Chrysanthemums - Culture Description
... PREFACE: Chrysanthemums are herbaceous perennial plants and consist of about 30 species that are found in nature. The flowers come in various forms, and can be daisy-like, decorative, pompon or anemone. The chrysanthemum industry is enormous and is found among the 10 biggest crops commercially used ...
... PREFACE: Chrysanthemums are herbaceous perennial plants and consist of about 30 species that are found in nature. The flowers come in various forms, and can be daisy-like, decorative, pompon or anemone. The chrysanthemum industry is enormous and is found among the 10 biggest crops commercially used ...
Japanese Stewartia
... This tree performs well in both full sun and full shade. It requires an evenly moist well-drained soil for optimal growth, but will die in standing water. It is very fussy about its soil conditions and must have rich, acidic soils to ensure success, and is subject to chlorosis (yellowing) of the le ...
... This tree performs well in both full sun and full shade. It requires an evenly moist well-drained soil for optimal growth, but will die in standing water. It is very fussy about its soil conditions and must have rich, acidic soils to ensure success, and is subject to chlorosis (yellowing) of the le ...
Stained Glass Hosta - Holcomb Garden Center
... should be spaced approximately 30 inches apart. Its foliage tends to remain low and dense right to the ground. It grows at a slow rate, and under ideal conditions can be expected to live for approximately 10 years. This plant does best in partial shade to shade. It prefers to grow in average to mois ...
... should be spaced approximately 30 inches apart. Its foliage tends to remain low and dense right to the ground. It grows at a slow rate, and under ideal conditions can be expected to live for approximately 10 years. This plant does best in partial shade to shade. It prefers to grow in average to mois ...
Print a copy of this guide - USA National Phenology Network
... and dogwood plants for observation. Cloned plants are genetically identical, grown from the same “mother plant.” The value of observations of cloned plants is that differences in individual plants’ phenology can be attributed to differences in local environmental conditions, rather than to differenc ...
... and dogwood plants for observation. Cloned plants are genetically identical, grown from the same “mother plant.” The value of observations of cloned plants is that differences in individual plants’ phenology can be attributed to differences in local environmental conditions, rather than to differenc ...
Plants notes - WordPress.com
... • Leaves evolved because plants that had broad, flat, surfaces were able to ‘capture’ more solar energy than plants that did not have these surfaces. • These leaves have a waxy coating, called a cuticle, to prevent water loss to dry air. ...
... • Leaves evolved because plants that had broad, flat, surfaces were able to ‘capture’ more solar energy than plants that did not have these surfaces. • These leaves have a waxy coating, called a cuticle, to prevent water loss to dry air. ...
Privet (Ligustrum spp.) - University of Tennessee Extension
... Dense privet hedges prevent the growth of native species and can create a monoculture over time. Many bird and animal species feed on privet fruit and will spread the seed through their feces. All species of Ligustrum produce fruit toxic to humans that can cause symptoms including headache, nausea, ...
... Dense privet hedges prevent the growth of native species and can create a monoculture over time. Many bird and animal species feed on privet fruit and will spread the seed through their feces. All species of Ligustrum produce fruit toxic to humans that can cause symptoms including headache, nausea, ...
UNIT 4: PLANTAE: Chapters 9, 10, 11
... sugar cane the stalk of the plant is used. We eat the roots of carrots, leaves of lettuce, and stalk and flowers of broccoli. However, one group of fruits has an extremely large effect on world nutrition. These are the grains. Wheat, corn and rice are consumed worldwide as a base of consumption, pro ...
... sugar cane the stalk of the plant is used. We eat the roots of carrots, leaves of lettuce, and stalk and flowers of broccoli. However, one group of fruits has an extremely large effect on world nutrition. These are the grains. Wheat, corn and rice are consumed worldwide as a base of consumption, pro ...
Scentless Chamomile
... It can also be confused with stinking mayweed or pineapple weed, but the foliage of these two plants has an odour. ...
... It can also be confused with stinking mayweed or pineapple weed, but the foliage of these two plants has an odour. ...
