November 2014 (v2) QP - Paper 1 CIE Biology IGCSE
... Which process produces carbon dioxide from substances made by photosynthesis millions of ...
... Which process produces carbon dioxide from substances made by photosynthesis millions of ...
Bonfire Cushion Spurge
... chartreuse bracts at the ends of the stems from mid to late spring, which are most effective when planted in groupings. It's attractive narrow leaves emerge green in spring, turning burgundy in color. As an added bonus, the foliage turns a gorgeous red in the fall. The fruit is not ornamentally sign ...
... chartreuse bracts at the ends of the stems from mid to late spring, which are most effective when planted in groupings. It's attractive narrow leaves emerge green in spring, turning burgundy in color. As an added bonus, the foliage turns a gorgeous red in the fall. The fruit is not ornamentally sign ...
UAA Natural Heritage Program, Weed Ranking Project (PDF)
... by wind because of their light weight and small wings (Gubanov et al. 2004). Potential to be spread by human activity: Creeping bellflower was introduced to North America as an ornamental plant (Royer and Dickinson 1999). It frequently escapes from gardens (Whitson et al. 2000). This plant also disp ...
... by wind because of their light weight and small wings (Gubanov et al. 2004). Potential to be spread by human activity: Creeping bellflower was introduced to North America as an ornamental plant (Royer and Dickinson 1999). It frequently escapes from gardens (Whitson et al. 2000). This plant also disp ...
Excavations (Part 1)
... A designated competent person who has training in soil analysis, protective systems, and federal or state regulatory requirements for excavations must be on site to classify the soil, select a protective system, oversee installation, and inspect the system after installation. If there are no existin ...
... A designated competent person who has training in soil analysis, protective systems, and federal or state regulatory requirements for excavations must be on site to classify the soil, select a protective system, oversee installation, and inspect the system after installation. If there are no existin ...
We would like to thank the Commission for the opportunity given to
... nutrient to a supplement at a level at which a claim can be made may generate a risk of over-exposure. It should be allowed that nutrients with very small therapeutic windows can be added to supplements at an amount smaller than needed for a certain health-claim. Should different minimum amounts be ...
... nutrient to a supplement at a level at which a claim can be made may generate a risk of over-exposure. It should be allowed that nutrients with very small therapeutic windows can be added to supplements at an amount smaller than needed for a certain health-claim. Should different minimum amounts be ...
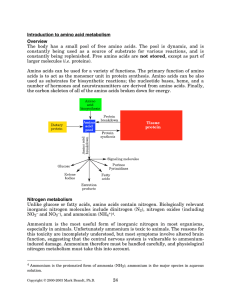
Introduction to amino acid metabolism Overview - Rose
... Ammonium can come from several sources depending on the organism: 1) organic nitrogen: nitrogen attached to organic molecules that can be metabolized; 2) free ammonium; 3) nitrogen oxides (especially nitrate); and 4) dinitrogen. Nitrogen fixation N2 is inaccessible to most organisms, because of the ...
... Ammonium can come from several sources depending on the organism: 1) organic nitrogen: nitrogen attached to organic molecules that can be metabolized; 2) free ammonium; 3) nitrogen oxides (especially nitrate); and 4) dinitrogen. Nitrogen fixation N2 is inaccessible to most organisms, because of the ...
Minerals - WordPress.com
... Found in plants and animals. Content in plant foods depends on soil content (where plant was grown). They are difficult to quantify biochemically. Bioavailability often influenced by other dietary factors (especially other minerals) ...
... Found in plants and animals. Content in plant foods depends on soil content (where plant was grown). They are difficult to quantify biochemically. Bioavailability often influenced by other dietary factors (especially other minerals) ...
17. Plants and fungi - umdberg / BERG FrontPage
... • Cell walls made of chitin - an amino-sugar polymer ...
... • Cell walls made of chitin - an amino-sugar polymer ...
How to Read a Seed Packet
... • A seed contains the beginnings of a new plant. In simple terms, seeds contain three main parts – the outer seed coat, an embryo (or immature plant) and a large food store. • Seeds remain in a stage of dormancy until presented with the proper conditions for germination. In order for seeds to succes ...
... • A seed contains the beginnings of a new plant. In simple terms, seeds contain three main parts – the outer seed coat, an embryo (or immature plant) and a large food store. • Seeds remain in a stage of dormancy until presented with the proper conditions for germination. In order for seeds to succes ...
