Plant Structure and Function
... the leaves to stems and roots. Minerals that travel up the xylem can also move into the phloem through specialized parenchyma transfer cells in the leaves. Unlike xylem, phloem tissue is alive. Phloem is a complex tissue made mostly of cells called sieve tube elements. Their name comes from the sm ...
... the leaves to stems and roots. Minerals that travel up the xylem can also move into the phloem through specialized parenchyma transfer cells in the leaves. Unlike xylem, phloem tissue is alive. Phloem is a complex tissue made mostly of cells called sieve tube elements. Their name comes from the sm ...
Preparation and submission of extended ab
... Soil structure was assessed using a visual and tactile technique designed for use in Scottish soils (Ball and Douglas, 2003). The size, porosity and strength of the aggregates present on a spadeful of soil were assessed subjectively and used to allocate a score between 1 and 10. Score 1 is for a mas ...
... Soil structure was assessed using a visual and tactile technique designed for use in Scottish soils (Ball and Douglas, 2003). The size, porosity and strength of the aggregates present on a spadeful of soil were assessed subjectively and used to allocate a score between 1 and 10. Score 1 is for a mas ...
Investigation 19- A survey of plant kingdom
... Introduction: All plants are placed in the Kingdom Plantae. Plants are then divided in two Divisions: Vascular and Non-Vascular. Vascular plants known as Tracheophyta have vascular bundles consisting of xylem vessels and phloem vessels. Xylem vessels carry water and minerals and phloem vessels carry ...
... Introduction: All plants are placed in the Kingdom Plantae. Plants are then divided in two Divisions: Vascular and Non-Vascular. Vascular plants known as Tracheophyta have vascular bundles consisting of xylem vessels and phloem vessels. Xylem vessels carry water and minerals and phloem vessels carry ...
5# SUMMARY Biological N2 fixation as a major means of
... economy of paddy soils# particularly under tropical conditions* However* information on the effect of increasingly used pesticides and fertilisers and their interaction on I$2 fixation and N2-fixing microorganisms in rice soils is scanty* Experiments were conducted to determine the s~ influenca of o ...
... economy of paddy soils# particularly under tropical conditions* However* information on the effect of increasingly used pesticides and fertilisers and their interaction on I$2 fixation and N2-fixing microorganisms in rice soils is scanty* Experiments were conducted to determine the s~ influenca of o ...
chapter25
... separate pistils. Five sepals are also present but barely visible against the background. ...
... separate pistils. Five sepals are also present but barely visible against the background. ...
Photosynthesis Research
... had been treated with the indicated concentration of either Lvolicitin (closed circles) or linolenoyl-L-glutamine (open circles). The combined amount in nanograms of caryophyllene, a-transbergamontene, (E)-b-farnesene, (E)-nerolidol, and (3E,7E)4,8,12-trimethyl-1,3,7,11,-tridecatetraene was used to ...
... had been treated with the indicated concentration of either Lvolicitin (closed circles) or linolenoyl-L-glutamine (open circles). The combined amount in nanograms of caryophyllene, a-transbergamontene, (E)-b-farnesene, (E)-nerolidol, and (3E,7E)4,8,12-trimethyl-1,3,7,11,-tridecatetraene was used to ...
China (PRC) – Cabbage, Celery and Green Onion
... The plants tested were the principal flowers and plants on display for the October 1, 1996 - Chinese National Day. These plants were displayed in Tiananmen Square and on major streets and around government buildings in Beijing. These Agrostim efficacy tests were initiated to coincide with the Octobe ...
... The plants tested were the principal flowers and plants on display for the October 1, 1996 - Chinese National Day. These plants were displayed in Tiananmen Square and on major streets and around government buildings in Beijing. These Agrostim efficacy tests were initiated to coincide with the Octobe ...