A2 Module 2814: Chains, Rings and Spectroscopy
... polypeptide, this is an example of condensation polymerisation. If more than about forty amino acid units are involved, the polymer is classed as a protein. Natural peptides and proteins can use any of the twenty natural amino acids, combined together in a very specific order. This produces a vast r ...
... polypeptide, this is an example of condensation polymerisation. If more than about forty amino acid units are involved, the polymer is classed as a protein. Natural peptides and proteins can use any of the twenty natural amino acids, combined together in a very specific order. This produces a vast r ...
Plant WebQuest - Balfour Collegiate
... Different types of plants have different characteristics. In this activity, you will find out just how different they are by gathering information on plant diversity. ...
... Different types of plants have different characteristics. In this activity, you will find out just how different they are by gathering information on plant diversity. ...
HiQ® pharma specialty gas concept. TRACE Pharma Nitrogen
... With HiQ® specialty gases from Linde Gas, the producing pharmaceutical industry is able to obtain gases that conform to agreed and internationally harmonized specifications from an approved supplier. Such pharmaceutical grade products are delivered in accordance with applicable pharmacopoeia monogra ...
... With HiQ® specialty gases from Linde Gas, the producing pharmaceutical industry is able to obtain gases that conform to agreed and internationally harmonized specifications from an approved supplier. Such pharmaceutical grade products are delivered in accordance with applicable pharmacopoeia monogra ...
Sample Question Paper Class XII Agriculture (Theory) Time : 3 hours
... Examples: Raat ki Rani, Roses, Bougainvillea etc. (iii) Cutting and layering methods of propagation a) The cuttings are first detached from the scion plant and then rooted while in layering, the branch is first rooted on the scion plant and then detached. b) The percentage of success is more in laye ...
... Examples: Raat ki Rani, Roses, Bougainvillea etc. (iii) Cutting and layering methods of propagation a) The cuttings are first detached from the scion plant and then rooted while in layering, the branch is first rooted on the scion plant and then detached. b) The percentage of success is more in laye ...
March - Barrie`s Garden Club
... mix as it is lighter & formulated specifically to ensure a good start for the seedlings. Avoid planting a seed deeper than it is wide. A seed planted too deep will use up its stored energy before it reaches the surface. Read the seed package directions as some seeds require light to germinate & are ...
... mix as it is lighter & formulated specifically to ensure a good start for the seedlings. Avoid planting a seed deeper than it is wide. A seed planted too deep will use up its stored energy before it reaches the surface. Read the seed package directions as some seeds require light to germinate & are ...
39E-PlantDefense
... • Even if a plant is infected by a virulent strain of a pathogen - one for which that particular plant has no genetic resistance - the plant is able to mount a localized chemical attack in response to molecular signals released from cells damaged by infection. ...
... • Even if a plant is infected by a virulent strain of a pathogen - one for which that particular plant has no genetic resistance - the plant is able to mount a localized chemical attack in response to molecular signals released from cells damaged by infection. ...
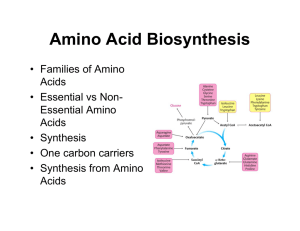
Amino Acid Biosynthesis
... Prokaryotic cells Nitrogenase reaction: N2 + 8 H+ + 8 e- + 16 ATP Æ 2 NH3 + H2 + 16 ATP + 16 Pi Ammonia assimilated in amino acids ...
... Prokaryotic cells Nitrogenase reaction: N2 + 8 H+ + 8 e- + 16 ATP Æ 2 NH3 + H2 + 16 ATP + 16 Pi Ammonia assimilated in amino acids ...
Cert Bio II - Asexual reproduction Answer
... 44. Which of the following provides the major source of food for the development of the daughter plant from structure A? A. P B. Q C. R D. S ...
... 44. Which of the following provides the major source of food for the development of the daughter plant from structure A? A. P B. Q C. R D. S ...