Lesson 1
... water retention and air circulation structures while increasing microbial activity and the availability of nutrients. Because the most fertile soil is alive with organisms that work in tandem with plants, soil structure and microbial balance is continually adapting to environmental conditions and nu ...
... water retention and air circulation structures while increasing microbial activity and the availability of nutrients. Because the most fertile soil is alive with organisms that work in tandem with plants, soil structure and microbial balance is continually adapting to environmental conditions and nu ...
Yeast Nutrition - Pennsylvania Winery Association
... Nutriferm Arom Plus contains a high content of moderately-absorbed amino acids (absorbed at end of growth phase), selected for their aromatic precursors potential, vitamins and mineral salts. It stimulates yeast multiplication, enhances fermentation aromas production and increases aromatic intensit ...
... Nutriferm Arom Plus contains a high content of moderately-absorbed amino acids (absorbed at end of growth phase), selected for their aromatic precursors potential, vitamins and mineral salts. It stimulates yeast multiplication, enhances fermentation aromas production and increases aromatic intensit ...
6-2 Plants
... How they reproduce (e.g., by spores or different kinds of seeds); and Their size or stature To describe all plant species, the following divisions (or phyla) are most commonly used to sort them. Nonvascular and Vascular Nonvascular Plants Plants that cannot circulate rainwater through their stem ...
... How they reproduce (e.g., by spores or different kinds of seeds); and Their size or stature To describe all plant species, the following divisions (or phyla) are most commonly used to sort them. Nonvascular and Vascular Nonvascular Plants Plants that cannot circulate rainwater through their stem ...
Recipes for Flowers - LED Industrial Group
... is the cheapest source available, but for horticulture it is not always attainable in sufficient quantities. Therefore, the use of artificial light has become very common in order to increase production and quality. Plants have a completely different sensitivity to light colors than humans. With reg ...
... is the cheapest source available, but for horticulture it is not always attainable in sufficient quantities. Therefore, the use of artificial light has become very common in order to increase production and quality. Plants have a completely different sensitivity to light colors than humans. With reg ...
Shorter Days - Marion County, FL
... by Pat Greenfield, Master Gardener It’s that time of year when the temperatures have cooled and gardening is at a minimum. Our attention turns to the coming holidays, and we are filled with memories of the aromas of savory meats and veggie casseroles cooking and the smell of spicy goodies baking. Th ...
... by Pat Greenfield, Master Gardener It’s that time of year when the temperatures have cooled and gardening is at a minimum. Our attention turns to the coming holidays, and we are filled with memories of the aromas of savory meats and veggie casseroles cooking and the smell of spicy goodies baking. Th ...
Plant Guide COMMON
... birds and animals and by overflow water in bottomlands. Persimmon is slow growing and usually does not make a large tree, although it may reach 21-24 meters tall on optimal sites. Trees have been reported to reach 150 years of age. ...
... birds and animals and by overflow water in bottomlands. Persimmon is slow growing and usually does not make a large tree, although it may reach 21-24 meters tall on optimal sites. Trees have been reported to reach 150 years of age. ...
Section 24–1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers
... 20. What important crops were unknown in Europe before they were introduced there from the Americas? Important crops include corn, peanuts, beans, and potatoes. 21. What are two ways in which the efficiency of agriculture has been improved? a. One way is the selective breeding of crop plants. b. A s ...
... 20. What important crops were unknown in Europe before they were introduced there from the Americas? Important crops include corn, peanuts, beans, and potatoes. 21. What are two ways in which the efficiency of agriculture has been improved? a. One way is the selective breeding of crop plants. b. A s ...
effect of fertigation on availability of nutrients (n, p
... 15 cm and thereafter reduced. Comparatively higher available nutrients were observed in Richfield water soluble fertilizer than straight fertilizer because Richfield water soluble fertilizer contains high soluble nutrients. Among the different levels of fertilizer, the treatment that received 125 pe ...
... 15 cm and thereafter reduced. Comparatively higher available nutrients were observed in Richfield water soluble fertilizer than straight fertilizer because Richfield water soluble fertilizer contains high soluble nutrients. Among the different levels of fertilizer, the treatment that received 125 pe ...
document
... Secondary Growth of The Stem • Formation of secondary vascular tissue – Secondary xylem & phloem ...
