Bio 101: Plant Evolution (Karoly) Midterm Review
... VOCABULARY: the third page includes a list of terms, organized by chapters in the text. These terms have been used in the reading, lab, and lecture, and should be terms that have meaning for you. STUDY GUIDLEINES: information provided below is meant to give you an outline to guide your studying of t ...
... VOCABULARY: the third page includes a list of terms, organized by chapters in the text. These terms have been used in the reading, lab, and lecture, and should be terms that have meaning for you. STUDY GUIDLEINES: information provided below is meant to give you an outline to guide your studying of t ...
PLANTS: The Giver of Life The Earth is sometimes known as the
... Plants are the living entities that ‘gave life’ to this planet. Long time ago there was no oxygen on Earth. The plants of the Earth, through photosynthesis, produced oxygen on Earth. So you can say that plants actually ‘gave life’ to the Earth. You and I cannot be alive today without plants. Plants ...
... Plants are the living entities that ‘gave life’ to this planet. Long time ago there was no oxygen on Earth. The plants of the Earth, through photosynthesis, produced oxygen on Earth. So you can say that plants actually ‘gave life’ to the Earth. You and I cannot be alive today without plants. Plants ...
Different groups of plants
... amazing. Giant sequoia trees are plants just as much as strawberries or tiny mosses. Plantae is the scientific name for the plant kingdom. It consists of many different divisions and groups of plants. Scientists group plants according to their common characteristics. ...
... amazing. Giant sequoia trees are plants just as much as strawberries or tiny mosses. Plantae is the scientific name for the plant kingdom. It consists of many different divisions and groups of plants. Scientists group plants according to their common characteristics. ...
Adapting the flower species Sparaxis tricolor to aquaponic organic
... features that make it fit for this type of culture. A first argument is its origin – Cape Floral Kingdom, South Africa – characterised by droughty summers and rainy winters, where it can be cultivated in temperate areas by saving heating; the second factor was its preference for moist soils rich in ...
... features that make it fit for this type of culture. A first argument is its origin – Cape Floral Kingdom, South Africa – characterised by droughty summers and rainy winters, where it can be cultivated in temperate areas by saving heating; the second factor was its preference for moist soils rich in ...
BIODIVERSITY OF PLANTS
... Other important crops are soybeans or other beans. The edible portion of these crops are the seeds The seeds of these plants are high in protein, carbohydrates and fibre. ...
... Other important crops are soybeans or other beans. The edible portion of these crops are the seeds The seeds of these plants are high in protein, carbohydrates and fibre. ...
HM6 Science Unit A Chapter 1 Lesson 2 Outline - Spring
... 1) There are three living kinds of gnetophytes: Ephedra, Gnetum, and Welwitschia a) Most species of Ephedra are branched shrubs (or rarely small trees) while others are vine-like. b) Most of the Gnetum are woody vines that climb high into trees of tropical rain forests in central Africa, Asia, north ...
... 1) There are three living kinds of gnetophytes: Ephedra, Gnetum, and Welwitschia a) Most species of Ephedra are branched shrubs (or rarely small trees) while others are vine-like. b) Most of the Gnetum are woody vines that climb high into trees of tropical rain forests in central Africa, Asia, north ...
White Fleeceflower
... flowers rising above the foliage from early summer to early fall. The flowers are excellent for cutting. It's pointy leaves remain green in color throughout the season. The fruit is not ornamentally significant. Landscape Attributes: White Fleeceflower is an herbaceous perennial with a mounded form. ...
... flowers rising above the foliage from early summer to early fall. The flowers are excellent for cutting. It's pointy leaves remain green in color throughout the season. The fruit is not ornamentally significant. Landscape Attributes: White Fleeceflower is an herbaceous perennial with a mounded form. ...
PPT File - Petal School District
... Use of a part of a plant for reproducing new plants, other than the seed. (leaf, stem, root, tissue culture) Also called vegetative propagation. The new plant is an exact duplication of the parent plant. (same DNA) ...
... Use of a part of a plant for reproducing new plants, other than the seed. (leaf, stem, root, tissue culture) Also called vegetative propagation. The new plant is an exact duplication of the parent plant. (same DNA) ...
Unit 16 - Plant Systems
... A hormone is a chemical produced in one part of an organism that is transported to another part where it causes a physiological change - plant hormones regulate the growth and development in plants – ...
... A hormone is a chemical produced in one part of an organism that is transported to another part where it causes a physiological change - plant hormones regulate the growth and development in plants – ...
Chapter 26 Active Reading Guide The Colonization of Land by Plants
... also correct. Whatever your response was, modify your answer above to include the other term. Read this section and you will review a number of traits of plants that they share with various groups of algae. We are most interested in those adaptations that are unique to plants and enabled life on lan ...
