Mitochondrial type-I prohibitins of Arabidopsis thaliana are required
... phylogenetic relationships with yeast PHB1 and PHB2, respectively. Yeast and animal PHBs are reported to have diverse roles in the cell cycle, mitochondrial electron transport, aging and apoptosis. All transcribed Arabidopsis PHB genes are primarily expressed in both shoot and root proliferative tis ...
... phylogenetic relationships with yeast PHB1 and PHB2, respectively. Yeast and animal PHBs are reported to have diverse roles in the cell cycle, mitochondrial electron transport, aging and apoptosis. All transcribed Arabidopsis PHB genes are primarily expressed in both shoot and root proliferative tis ...
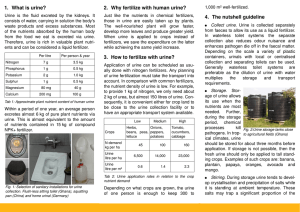
Nitrogen Metabolism Overview
... • List all the reactions in this chapter that generate free ammonia. ...
... • List all the reactions in this chapter that generate free ammonia. ...
wildflowers of texas - Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center
... Their roots are not strong enough to absorb all the necessary water and dissolved minerals that the plants need on their own. So, paintbrush roots “buddy up” with the roots of other plants, most commonly bluebonnets and grasses. They then siphon off some of the water and dissolved minerals their “pa ...
... Their roots are not strong enough to absorb all the necessary water and dissolved minerals that the plants need on their own. So, paintbrush roots “buddy up” with the roots of other plants, most commonly bluebonnets and grasses. They then siphon off some of the water and dissolved minerals their “pa ...
Lecture 12: Gymnosperms and Angiosperms
... Evolution of gymnosperms • Gymnosperms evolved from fern-like ancestors • Advancements of gymnosperms over ferns: Gymnosperms do not depend on water for fertilization (have air-borne pollen) Have a more efficient vascular system ...
... Evolution of gymnosperms • Gymnosperms evolved from fern-like ancestors • Advancements of gymnosperms over ferns: Gymnosperms do not depend on water for fertilization (have air-borne pollen) Have a more efficient vascular system ...
Aster Production - Sakata Ornamentals
... media, with a pH between 5.86.2. Before sowing, moisten the media to the point of drip. Afterwards, sow the seed and lightly cover with medium vermiculite. Do not water the tray after sowing or the day ...
... media, with a pH between 5.86.2. Before sowing, moisten the media to the point of drip. Afterwards, sow the seed and lightly cover with medium vermiculite. Do not water the tray after sowing or the day ...
Native Herbaceous Plants in Our Gardens
... public grounds. Populations are easily devastated by over-picking of seed and digging of plants. Unforeseen damage can occur in the interdependent communities of native plants and animals. Responsibly collected and propagated native plants are becoming more easily available through local nurseries a ...
... public grounds. Populations are easily devastated by over-picking of seed and digging of plants. Unforeseen damage can occur in the interdependent communities of native plants and animals. Responsibly collected and propagated native plants are becoming more easily available through local nurseries a ...
hardy hibiscus border - Garden Gate Magazine
... ith such a wide range of sizes, hardy hibiscus can play many roles in the garden. Their late bloom season gives any garden a dash of tropical color just when the other flowers start to lag. Here’s a pretty, full-sun garden plan with hardy hibiscus and some equally floriferous garden companions. The ...
... ith such a wide range of sizes, hardy hibiscus can play many roles in the garden. Their late bloom season gives any garden a dash of tropical color just when the other flowers start to lag. Here’s a pretty, full-sun garden plan with hardy hibiscus and some equally floriferous garden companions. The ...
Physical and chemical characteristics of forest soil in southern
... and is expressed in terms of milliequivalents of hydrogen ion per 100 grams of soil. A colloid is a small, insoluble, non-diffusible particle larger than a molecule but small enough to remain suspended in a fluid medium without settling. Most soils contain organic colloidal particles as well as the ...
... and is expressed in terms of milliequivalents of hydrogen ion per 100 grams of soil. A colloid is a small, insoluble, non-diffusible particle larger than a molecule but small enough to remain suspended in a fluid medium without settling. Most soils contain organic colloidal particles as well as the ...
straw bale gardening - UC Cooperative Extension Capitol Corridor
... Thank you for your inquiry. I have been looking through my manuals and have come up with a few suggestions for your project. ...
... Thank you for your inquiry. I have been looking through my manuals and have come up with a few suggestions for your project. ...