... Secondary Growth of The Stem • Formation of secondary vascular tissue – Secondary xylem & phloem ...
the plant kingdom - National Botanic Gardens
... The divisions of the plant kingdom approximate to a pseudo-evolutionary sequence. That is the earlier divisions represent a life style that might be considered ‘primitive’, but we must remember that all living plants are equally ‘modern’. All the members exhibit a characteristic alternation of gener ...
... The divisions of the plant kingdom approximate to a pseudo-evolutionary sequence. That is the earlier divisions represent a life style that might be considered ‘primitive’, but we must remember that all living plants are equally ‘modern’. All the members exhibit a characteristic alternation of gener ...
Soil Composition
... Soil supports most of the plant life on Earth. This is why it is important that we look after our soil. In areas all around the world, soils are being damaged because of human activity. Soils are being stripped of their nutrients, and with it, their ability to support life. The greater the soil qual ...
... Soil supports most of the plant life on Earth. This is why it is important that we look after our soil. In areas all around the world, soils are being damaged because of human activity. Soils are being stripped of their nutrients, and with it, their ability to support life. The greater the soil qual ...
Plant Biology - Goodheart
... substances enter or leave the cell. These include substances, such as the gases carbon dioxide or oxygen, that might passively diffuse across the membrane. Other ions or molecules, such as sugars or salts, require the cell to expend energy in active transport, often with the help of specialized prot ...
... substances enter or leave the cell. These include substances, such as the gases carbon dioxide or oxygen, that might passively diffuse across the membrane. Other ions or molecules, such as sugars or salts, require the cell to expend energy in active transport, often with the help of specialized prot ...
Capeweed and Erodium in pastures
... early autumn break is followed by weather which is dry enough to kill or severely set back the sub clover which has germinated. Once further rain falls the desirable pasture plants offer little competition to the surviving weeds. • In early spring both plants flourish, flower and set seed. Once matu ...
... early autumn break is followed by weather which is dry enough to kill or severely set back the sub clover which has germinated. Once further rain falls the desirable pasture plants offer little competition to the surviving weeds. • In early spring both plants flourish, flower and set seed. Once matu ...
Plant Reproduction - Scientist in Residence Program
... People do not often make the connection between flower and fruit. Both are all about reproduction. To be able to look at the structure of a flower and actually see how it develops into fruit is a very powerful way of demonstrating this relationship. Ovaries, which contain eggs, will ultimately devel ...
... People do not often make the connection between flower and fruit. Both are all about reproduction. To be able to look at the structure of a flower and actually see how it develops into fruit is a very powerful way of demonstrating this relationship. Ovaries, which contain eggs, will ultimately devel ...
How to plant and grow agapanthus
... but the number of flowers maybe reduced the following summer. Planting in beds against house walls can reduce the likeliness of frost damage. ...
... but the number of flowers maybe reduced the following summer. Planting in beds against house walls can reduce the likeliness of frost damage. ...
RBC Enzymopathies
... 78 yo man with history of diabetes admitted for aortic valve replacement, the week prior had a carotid endarterectomy. CMP, cbc and coags all within normal limits. When the carotid endarterectomy was performed patient got a cervical plexus block with lidocaine and ropivacaine. Patient noted to have ...
... 78 yo man with history of diabetes admitted for aortic valve replacement, the week prior had a carotid endarterectomy. CMP, cbc and coags all within normal limits. When the carotid endarterectomy was performed patient got a cervical plexus block with lidocaine and ropivacaine. Patient noted to have ...