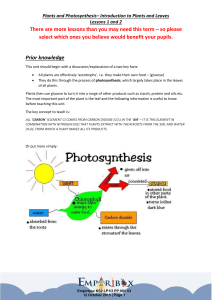
There are more lessons than you may need this term
... animals or protozoans, typically insects and other arthropods. Carnivorous plants have adapted to grow in places where the soil is thin or poor in nutrients, especially nitrogen, such as acidic bogs and rock outcroppings. Charles Darwin wrote Insectivorous Plants, the first well-known treatise on ca ...
... animals or protozoans, typically insects and other arthropods. Carnivorous plants have adapted to grow in places where the soil is thin or poor in nutrients, especially nitrogen, such as acidic bogs and rock outcroppings. Charles Darwin wrote Insectivorous Plants, the first well-known treatise on ca ...
IN VITRO EXTRACT AGAINST IMPORTANT PATHOGENIC ORGANISMS Research Article
... The antifungal activities of C. roseus plant leaves extract obtained by the disc diffusion method are shown in the table. The leaves extract were tested exhibited the antifungal activity against Aspergillus niger, Aspergillus flavus, Aspergillus fumigates, Candida albicans and Penicillium species. A ...
... The antifungal activities of C. roseus plant leaves extract obtained by the disc diffusion method are shown in the table. The leaves extract were tested exhibited the antifungal activity against Aspergillus niger, Aspergillus flavus, Aspergillus fumigates, Candida albicans and Penicillium species. A ...
Paullinia pinnata (Sapindaceae) The plant Plant parts used
... P. pinnata is a climbing shrub, the leaves are compound with winged rhachis, inflorescences stand axillary on long stalks, and bearing paired collected tendrils with white flowers. In Zimbabwe and Zambia P. pinnata is growing in evergreen and mixed forests up to an altitude of 1200m. ...
... P. pinnata is a climbing shrub, the leaves are compound with winged rhachis, inflorescences stand axillary on long stalks, and bearing paired collected tendrils with white flowers. In Zimbabwe and Zambia P. pinnata is growing in evergreen and mixed forests up to an altitude of 1200m. ...
32. Nutrient assimilation.pptx
... Definition - the uptake of non-gaseous molecules from the environment into the cell Common features with gas exchange 1) Transmembrane process dependent on surface area 2) Passive diffusion down chemical (concentration) gradients for a few molecules (such as water), but not true for most nutrient ...
... Definition - the uptake of non-gaseous molecules from the environment into the cell Common features with gas exchange 1) Transmembrane process dependent on surface area 2) Passive diffusion down chemical (concentration) gradients for a few molecules (such as water), but not true for most nutrient ...
6-2.4 - S2TEM Centers SC
... 5. In cooperative groups, have students observe, classify, and dissect a number of examples of these plant structures (obtained from the supermarket). Students should observe each plant structure, describe both its external and internal structure in detail, determine what plant part the vegetable re ...
... 5. In cooperative groups, have students observe, classify, and dissect a number of examples of these plant structures (obtained from the supermarket). Students should observe each plant structure, describe both its external and internal structure in detail, determine what plant part the vegetable re ...
Effects of light availability on Streptanthus bracteatus, a rare annual
... Though S. bracteatus is found primarily beneath woodland canopy, researchers who have grown the plant note its apparent preference for higher light than a plant suited for shady conditions might have (N. Fowler, pers. comm.). In Medina County, Zippin found that plants growing in less shaded areas we ...
... Though S. bracteatus is found primarily beneath woodland canopy, researchers who have grown the plant note its apparent preference for higher light than a plant suited for shady conditions might have (N. Fowler, pers. comm.). In Medina County, Zippin found that plants growing in less shaded areas we ...
Weathering, soil formation and initial ecosystem evolution on a
... specific organic compounds separated either by gas chromatography (Eglington et al., 1996) or by HPLC (Smittenberg et al., 2002). These methods ...
... specific organic compounds separated either by gas chromatography (Eglington et al., 1996) or by HPLC (Smittenberg et al., 2002). These methods ...