The evolution of plants: a major problem for Darwinism
... or mould in the rock which retains the shape and size of the entombed plant part. A cast results when the mould is filled with minerals deposited by ground water. The most important type of plant fossil used for research in plant evolution is petrifaction, in which plant tissues (especially wood, ro ...
... or mould in the rock which retains the shape and size of the entombed plant part. A cast results when the mould is filled with minerals deposited by ground water. The most important type of plant fossil used for research in plant evolution is petrifaction, in which plant tissues (especially wood, ro ...
FEATURED GREEK HERB BLENDS
... Clinical studies: Clinical studies have shown that carob has an effect on weight loss, and is also suitable for infant colic pain. Carob may substitute chocolate and cocoa in pastry and bakery. Carob pods boiled in water produce carob syrup, which has a chocolate like flavor, but excels chocolate in ...
... Clinical studies: Clinical studies have shown that carob has an effect on weight loss, and is also suitable for infant colic pain. Carob may substitute chocolate and cocoa in pastry and bakery. Carob pods boiled in water produce carob syrup, which has a chocolate like flavor, but excels chocolate in ...
Favorites Plants for North Texas Gardens
... • Bloom time: May to September • Leaves: long bluish-green, fine fern-like texture Pest or Disease Problems: None Note: Seed pods and seeds are poisonous. Bird of Paradise can be considered aggressive if not deadheaded because the seeds take root. ...
... • Bloom time: May to September • Leaves: long bluish-green, fine fern-like texture Pest or Disease Problems: None Note: Seed pods and seeds are poisonous. Bird of Paradise can be considered aggressive if not deadheaded because the seeds take root. ...
A phylogenetic analysis of the land plants
... Also, i t is a way we can adopt a common universal language, a necessity if we wish to understand the phylogenetic hypothesis underlying classifications. Cronquist’s ( 197 1) classification is used as a basis for criticism since it deals with the land plants as a whole, even though other and more re ...
... Also, i t is a way we can adopt a common universal language, a necessity if we wish to understand the phylogenetic hypothesis underlying classifications. Cronquist’s ( 197 1) classification is used as a basis for criticism since it deals with the land plants as a whole, even though other and more re ...
Characteristics of the Hairy Roots Cultures
... transformed roots is genetically controlled but it is influenced by nutritional and environmental factors. The composition of the culture medium affects growth and secondary metabolite production. The sucrose level, exogenous growth hormone, the nature of the nitrogen source and their relative amoun ...
... transformed roots is genetically controlled but it is influenced by nutritional and environmental factors. The composition of the culture medium affects growth and secondary metabolite production. The sucrose level, exogenous growth hormone, the nature of the nitrogen source and their relative amoun ...
Apéndice Formas de Manejo en especies
... releasing their seeds in different areas of the homegarden or coffee plantations. Some people use to envelop inflorescences with mature fruits in bags and leave them dry for up 8 days in order to complete fruit maturation. Then, people spread by hand the fruits throughout selected areas. Some labors ...
... releasing their seeds in different areas of the homegarden or coffee plantations. Some people use to envelop inflorescences with mature fruits in bags and leave them dry for up 8 days in order to complete fruit maturation. Then, people spread by hand the fruits throughout selected areas. Some labors ...
First International Workshop on Growing Plants for Increased
... certain transcription factors have been shown to result in efficient enhancement of anthocyanin accumulation in for instance tomato (Martin). Biochemical studies of a pathway by inhibiting specific enzymatic steps can be useful in predicting the effects of genetic engineering and will assist in rati ...
... certain transcription factors have been shown to result in efficient enhancement of anthocyanin accumulation in for instance tomato (Martin). Biochemical studies of a pathway by inhibiting specific enzymatic steps can be useful in predicting the effects of genetic engineering and will assist in rati ...
Snapdragons
... The Latin name (Antirrhinum majus) means “like a snout” which tries to describe their calf-like (or dragon-like) faces. Individual flowers of the basic snapdragon have 5 lobes, which are divided into unequal Snapdragons are a very popular cut flower. upper and lower “jaws”. Children love to press li ...
... The Latin name (Antirrhinum majus) means “like a snout” which tries to describe their calf-like (or dragon-like) faces. Individual flowers of the basic snapdragon have 5 lobes, which are divided into unequal Snapdragons are a very popular cut flower. upper and lower “jaws”. Children love to press li ...
heavy metals accumulation in paddy cultivation area of kompipinan
... would subsequently be enhanced (Sridhara et al., 2008). Heavy metals in soil with high concentration will increase the potential of being taken up by plants. The pollutants will then be translocated from roots to shoots then to the grains, which are consumed by human population. Toxic metals are mos ...