Programme for HELCOM Workshop on nutrient recycling in the
... Eutrophication, caused by nutrient leaching, is one of the major threats to the Baltic. The valuable resources, phosphorus and nitrogen, have turned into a serious problem when in the wrong place. There is a need to start recycling nutrients to reduce the impact on watercourses and the climate as we ...
... Eutrophication, caused by nutrient leaching, is one of the major threats to the Baltic. The valuable resources, phosphorus and nitrogen, have turned into a serious problem when in the wrong place. There is a need to start recycling nutrients to reduce the impact on watercourses and the climate as we ...
Plant Hormones
... in seed germination – gibberellins will induce genes to make enzymes that break down starch ...
... in seed germination – gibberellins will induce genes to make enzymes that break down starch ...
Tagasaste - Boom Lusern
... Established tagasaste (i.e. >three years old) does not respond to potash fertiliser even on highly leached sands. Tagasaste typically delivers low soil test results for potassium (K), because the shrub’s extensive root system can recycle K from depth. Phosphorus and trace elements are far less mobil ...
... Established tagasaste (i.e. >three years old) does not respond to potash fertiliser even on highly leached sands. Tagasaste typically delivers low soil test results for potassium (K), because the shrub’s extensive root system can recycle K from depth. Phosphorus and trace elements are far less mobil ...
The major terrestrial or land-based ecosystems can be divided into
... Freshwater Ecosystems: Rivers As streams flow and are joined by other streams, they collect more water and become larger bodies of moving water called rivers. Rivers can be wide and slow moving or narrow and rapid. Like streams, a river is affected by the ...
... Freshwater Ecosystems: Rivers As streams flow and are joined by other streams, they collect more water and become larger bodies of moving water called rivers. Rivers can be wide and slow moving or narrow and rapid. Like streams, a river is affected by the ...
What is a Diet
... •In US, a primary deficiency of just one nutrient is rare •Possible exception: iron Secondary Nutrient Deficiency is Due to Other Factors ...
... •In US, a primary deficiency of just one nutrient is rare •Possible exception: iron Secondary Nutrient Deficiency is Due to Other Factors ...
Nutrient PPT
... the body does not function properly. Energy can be released when the body has the correct amount of nutrients. ...
... the body does not function properly. Energy can be released when the body has the correct amount of nutrients. ...
Holiday Flowering Plants
... appear. When there are no leaves left stop watering and let the tuber rest for at least 4-6 weeks in dry soil stored in a cool (50°) room. ...
... appear. When there are no leaves left stop watering and let the tuber rest for at least 4-6 weeks in dry soil stored in a cool (50°) room. ...
Plant nutrition
.jpg?width=300)
Plant nutrition is the study of the chemical elements and compounds that are necessary for plant growth, and also of their external supply and internal metabolism. In 1972, E. Epstein defined two criteria for an element to be essential for plant growth: in its absence the plant is unable to complete a normal life cycle; or that the element is part of some essential plant constituent or metabolite.This is in accordance with Liebig's law of the minimum. There are 14 essential plant nutrients. Carbon and oxygen are absorbed from the air, while other nutrients including water are typically obtained from the soil (exceptions include some parasitic or carnivorous plants).Plants must obtain the following mineral nutrients from the growing media: the primary macronutrients: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K) the three secondary macronutrients: calcium (Ca), sulfur (S), magnesium (Mg) the micronutrients/trace minerals: boron (B), chlorine (Cl), manganese (Mn), iron (Fe), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), molybdenum (Mo), nickel (Ni)The macronutrients are consumed in larger quantities and are present in plant tissue in quantities from 0.2% to 4.0% (on a dry matter weight basis). Micro nutrients are present in plant tissue in quantities measured in parts per million, ranging from 5 to 200 ppm, or less than 0.02% dry weight.Most soil conditions across the world can provide plants with adequate nutrition and do not require fertilizer for a complete life cycle. However, humans can artificially modify soil through the addition of fertilizer to promote vigorous growth and increase yield. The plants are able to obtain their required nutrients from the fertilizer added to the soil. A colloidal carbonaceous residue, known as humus, can serve as a nutrient reservoir. Even with adequate water and