ...
... •Ethylene causes chlorophyll to break down and other pigments to form (e.g., the change in apple skin color with ripening). •It also causes fruit softening by causing the production of the enzymes cellulase and pectinase, which break down cellulose and pectin, structural components of the cell wall. ...
08. mechanism of uptake - physiological role of nutrients
... membrane. Similarly anion may be exchanged with OH ions. There are two theories regarding the mechanism of ion exchange. ...
... membrane. Similarly anion may be exchanged with OH ions. There are two theories regarding the mechanism of ion exchange. ...
Plant nutrition
.jpg?width=300)
Plant nutrition is the study of the chemical elements and compounds that are necessary for plant growth, and also of their external supply and internal metabolism. In 1972, E. Epstein defined two criteria for an element to be essential for plant growth: in its absence the plant is unable to complete a normal life cycle; or that the element is part of some essential plant constituent or metabolite.This is in accordance with Liebig's law of the minimum. There are 14 essential plant nutrients. Carbon and oxygen are absorbed from the air, while other nutrients including water are typically obtained from the soil (exceptions include some parasitic or carnivorous plants).Plants must obtain the following mineral nutrients from the growing media: the primary macronutrients: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K) the three secondary macronutrients: calcium (Ca), sulfur (S), magnesium (Mg) the micronutrients/trace minerals: boron (B), chlorine (Cl), manganese (Mn), iron (Fe), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), molybdenum (Mo), nickel (Ni)The macronutrients are consumed in larger quantities and are present in plant tissue in quantities from 0.2% to 4.0% (on a dry matter weight basis). Micro nutrients are present in plant tissue in quantities measured in parts per million, ranging from 5 to 200 ppm, or less than 0.02% dry weight.Most soil conditions across the world can provide plants with adequate nutrition and do not require fertilizer for a complete life cycle. However, humans can artificially modify soil through the addition of fertilizer to promote vigorous growth and increase yield. The plants are able to obtain their required nutrients from the fertilizer added to the soil. A colloidal carbonaceous residue, known as humus, can serve as a nutrient reservoir. Even with adequate water and sunshine, nutrient deficiency can limit growth.Nutrient uptake from the soil is achieved by cation exchange, where root hairs pump hydrogen ions (H+) into the soil through proton pumps. These hydrogen ions displace cations attached to negatively charged soil particles so that the cations are available for uptake by the root.Plant nutrition is a difficult subject to understand completely, partly because of the variation between different plants and even between different species or individuals of a given clone. An element present at a low level may cause deficiency symptoms, while the same element at a higher level may cause toxicity. Further, deficiency of one element may present as symptoms of toxicity from another element. An abundance of one nutrient may cause a deficiency of another nutrient. For example, lower availability of a given nutrient such as SO42− can affect the uptake of another nutrient, such as NO3−. As another example, K+ uptake can be influenced by the amount of NH4+ available.The root, especially the root hair, is the most essential organ for the uptake of nutrients. The structure and architecture of the root can alter the rate of nutrient uptake. Nutrient ions are transported to the center of the root, the stele in order for the nutrients to reach the conducting tissues, xylem and phloem. The Casparian strip, a cell wall outside the stele but within the root, prevents passive flow of water and nutrients, helping to regulate the uptake of nutrients and water. Xylem moves water and inorganic molecules within the plant and phloem accounts for organic molecule transportation. Water potential plays a key role in a plants nutrient uptake. If the water potential is more negative within the plant than the surrounding soils, the nutrients will move from the region of higher solute concentration—in the soil—to the area of lower solute concentration: in the plant.There are three fundamental ways plants uptake nutrients through the root: simple diffusion, occurs when a nonpolar molecule, such as O2, CO2, and NH3 follows a concentration gradient, moving passively through the cell lipid bilayer membrane without the use of transport proteins. facilitated diffusion, is the rapid movement of solutes or ions following a concentration gradient, facilitated by transport proteins. Active transport, is the uptake by cells of ions or molecules against a concentration gradient; this requires an energy source, usually ATP, to power molecular pumps that move the ions or molecules through the membrane. Nutrients are moved inside a plant to where they are most needed. For example, a plant will try to supply more nutrients to its younger leaves than to its older ones. When nutrients are mobile, symptoms of any deficiency become apparent first on the older leaves. However, not all nutrients are equally mobile. Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are mobile nutrients, while the others have varying degrees of mobility. When a less mobile nutrient is deficient, the younger leaves suffer because the nutrient does not move up to them but stays in the older leaves. This phenomenon is helpful in determining which nutrients a plant may be lacking.Many plants engage in symbiosis with microorganisms. Two important types of these relationship are with bacteria such as rhizobia, that carry out biological nitrogen fixation, in which atmospheric nitrogen (N2) is converted into ammonium (NH4); and with mycorrhizal fungi, which through their association with the plant roots help to create a larger effective root surface area. Both of these mutualistic relationships enhance nutrient uptake. Though nitrogen is plentiful in the Earth's atmosphere, relatively few plants harbor nitrogen fixing bacteria, so most plants rely on nitrogen compounds present in the soil to support their growth. These can be supplied by mineralization of soil organic matter or added plant residues, nitrogen fixing bacteria, animal waste, or through the application of fertilizers.Hydroponics, is a method for growing plants in a water-nutrient solution without the use of nutrient-rich soil. It allows researchers and home gardeners to grow their plants in a controlled environment. The most common solution, is the Hoagland solution, developed by D. R. Hoagland in 1933, the solution consists of all the essential nutrients in the correct proportions necessary for most plant growth. An aerator is used to prevent an anoxic event or hypoxia. Hypoxia can affect nutrient uptake of a plant because without oxygen present, respiration becomes inhibited within the root cells. The Nutrient film technique is a variation of hydroponic technique. The roots are not fully submerged, which allows for adequate aeration of the roots, while a ""film"" thin layer of nutrient rich water is pumped through the system to provide nutrients and water to the plant.