... also correct. Whatever your response was, modify your answer above to include the other term. Read this section and you will review a number of traits of plants that they share with various groups of algae. We are most interested in those adaptations that are unique to plants and enabled life on lan ...
TAXONOMY Common Synonym(s) GENERAL INFORMATION
... include commonly associated species Plant strategy type / successional stage (stress-tolerator, competitor, ...
... include commonly associated species Plant strategy type / successional stage (stress-tolerator, competitor, ...
Lesson 8: Life Cycles
... don’t have proper nutrition in your diet. Many traits are determined by more than one gene, and this leads to lots of variation within species. For example, if one parent has blue eyes and the other has brown eyes, their kids could either have blue or brown eyes. This is important because if there w ...
... don’t have proper nutrition in your diet. Many traits are determined by more than one gene, and this leads to lots of variation within species. For example, if one parent has blue eyes and the other has brown eyes, their kids could either have blue or brown eyes. This is important because if there w ...
Document
... Auxins are synthesized mainly in shoot meristem. These hormones increase plant growth by stimulating cells to lengthen. ...
... Auxins are synthesized mainly in shoot meristem. These hormones increase plant growth by stimulating cells to lengthen. ...
Chapter 9: Fungi and Aquatic Plants
... DIVISION OF LABOUR). Some algae; cyanobacteria (a.k.a. blue-green algae) were also considered part of this group. ¾ In multi-cellular organisms individual cells have varying degrees of specialization, beginning with ‘higher’ algae and fungi. DIVISION OF LABOUR is now carried out by similar groups of ...
... DIVISION OF LABOUR). Some algae; cyanobacteria (a.k.a. blue-green algae) were also considered part of this group. ¾ In multi-cellular organisms individual cells have varying degrees of specialization, beginning with ‘higher’ algae and fungi. DIVISION OF LABOUR is now carried out by similar groups of ...
Mandevilla FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS FIRST
... Prune to remove old wood and to shape the bush is best done in late winter. Flowers appear only on new wood so pruning is beneficial to promote more flowers. MY PLANT LOST IT LEAVES. If you leave it outside in the fall too late and temperatures drop below 40 to 45F, some of the leaves will probably ...
... Prune to remove old wood and to shape the bush is best done in late winter. Flowers appear only on new wood so pruning is beneficial to promote more flowers. MY PLANT LOST IT LEAVES. If you leave it outside in the fall too late and temperatures drop below 40 to 45F, some of the leaves will probably ...
July 3, 2008 Hale Pono Lesson - Hoakalei Cultural Foundation
... wind, wing (birds), or waves (jet stream in the ocean). These indigenous species are native to Hawaii and can also be found outside the islands. Endemic plants are completely unique to Hawai‘i. • Naupaka (Hawaiians used to eat the fruit when there was not enough food. It was also used for medicine) ...
... wind, wing (birds), or waves (jet stream in the ocean). These indigenous species are native to Hawaii and can also be found outside the islands. Endemic plants are completely unique to Hawai‘i. • Naupaka (Hawaiians used to eat the fruit when there was not enough food. It was also used for medicine) ...
3 AIM: To help children understand how light is necessary for plant...
... AIM: To help children understand how light is necessary for plant growth. YOU WILL NEED ...
... AIM: To help children understand how light is necessary for plant growth. YOU WILL NEED ...
Guide 17
... (d) “Tolland Man,” a bog mummy dating from 405–100 B.C. The acidic, oxygen-poor conditions produced by Sphagnum canpreserve human or other animal bodies for thousands of years. ...
... (d) “Tolland Man,” a bog mummy dating from 405–100 B.C. The acidic, oxygen-poor conditions produced by Sphagnum canpreserve human or other animal bodies for thousands of years. ...
Shamrock Care Sheet
... starts to turn yellow, gradually reduce the amount of water and eliminate fertilizer altogether. Leave bulbs in their pots until fall when they can be repotted and planted again. Take some care during this replanting operation. The bulbs will have produced a pot full of small bulblets, and even the ...
... starts to turn yellow, gradually reduce the amount of water and eliminate fertilizer altogether. Leave bulbs in their pots until fall when they can be repotted and planted again. Take some care during this replanting operation. The bulbs will have produced a pot full of small bulblets, and even the ...
NATIVE PLANT RESOURCES IN SOUTHWEST OREGON
... Has a small selection of native plants amongst their stock of drought tolerant and deer resistant plants. Open Monday-Friday, 7:30am-4pm; Saturday 9am-5pm; later appointments can be made -please call ahead. 10% native plants depending on season; shrubs, perennials, small tree stock. Callahan Seeds 6 ...