Plant nutrition
.jpg?width=300)
Plant nutrition is the study of the chemical elements and compounds that are necessary for plant growth, and also of their external supply and internal metabolism. In 1972, E. Epstein defined two criteria for an element to be essential for plant growth: in its absence the plant is unable to complete a normal life cycle; or that the element is part of some essential plant constituent or metabolite.This is in accordance with Liebig's law of the minimum. There are 14 essential plant nutrients. Carbon and oxygen are absorbed from the air, while other nutrients including water are typically obtained from the soil (exceptions include some parasitic or carnivorous plants).Plants must obtain the following mineral nutrients from the growing media: the primary macronutrients: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K) the three secondary macronutrients: calcium (Ca), sulfur (S), magnesium (Mg) the micronutrients/trace minerals: boron (B), chlorine (Cl), manganese (Mn), iron (Fe), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), molybdenum (Mo), nickel (Ni)The macronutrients are consumed in larger quantities and are present in plant tissue in quantities from 0.2% to 4.0% (on a dry matter weight basis). Micro nutrients are present in plant tissue in quantities measured in parts per million, ranging from 5 to 200 ppm, or less than 0.02% dry weight.Most soil conditions across the world can provide plants with adequate nutrition and do not require fertilizer for a complete life cycle. However, humans can artificially modify soil through the addition of fertilizer to promote vigorous growth and increase yield. The plants are able to obtain their required nutrients from the fertilizer added to the soil. A colloidal carbonaceous residue, known as humus, can serve as a nutrient reservoir. Even with adequate water and sunshine, nutrient deficiency can limit growth.Nutrient uptake from the soil is achieved by cation exchange, where root hairs pump hydrogen ions (H+) into the soil through proton pumps. These hydrogen ions displace cations attached to negatively charged soil particles so that the cations are available for uptake by the root.Plant nutrition is a difficult subject to understand completely, partly because of the variation between different plants and even between different species or individuals of a given clone. An element present at a low level may cause deficiency symptoms, while the same element at a higher level may cause toxicity. Further, deficiency of one element may present as symptoms of toxicity from another element. An abundance of one nutrient may cause a deficiency of another nutrient. For example, lower availability of a given nutrient such as SO42− can affect the uptake of another nutrient, such as NO3−. As another example, K+ uptake can be influenced by the amount of NH4+ available.The root, especially the root hair, is the most essential organ for the uptake of nutrients. The structure and architecture of the root can alter the rate of nutrient uptake. Nutrient ions are transported to the center of the root, the stele in order for the nutrients to reach the conducting tissues, xylem and phloem. The Casparian strip, a cell wall outside the stele but within the root, prevents passive flow of water and nutrients, helping to regulate the uptake of nutrients and water. Xylem moves water and inorganic molecules within the plant and phloem accounts for organic molecule transportation. Water potential plays a key role in a plants nutrient uptake. If the water potential is more negative within the plant than the surrounding soils, the nutrients will move from the region of higher solute concentration—in the soil—to the area of lower solute concentration: in the plant.There are three fundamental ways plants uptake nutrients through the root: simple diffusion, occurs when a nonpolar molecule, such as O2, CO2, and NH3 follows a concentration gradient, moving passively through the cell lipid bilayer membrane without the use of transport proteins. facilitated diffusion, is the rapid movement of solutes or ions following a concentration gradient, facilitated by transport proteins. Active transport, is the uptake by cells of ions or molecules against a concentration gradient; this requires an energy source, usually ATP, to power molecular pumps that move the ions or molecules through the membrane. Nutrients are moved inside a plant to where they are most needed. For example, a plant will try to supply more nutrients to its younger leaves than to its older ones. When nutrients are mobile, symptoms of any deficiency become apparent first on the older leaves. However, not all nutrients are equally mobile. Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are mobile nutrients, while the others have varying degrees of mobility. When a less mobile nutrient is deficient, the younger leaves suffer because the nutrient does not move up to them but stays in the older leaves. This phenomenon is helpful in determining which nutrients a plant may be lacking.Many plants engage in symbiosis with microorganisms. Two important types of these relationship are with bacteria such as rhizobia, that carry out biological nitrogen fixation, in which atmospheric nitrogen (N2) is converted into ammonium (NH4); and with mycorrhizal fungi, which through their association with the plant roots help to create a larger effective root surface area. Both of these mutualistic relationships enhance nutrient uptake. Though nitrogen is plentiful in the Earth's atmosphere, relatively few plants harbor nitrogen fixing bacteria, so most plants rely on nitrogen compounds present in the soil to support their growth. These can be supplied by mineralization of soil organic matter or added plant residues, nitrogen fixing bacteria, animal waste, or through the application of fertilizers.Hydroponics, is a method for growing plants in a water-nutrient solution without the use of nutrient-rich soil. It allows researchers and home gardeners to grow their plants in a controlled environment. The most common solution, is the Hoagland solution, developed by D. R. Hoagland in 1933, the solution consists of all the essential nutrients in the correct proportions necessary for most plant growth. An aerator is used to prevent an anoxic event or hypoxia. Hypoxia can affect nutrient uptake of a plant because without oxygen present, respiration becomes inhibited within the root cells. The Nutrient film technique is a variation of hydroponic technique. The roots are not fully submerged, which allows for adequate aeration of the roots, while a ""film"" thin layer of nutrient rich water is pumped through the system to provide nutrients and water to the plant.