What is a Plant? - EDIS
... how we use them. For example: edible and non-edible; fruits and vegetables; poisonous and nonpoisonous; and terrestrial and aquatic plants. Can you think of some other ways plants are grouped? (Answers will vary, examples include: herbaceous and woody; deciduous and evergreen; and temperate and trop ...
... how we use them. For example: edible and non-edible; fruits and vegetables; poisonous and nonpoisonous; and terrestrial and aquatic plants. Can you think of some other ways plants are grouped? (Answers will vary, examples include: herbaceous and woody; deciduous and evergreen; and temperate and trop ...
Greenhouse History and Operation
... 5% perlite, a wetting agent, fertilizer and trace elements. Other soil mixes may be made with peat substitutes such as coir fiber derived from coconut husks. Coir dries out less quickly than peat, however, plants grown in coir fiber require more feeding. Coir is more sustainable than peat. Peat bogs ...
... 5% perlite, a wetting agent, fertilizer and trace elements. Other soil mixes may be made with peat substitutes such as coir fiber derived from coconut husks. Coir dries out less quickly than peat, however, plants grown in coir fiber require more feeding. Coir is more sustainable than peat. Peat bogs ...
A New Hampshire Plant Palette
... variety of landscape plants. As dependable and useful as many of our old standards may be, the quest for plants that are lesser known, under used, and often not fully appreciated is a worthwhile pursuit in a region where plant choices are limited. The trees and shrubs described below are grouped by ...
... variety of landscape plants. As dependable and useful as many of our old standards may be, the quest for plants that are lesser known, under used, and often not fully appreciated is a worthwhile pursuit in a region where plant choices are limited. The trees and shrubs described below are grouped by ...
nutrient composition of plants most favoured by black rhinoceros
... been due to the difference in the relative proportions of leaves and twigs, to the age of the leaves and to species variability. Booth and Hobson-Frohock (1961) reported that the concentrations of alphatocopherol were high in old, in dormant and in dying ...
... been due to the difference in the relative proportions of leaves and twigs, to the age of the leaves and to species variability. Booth and Hobson-Frohock (1961) reported that the concentrations of alphatocopherol were high in old, in dormant and in dying ...
Hints on Growing Tulips - Michigan State University
... should provide adequate moisture through the winter. However, water your bulbs if there is an extended dry spell to replenish natural moisture. In cold areas, after the frost has penetrated 1-2 inches, cover bulb beds with a 3-inch mulch of leaves, peat moss, straw or evergreen boughs. ...
... should provide adequate moisture through the winter. However, water your bulbs if there is an extended dry spell to replenish natural moisture. In cold areas, after the frost has penetrated 1-2 inches, cover bulb beds with a 3-inch mulch of leaves, peat moss, straw or evergreen boughs. ...
Hormonal Regulation of Moss Protonema Development and the
... especially the role calciumlCaM dependent protein kinases and phosphatases, enables one to devise novel and viable strategies for engineering tolerance against stresses. As the protein kinases such as COPKs operate early in the signaling pathway, their manipulation also makes it possible to regulate ...
... especially the role calciumlCaM dependent protein kinases and phosphatases, enables one to devise novel and viable strategies for engineering tolerance against stresses. As the protein kinases such as COPKs operate early in the signaling pathway, their manipulation also makes it possible to regulate ...
Grow Your Own Peppers - OSU Extension Catalog
... temperatures are below these ranges or if soil is too dry. Some varieties that experience temperatures below 60°F will not even blossom. Select the variety most suited to your area’s temperature. Peppers mature slowly. Under good growing conditions, they take at least 45 to 55 days after pollination ...
... temperatures are below these ranges or if soil is too dry. Some varieties that experience temperatures below 60°F will not even blossom. Select the variety most suited to your area’s temperature. Peppers mature slowly. Under good growing conditions, they take at least 45 to 55 days after pollination ...
