brain development - EDUC111ChildGrowthDevelopment
... Infants are active learners. They are attracted by novelty; this helps them learn. When they become bored with a stimulus (habituation), they seek a new stimulus to focus on (recovery). Imitation is also an important learning process for infants. Habituation/recovery helps us to know more about infa ...
... Infants are active learners. They are attracted by novelty; this helps them learn. When they become bored with a stimulus (habituation), they seek a new stimulus to focus on (recovery). Imitation is also an important learning process for infants. Habituation/recovery helps us to know more about infa ...
Fellmann et al/Human Geography, 8/e
... are responsible for monitoring and coordinating body movements. The medulla oblongata is also part of the hindbrain and is responsible for coordinating and controlling many of the body’s functions such as breathing and maintaining homeostasis. The midbrain - This part of the brain acts as a processi ...
... are responsible for monitoring and coordinating body movements. The medulla oblongata is also part of the hindbrain and is responsible for coordinating and controlling many of the body’s functions such as breathing and maintaining homeostasis. The midbrain - This part of the brain acts as a processi ...
Primary motor cortex (M1)
... • Internal models adapt when there is a discrepancy between expected and actual sensory feedback. • In amputation, internal models must adapt in response to very large errors. ...
... • Internal models adapt when there is a discrepancy between expected and actual sensory feedback. • In amputation, internal models must adapt in response to very large errors. ...
The Biology of Mind
... How a Neuron Fires It is an electrochemical process Electrical inside the neuron Chemical outside the neuron (in the synapse in the form of a neurotransmitter) The firing is call Action Potential ...
... How a Neuron Fires It is an electrochemical process Electrical inside the neuron Chemical outside the neuron (in the synapse in the form of a neurotransmitter) The firing is call Action Potential ...
The Human Brain
... below his left cheek bone and exited after passing through the anterior frontal lobe of his brain. ...
... below his left cheek bone and exited after passing through the anterior frontal lobe of his brain. ...
PCL - mmc7
... brainstem and conducts nerve impulses down to the appropriate spinal level. An upper motor neuron lesion is also known as a pyramidal lesion. Lower motor neurons: these carry nerve impulses from the spinal cord (or brainstem for cranial nerves) to the muscle Decussation: the crossing over of upper m ...
... brainstem and conducts nerve impulses down to the appropriate spinal level. An upper motor neuron lesion is also known as a pyramidal lesion. Lower motor neurons: these carry nerve impulses from the spinal cord (or brainstem for cranial nerves) to the muscle Decussation: the crossing over of upper m ...
LIMBIC SYSTEM
... Gyrus (DG) and CA3 pyramidal neurons via the Perforant Path (PP). CA3 neurons also receive input from the DG via the Mossy Fibres (MF). They send axons to CA1 pyramidal cells via the Schaffer Collateral Pathway (SC), as well as to CA1 cells in the contralateral hippocampus via the Associational Comm ...
... Gyrus (DG) and CA3 pyramidal neurons via the Perforant Path (PP). CA3 neurons also receive input from the DG via the Mossy Fibres (MF). They send axons to CA1 pyramidal cells via the Schaffer Collateral Pathway (SC), as well as to CA1 cells in the contralateral hippocampus via the Associational Comm ...
... Brain Scans • Brain scans, such as CAT, MRI or PET scans, provide a more detailed images of the brain. • They can detect activity through changes in blood flow or uptake of glucose and can allow localisation of function to be identified by showing which areas are most active whilst carrying out a p ...
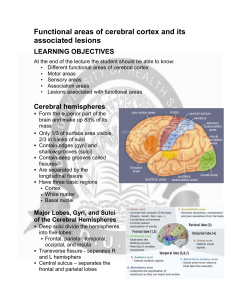
Functional areas of cerebral cortex and its associated lesions
... Exhibits spatial discrimination • Precisely locates a stimulus Projection is contralateral Receives sensory input from the opposite side of the body ...
... Exhibits spatial discrimination • Precisely locates a stimulus Projection is contralateral Receives sensory input from the opposite side of the body ...
on Brain/ Behavior
... representation into auditory code; Subjects of researchers in Switzerland recently reported “out of body” experiences when their a.g. was stimulated A cluster of neurons (nuclei) at the base of the forebrain which connect to the cerebral cortex and that thalamus. Involved in “action selection” (whic ...
... representation into auditory code; Subjects of researchers in Switzerland recently reported “out of body” experiences when their a.g. was stimulated A cluster of neurons (nuclei) at the base of the forebrain which connect to the cerebral cortex and that thalamus. Involved in “action selection” (whic ...
Slide 1
... – What do you think this might be? – How do you think it might cause MS symptoms? – Which divisions of the NS might be involved? ...
... – What do you think this might be? – How do you think it might cause MS symptoms? – Which divisions of the NS might be involved? ...
Motor Cortex
... M1: Coding Movement Movement for limbs Neuron most active Preferred direction but active at 45 from preferred How is direction determined? Populations of M1 neurons Net activity of neurons with different preferred directions vectors ~ ...