... would subsequently be enhanced (Sridhara et al., 2008). Heavy metals in soil with high concentration will increase the potential of being taken up by plants. The pollutants will then be translocated from roots to shoots then to the grains, which are consumed by human population. Toxic metals are mos ...
Document
... a. 10% to 12% reduction of body weight: decreased heat tolerance and weakness b. 20% reduction: coma and death Minerals A. General functions B. Mineral bioavailability 1. Our bodies vary in their capabilities to absorb and use available minerals; minerals are not bioavailable unless we can absorb th ...
... a. 10% to 12% reduction of body weight: decreased heat tolerance and weakness b. 20% reduction: coma and death Minerals A. General functions B. Mineral bioavailability 1. Our bodies vary in their capabilities to absorb and use available minerals; minerals are not bioavailable unless we can absorb th ...
Soils
... – Unloading – exfoliation of igneous and metamorphic rocks at the Earth’s surface due to a reduction in confining pressure – Thermal expansion – alternate expansion and contraction due to heating and cooling – Biological activity – disintegration resulting from plants and animals ...
... – Unloading – exfoliation of igneous and metamorphic rocks at the Earth’s surface due to a reduction in confining pressure – Thermal expansion – alternate expansion and contraction due to heating and cooling – Biological activity – disintegration resulting from plants and animals ...
PDF file
... – Unloading – exfoliation of igneous and metamorphic rocks at the Earth’s surface due to a reduction in confining pressure – Thermal expansion – alternate expansion and contraction due to heating and cooling – Biological activity – disintegration resulting from plants and animals ...
... – Unloading – exfoliation of igneous and metamorphic rocks at the Earth’s surface due to a reduction in confining pressure – Thermal expansion – alternate expansion and contraction due to heating and cooling – Biological activity – disintegration resulting from plants and animals ...
united - Stockholm Convention
... P.D. Noyes, D.E. Hinton and H.M. Stapleton, Accumulation of debromination of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209) in juvenile fathead minnows (Pimephales promelas) induces thyroid disruption and liver alternations, Toxicological Sciences, 2011, 122(2), 265-274. Young fish received BDE-209 at microgram ...
... P.D. Noyes, D.E. Hinton and H.M. Stapleton, Accumulation of debromination of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209) in juvenile fathead minnows (Pimephales promelas) induces thyroid disruption and liver alternations, Toxicological Sciences, 2011, 122(2), 265-274. Young fish received BDE-209 at microgram ...
Plant Science
... food in the seed into energy for germination. • Some seeds require less oxygen than others. • Oxygen deficiency occurs if seeds are planted in flooded or compacted soil. ...
... food in the seed into energy for germination. • Some seeds require less oxygen than others. • Oxygen deficiency occurs if seeds are planted in flooded or compacted soil. ...
VALLEY VIEW UNIVERSITY 2008 Fertilisation with human urine in a nutshell_0
... Urine is ideally applied before light rainfall. This will ensure that the nutrients are washed into the soil. On very dry soils, more nitrogen evaporates, and in the case of heavy rains, nutrients are washed away from the crops. Application. Fertilization w ...
... Urine is ideally applied before light rainfall. This will ensure that the nutrients are washed into the soil. On very dry soils, more nitrogen evaporates, and in the case of heavy rains, nutrients are washed away from the crops. Application. Fertilization w ...
Class Notes
... o This popular ornamental species has fanlike leaves that turn gold before they fall off in the autumn. o Landscapers usually plant only male trees because the coats of seeds produced by female plants produce a repulsive odor as they decay. ...
... o This popular ornamental species has fanlike leaves that turn gold before they fall off in the autumn. o Landscapers usually plant only male trees because the coats of seeds produced by female plants produce a repulsive odor as they decay. ...