sunshine, nutrient deficiency can limit growth.Nutrient uptake from the soil is achieved by cation exchange, where root hairs pump hydrogen ions (H+) into the soil through proton pumps. These hydrogen ions displace cations attached to negatively charged soil particles so that the cations are available for uptake by the root.Plant nutrition is a difficult subject to understand completely, partly because of the variation between different plants and even between different species or individuals of a given clone. An element present at a low level may cause deficiency symptoms, while the same element at a higher level may cause toxicity. Further, deficiency of one element may present as symptoms of toxicity from another element. An abundance of one nutrient may cause a deficiency of another nutrient. For example, lower availability of a given nutrient such as SO42− can affect the uptake of another nutrient, such as NO3−. As another example, K+ uptake can be influenced by the amount of NH4+ available.The root, especially the root hair, is the most essential organ for the uptake of nutrients. The structure and architecture of the root can alter the rate of nutrient uptake. Nutrient ions are transported to the center of the root, the stele in order for the nutrients to reach the conducting tissues, xylem and phloem. The Casparian strip, a cell wall outside the stele but within the root, prevents passive flow of water and nutrients, helping to regulate the uptake of nutrients and water. Xylem moves water and inorganic molecules within the plant and phloem accounts for organic molecule transportation. Water potential plays a key role in a plants nutrient uptake. If the water potential is more negative within the plant than the surrounding soils, the nutrients will move from the region of higher solute concentration—in the soil—to the area of lower solute concentration: in the plant.There are three fundamental ways plants uptake nutrients through the root: simple diffusion, occurs when a nonpolar molecule, such as O2, CO2, and NH3 follows a concentration gradient, moving passively through the cell lipid bilayer membrane without the use of transport proteins. facilitated diffusion, is the rapid movement of solutes or ions following a concentration gradient, facilitated by transport proteins. Active transport, is the uptake by cells of ions or molecules against a concentration gradient; this requires an energy source, usually ATP, to power molecular pumps that move the ions or molecules through the membrane. Nutrients are moved inside a plant to where they are most needed. For example, a plant will try to supply more nutrients to its younger leaves than to its older ones. When nutrients are mobile, symptoms of any deficiency become apparent first on the older leaves. However, not all nutrients are equally mobile. Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are mobile nutrients, while the others have varying degrees of mobility. When a less mobile nutrient is deficient, the younger leaves suffer because the nutrient does not move up to them but stays in the older leaves. This phenomenon is helpful in determining which nutrients a plant may be lacking.Many plants engage in symbiosis with microorganisms. Two important types of these relationship are with bacteria such as rhizobia, that carry out biological nitrogen fixation, in which atmospheric nitrogen (N2) is converted into ammonium (NH4); and with mycorrhizal fungi, which through their association with the plant roots help to create a larger effective root surface area. Both of these mutualistic relationships enhance nutrient uptake. Though nitrogen is plentiful in the Earth's atmosphere, relatively few plants harbor nitrogen fixing bacteria, so most plants rely on nitrogen compounds present in the soil to support their growth. These can be supplied by mineralization of soil organic matter or added plant residues, nitrogen fixing bacteria, animal waste, or through the application of fertilizers.Hydroponics, is a method for growing plants in a water-nutrient solution without the use of nutrient-rich soil. It allows researchers and home gardeners to grow their plants in a controlled environment. The most common solution, is the Hoagland solution, developed by D. R. Hoagland in 1933, the solution consists of all the essential nutrients in the correct proportions necessary for most plant growth. An aerator is used to prevent an anoxic event or hypoxia. Hypoxia can affect nutrient uptake of a plant because without oxygen present, respiration becomes inhibited within the root cells. The Nutrient film technique is a variation of hydroponic technique. The roots are not fully submerged, which allows for adequate aeration of the roots, while a ""film"" thin layer of nutrient rich water is pumped through the system to provide nutrients and water to the plant.