... M1: Coding Movement Movement for limbs Neuron most active Preferred direction but active at 45 from preferred How is direction determined? Populations of M1 neurons Net activity of neurons with different preferred directions vectors ~ ...
Physiology Ch 57 p697-709 [4-25
... d. Area for Naming Objects – lateral area of ant occipital lobe and post temporal lobe is where naming objects takes place; learned through auditory input and physical natures are learned through visual input 2. Prefrontal Association Area – functions in association with motor cortex to plan comple ...
... d. Area for Naming Objects – lateral area of ant occipital lobe and post temporal lobe is where naming objects takes place; learned through auditory input and physical natures are learned through visual input 2. Prefrontal Association Area – functions in association with motor cortex to plan comple ...
Altman presentation - NeuronDevelopment.org
... Normal rats stay in the start box for a long time to passively avoid being ...
... Normal rats stay in the start box for a long time to passively avoid being ...
BGandcerebellum - UCSD Cognitive Science
... (MPG) therefore removing tonic inhibition and “releasing the brake” on that generator. GPi neurons projecting to other MPGs increase firing rate and therefore increase inhibition to “brake” other movements to prevent interference. _____________________________________________________________________ ...
... (MPG) therefore removing tonic inhibition and “releasing the brake” on that generator. GPi neurons projecting to other MPGs increase firing rate and therefore increase inhibition to “brake” other movements to prevent interference. _____________________________________________________________________ ...
Exercise and the Bra..
... The levels, however, had dropped back to normal within about 24 hours. That was not the case, though, if the animals continued to exercise. In those rats that ran for four weeks, the “supercompensation” became the new normal, with their baseline levels of glycogen showing substantial increases compa ...
... The levels, however, had dropped back to normal within about 24 hours. That was not the case, though, if the animals continued to exercise. In those rats that ran for four weeks, the “supercompensation” became the new normal, with their baseline levels of glycogen showing substantial increases compa ...
Seminar in Neuroscience Why Corticospinal Motor Neurons Are Important For
... degeneration is key in numerous motor neuron diseases, such as primary lateral scalerosis, hereditary spastic paraplegia, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. CSMN death also leads to long-term paralysis in spinal cord injury patients. Therefore, it is important to understand the cellular and molecula ...
... degeneration is key in numerous motor neuron diseases, such as primary lateral scalerosis, hereditary spastic paraplegia, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. CSMN death also leads to long-term paralysis in spinal cord injury patients. Therefore, it is important to understand the cellular and molecula ...
The Nervous System - Fulton County Schools
... Major (but not only) pathway between left & right hemispheres Corpus Callosum ...
... Major (but not only) pathway between left & right hemispheres Corpus Callosum ...
Analyzed by Symptoms and history Diagnosis 1. Walking down a
... while his eyes were closed. The impaired functioning of what part of Justin’s brain is responsible for these difficulties with motor coordination and balance? Which neurotransmitter is being stimulated? 5. Uncle Ed suffered a stroke which damaged a portion of his cortex. He shows some weakness and p ...
... while his eyes were closed. The impaired functioning of what part of Justin’s brain is responsible for these difficulties with motor coordination and balance? Which neurotransmitter is being stimulated? 5. Uncle Ed suffered a stroke which damaged a portion of his cortex. He shows some weakness and p ...
Lewy Body Diseases
... dementia - present in 30% of cases, possibly due to concomitant AD, DLB, or loss of subcortical neurons (subcortical or attention dementia) ...
... dementia - present in 30% of cases, possibly due to concomitant AD, DLB, or loss of subcortical neurons (subcortical or attention dementia) ...
Chapter 1 - Illinois State University Websites
... impairments – Disorder due to abnormal development of the basal ganglia – Basal ganglia modulates the procedural memory system. ...
... impairments – Disorder due to abnormal development of the basal ganglia – Basal ganglia modulates the procedural memory system. ...
Chapter 21 - The Nervous System: Organization
... Cerebral Cortex Thinking, intelligence, and cognitive functions are located here. Processing of sensory information and motor responses ...
... Cerebral Cortex Thinking, intelligence, and cognitive functions are located here. Processing of sensory information and motor responses ...
Mind from brain: physics & neuroscience
... in working memory, planning, inhibition, and other executive functions. • Executive processes such as voluntary eye movements slowly improve in time but do not reach typical adult levels. • Predicts stereotyped behavior and narrow interests. • No executive function deficits have been found in young ...
... in working memory, planning, inhibition, and other executive functions. • Executive processes such as voluntary eye movements slowly improve in time but do not reach typical adult levels. • Predicts stereotyped behavior and narrow interests. • No executive function deficits have been found in young ...
A circuitous journey “to and through” the TEEN BRAIN
... • Eventually more than 40% of all synapses are eliminated, largely in the prefrontal cortex and association cortex ...
... • Eventually more than 40% of all synapses are eliminated, largely in the prefrontal cortex and association cortex ...