... Has a small selection of native plants amongst their stock of drought tolerant and deer resistant plants. Open Monday-Friday, 7:30am-4pm; Saturday 9am-5pm; later appointments can be made -please call ahead. 10% native plants depending on season; shrubs, perennials, small tree stock. Callahan Seeds 6 ...
Plant Processes Chapter 12
... • Roots growing down and/or away from light are more likely to find the soil, water, and minerals they need. • Stems growing up and toward the light will be able to expose their leaves so that photosynthesis can occur. What is the adaptive value of gravitropism? • Think – Pair – Share ...
... • Roots growing down and/or away from light are more likely to find the soil, water, and minerals they need. • Stems growing up and toward the light will be able to expose their leaves so that photosynthesis can occur. What is the adaptive value of gravitropism? • Think – Pair – Share ...
Introduction to the Plant Kingdom
... An embryo is a zygote that has already started to develop and grow. Early growth and development of a plant embryo in a seed is called germination. The seed protects and nourishes the embryo and gives it a huge head start in the “race” of life. Many seeds can wait to germinate until conditions are f ...
... An embryo is a zygote that has already started to develop and grow. Early growth and development of a plant embryo in a seed is called germination. The seed protects and nourishes the embryo and gives it a huge head start in the “race” of life. Many seeds can wait to germinate until conditions are f ...
Structures and Functions of Organisms L.1.1., L.1.2
... Animals and plants have a great variety of body plans and internal structures that contribute to their being able to make or find food and reproduce. The process of sexual reproduction in flowering plants takes place in the flower, which is a complex structure made up of several parts. Some parts of ...
... Animals and plants have a great variety of body plans and internal structures that contribute to their being able to make or find food and reproduce. The process of sexual reproduction in flowering plants takes place in the flower, which is a complex structure made up of several parts. Some parts of ...
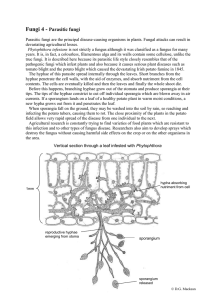
Parasitic fungi - Biology Resources
... devastating agricultural losses. Phytophthora infestans is not strictly a fungus although it was classified as a fungus for many years. It is, in fact, a colourless, filamentous alga and its walls contain some cellulose, unlike the true fungi. It is described here because its parasitic life style cl ...
... devastating agricultural losses. Phytophthora infestans is not strictly a fungus although it was classified as a fungus for many years. It is, in fact, a colourless, filamentous alga and its walls contain some cellulose, unlike the true fungi. It is described here because its parasitic life style cl ...
Sampling methods Sampling Daphnia Sampling Hydra
... • Male - microgametophytes (pollen grains) arise from microspores. • Female - megametophytes contain eggs and develop from megaspores produced within ovule. – Pollination - transfer of pollen. ...
... • Male - microgametophytes (pollen grains) arise from microspores. • Female - megametophytes contain eggs and develop from megaspores produced within ovule. – Pollination - transfer of pollen. ...
History of botany

The history of botany examines the human effort to understand life on Earth by tracing the historical development of the discipline of botany—that part of natural science dealing with organisms traditionally treated as plants.Rudimentary botanical science began with empirically-based plant lore passed from generation to generation in the oral traditions of paleolithic hunter-gatherers. The first written records of plants were made in the Neolithic Revolution about 10,000 years ago as writing was developed in the settled agricultural communities where plants and animals were first domesticated. The first writings that show human curiosity about plants themselves, rather than the uses that could be made of them, appears in the teachings of Aristotle's student Theophrastus at the Lyceum in ancient Athens in about 350 BC; this is considered the starting point for modern botany. In Europe, this early botanical science was soon overshadowed by a medieval preoccupation with the medicinal properties of plants that lasted more than 1000 years. During this time, the medicinal works of classical antiquity were reproduced in manuscripts and books called herbals. In China and the Arab world, the Greco-Roman work on medicinal plants was preserved and extended.In Europe the Renaissance of the 14th–17th centuries heralded a scientific revival during which botany gradually emerged from natural history as an independent science, distinct from medicine and agriculture. Herbals were replaced by floras: books that described the native plants of local regions. The invention of the microscope stimulated the study of plant anatomy, and the first carefully designed experiments in plant physiology were performed. With the expansion of trade and exploration beyond Europe, the many new plants being discovered were subjected to an increasingly rigorous process of naming, description, and classification.Progressively more sophisticated scientific technology has aided the development of contemporary botanical offshoots in the plant sciences, ranging from the applied fields of economic botany (notably agriculture, horticulture and forestry), to the detailed examination of the structure and function of plants and their interaction with the environment over many scales from the large-scale global significance of vegetation and plant communities (biogeography and ecology) through to the small scale of subjects like cell theory, molecular biology and plant biochemistry.