IOSR Journal of Environmental Science, Toxicology and Food Technology (IOSR-JESTFT)
... faecalis, for heavy metal uptake by the plant Scirpus mucronatus growing in lead-contaminated soil. The results showed that the toxic elements (As, Be, Cd, Cu, Mn, Mo, Ni, Pb, Sb, Se, and Zn) were transported from the soil to the plant and that the concentrations of the elements in the plant tissues ...
... faecalis, for heavy metal uptake by the plant Scirpus mucronatus growing in lead-contaminated soil. The results showed that the toxic elements (As, Be, Cd, Cu, Mn, Mo, Ni, Pb, Sb, Se, and Zn) were transported from the soil to the plant and that the concentrations of the elements in the plant tissues ...
Dudley Woods Wetlands Area Report 2016
... area. The depression appears to have been the result of past excavation, and there are several small earthen mounds and an abrupt irregular short slope. Gauging by the size of the trees within this area, the disturbance took place several tens of years ago. Thirteen wetland soil flags (HS-1 pcf thro ...
... area. The depression appears to have been the result of past excavation, and there are several small earthen mounds and an abrupt irregular short slope. Gauging by the size of the trees within this area, the disturbance took place several tens of years ago. Thirteen wetland soil flags (HS-1 pcf thro ...
Systematics - Elsevier Store
... organisms such as plants by the characteristics they possess. Thus, historically, “plants” included those organisms that possess photosynthesis, cell walls, spores, and a more or less sedentary behavior. This traditional grouping of plants contained a variety of microscopic organisms, all of the “al ...
... organisms such as plants by the characteristics they possess. Thus, historically, “plants” included those organisms that possess photosynthesis, cell walls, spores, and a more or less sedentary behavior. This traditional grouping of plants contained a variety of microscopic organisms, all of the “al ...
Part 5: Soil
... supply shops which you find in most small towns. Land clearing tools are not frequently needed in a Permaculture garden, so you could get learners to bring tools from home rather than buying such tools for sole use in the school garden. Answers to questions The functions of a legume cover crop (gree ...
... supply shops which you find in most small towns. Land clearing tools are not frequently needed in a Permaculture garden, so you could get learners to bring tools from home rather than buying such tools for sole use in the school garden. Answers to questions The functions of a legume cover crop (gree ...
Plant nutrition
.jpg?width=300)
Plant nutrition is the study of the chemical elements and compounds that are necessary for plant growth, and also of their external supply and internal metabolism. In 1972, E. Epstein defined two criteria for an element to be essential for plant growth: in its absence the plant is unable to complete a normal life cycle; or that the element is part of some essential plant constituent or metabolite.This is in accordance with Liebig's law of the minimum. There are 14 essential plant nutrients. Carbon and oxygen are absorbed from the air, while other nutrients including water are typically obtained from the soil (exceptions include some parasitic or carnivorous plants).Plants must obtain the following mineral nutrients from the growing media: the primary macronutrients: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K) the three secondary macronutrients: calcium (Ca), sulfur (S), magnesium (Mg) the micronutrients/trace minerals: boron (B), chlorine (Cl), manganese (Mn), iron (Fe), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), molybdenum (Mo), nickel (Ni)The macronutrients are consumed in larger quantities and are present in plant tissue in quantities from 0.2% to 4.0% (on a dry matter weight basis). Micro nutrients are present in plant tissue in quantities measured in parts per million, ranging from 5 to 200 ppm, or less than 0.02% dry weight.Most soil conditions across the world can provide plants with adequate nutrition and do not require fertilizer for a complete life cycle. However, humans can artificially modify soil through the addition of fertilizer to promote vigorous growth and increase yield. The plants are able to obtain their required nutrients from the fertilizer added to the soil. A colloidal carbonaceous residue, known as humus, can serve as a nutrient reservoir. Even with adequate water and sunshine, nutrient deficiency can limit growth.Nutrient uptake from the soil is achieved by cation exchange, where root hairs pump hydrogen ions (H+) into the soil through proton