Plant nutrition
.jpg?width=300)
Plant nutrition is the study of the chemical elements and compounds that are necessary for plant growth, and also of their external supply and internal metabolism. In 1972, E. Epstein defined two criteria for an element to be essential for plant growth: in its absence the plant is unable to complete a normal life cycle; or that the element is part of some essential plant constituent or metabolite.This is in accordance with Liebig's law of the minimum. There are 14 essential plant nutrients. Carbon and oxygen are absorbed from the air, while other nutrients including water are typically obtained from the soil (exceptions include some parasitic or carnivorous plants).Plants must obtain the following mineral nutrients from the growing media: the primary macronutrients: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K) the three secondary macronutrients: calcium (Ca), sulfur (S), magnesium (Mg) the micronutrients/trace minerals: boron (B), chlorine (Cl), manganese (Mn), iron (Fe), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), molybdenum (Mo), nickel (Ni)The macronutrients are consumed in larger quantities and are present in plant tissue in quantities from 0.2% to 4.0% (on a dry matter weight basis). Micro nutrients are present in plant tissue in quantities measured in parts per million, ranging from 5 to 200 ppm, or less than 0.02% dry weight.Most soil conditions across the world can provide plants with adequate nutrition and do not require fertilizer for a complete life cycle. However, humans can artificially modify soil through the addition of fertilizer to promote vigorous growth and increase yield. The plants are able to obtain their required nutrients from the fertilizer added to the soil. A colloidal carbonaceous residue, known as humus, can serve as a nutrient reservoir. Even with adequate water and sunshine, nutrient deficiency can limit growth.Nutrient uptake from the soil is achieved by cation exchange, where root hairs pump hydrogen ions (H+) into the soil through proton pumps. These hydrogen ions displace cations attached to negatively charged soil particles so that the cations are available for uptake by the root.Plant nutrition is a difficult subject to understand completely, partly because of the variation between different plants and even between different species or individuals of a given clone. An element present at a low level may cause deficiency symptoms, while the same element at a higher level may cause toxicity. Further, deficiency of one element may present as symptoms of toxicity from another element. An abundance of one nutrient may cause a deficiency of another nutrient. For example, lower availability of a given nutrient such as SO42− can affect the uptake of another nutrient, such as NO3−. As another example, K+ uptake can be influenced by the amount of NH4+ available.The root, especially the root hair, is the most essential organ for the uptake of nutrients. The structure and architecture of the root can alter the rate of nutrient uptake. Nutrient ions are transported to the center of the root, the stele in order for the nutrients to reach the conducting tissues, xylem and phloem. The Casparian strip, a cell wall outside the stele but within the root, prevents passive flow of water and nutrients, helping to regulate the uptake of nutrients and water. Xylem moves water and inorganic molecules within the plant and phloem accounts for organic molecule transportation. Water potential plays a key role in a plants nutrient uptake. If the water potential is more negative within the plant than the surrounding soils, the nutrients will move from the region of higher solute concentration—in the soil—to the area of lower solute concentration: in the plant.There are three fundamental ways plants uptake nutrients through the root: simple diffusion, occurs when a nonpolar molecule, such as O2, CO2, and NH3 follows a concentration gradient, moving passively through the cell lipid bilayer membrane without the use of transport proteins. facilitated diffusion, is the rapid movement of solutes or ions following a concentration gradient, facilitated by transport proteins. Active transport, is the uptake by cells of ions or molecules against a concentration gradient; this requires an energy source, usually ATP, to power molecular pumps that move the ions or molecules through the membrane. Nutrients are moved inside a plant to where they are most needed. For example, a plant will try to supply more nutrients to its younger leaves than to its older ones. When nutrients are mobile, symptoms of any deficiency become apparent first on the older leaves. However, not all nutrients are equally mobile. Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are mobile nutrients, while the others have varying degrees of mobility. When a less mobile nutrient is deficient, the younger leaves suffer because the nutrient does not move up to them but stays in the older leaves. This phenomenon is helpful in determining which nutrients a plant may be lacking.Many plants engage in symbiosis with microorganisms. Two important types of these relationship are with bacteria such as rhizobia, that carry out biological nitrogen fixation, in which atmospheric nitrogen (N2) is converted into ammonium (NH4); and with mycorrhizal fungi, which through their association with the plant roots help to create a larger effective root surface area. Both of these mutualistic relationships enhance nutrient uptake. Though nitrogen is plentiful in the Earth's atmosphere, relatively few plants harbor nitrogen fixing bacteria, so most plants rely on nitrogen compounds present in the soil to support their growth. These can be supplied by mineralization of soil organic matter or added plant residues, nitrogen fixing bacteria, animal waste, or through the application of fertilizers.Hydroponics, is a method for growing plants in a water-nutrient solution without the use of nutrient-rich soil. It allows researchers and home gardeners to grow their plants in a controlled environment. The most common solution, is the Hoagland solution, developed by D. R. Hoagland in 1933, the solution consists of all the essential nutrients in the correct proportions necessary for most plant growth. An aerator is used to prevent an anoxic event or hypoxia. Hypoxia can affect nutrient uptake of a plant because without oxygen present, respiration becomes inhibited within the root cells. The Nutrient film technique is a variation of hydroponic technique. The roots are not fully submerged, which allows for adequate aeration of the roots, while a ""film"" thin layer of nutrient rich water is pumped through the system to provide nutrients and water to the plant.