pumps. These hydrogen ions displace cations attached to negatively charged soil particles so that the cations are available for uptake by the root.Plant nutrition is a difficult subject to understand completely, partly because of the variation between different plants and even between different species or individuals of a given clone. An element present at a low level may cause deficiency symptoms, while the same element at a higher level may cause toxicity. Further, deficiency of one element may present as symptoms of toxicity from another element. An abundance of one nutrient may cause a deficiency of another nutrient. For example, lower availability of a given nutrient such as SO42− can affect the uptake of another nutrient, such as NO3−. As another example, K+ uptake can be influenced by the amount of NH4+ available.The root, especially the root hair, is the most essential organ for the uptake of nutrients. The structure and architecture of the root can alter the rate of nutrient uptake. Nutrient ions are transported to the center of the root, the stele in order for the nutrients to reach the conducting tissues, xylem and phloem. The Casparian strip, a cell wall outside the stele but within the root, prevents passive flow of water and nutrients, helping to regulate the uptake of nutrients and water. Xylem moves water and inorganic molecules within the plant and phloem accounts for organic molecule transportation. Water potential plays a key role in a plants nutrient uptake. If the water potential is more negative within the plant than the surrounding soils, the nutrients will move from the region of higher solute concentration—in the soil—to the area of lower solute concentration: in the plant.There are three fundamental ways plants uptake nutrients through the root: simple diffusion, occurs when a nonpolar molecule, such as O2, CO2, and NH3 follows a concentration gradient, moving passively through the cell lipid bilayer membrane without the use of transport proteins. facilitated diffusion, is the rapid movement of solutes or ions following a concentration gradient, facilitated by transport proteins. Active transport, is the uptake by cells of ions or molecules against a concentration gradient; this requires an energy source, usually ATP, to power molecular pumps that move the ions or molecules through the membrane. Nutrients are moved inside a plant to where they are most needed. For example, a plant will try to supply more nutrients to its younger leaves than to its older ones. When nutrients are mobile, symptoms of any deficiency become apparent first on the older leaves. However, not all nutrients are equally mobile. Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are mobile nutrients, while the others have varying degrees of mobility. When a less mobile nutrient is deficient, the younger leaves suffer because the nutrient does not move up to them but stays in the older leaves. This phenomenon is helpful in determining which nutrients a plant may be lacking.Many plants engage in symbiosis with microorganisms. Two important types of these relationship are with bacteria such as rhizobia, that carry out biological nitrogen fixation, in which atmospheric nitrogen (N2) is converted into ammonium (NH4); and with mycorrhizal fungi, which through their association with the plant roots help to create a larger effective root surface area. Both of these mutualistic relationships enhance nutrient uptake. Though nitrogen is plentiful in the Earth's atmosphere, relatively few plants harbor nitrogen fixing bacteria, so most plants rely on nitrogen compounds present in the soil to support their growth. These can be supplied by mineralization of soil organic matter or added plant residues, nitrogen fixing bacteria, animal waste, or through the application of fertilizers.Hydroponics, is a method for growing plants in a water-nutrient solution without the use of nutrient-rich soil. It allows researchers and home gardeners to grow their plants in a controlled environment. The most common solution, is the Hoagland solution, developed by D. R. Hoagland in 1933, the solution consists of all the essential nutrients in the correct proportions necessary for most plant growth. An aerator is used to prevent an anoxic event or hypoxia. Hypoxia can affect nutrient uptake of a plant because without oxygen present, respiration becomes inhibited within the root cells. The Nutrient film technique is a variation of hydroponic technique. The roots are not fully submerged, which allows for adequate aeration of the roots, while a ""film"" thin layer of nutrient rich water is pumped through the system to provide nutrients and water to the plant.