Chapter 6 The peripheral nervous system Unit
... groups of nerve cell bodies, ganglia, which lie outside the brain and spinal cord. The nerve cell nerve fibres are arranged into nerves that body arise from the brain and the spinal cord. Twelve pairs of nerves arise from the brain. These are the cranial nerves. The names of some cranial nerves, suc ...
... groups of nerve cell bodies, ganglia, which lie outside the brain and spinal cord. The nerve cell nerve fibres are arranged into nerves that body arise from the brain and the spinal cord. Twelve pairs of nerves arise from the brain. These are the cranial nerves. The names of some cranial nerves, suc ...
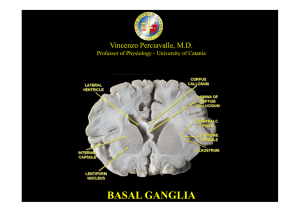
basal ganglia
... into two parts: the pars reticulata (SNpr) and pars compacta (SNpc). The SNpr bears a strong structural and functional resemblance to the internal part of the globus pallidus. The two are sometimes considered parts of the same structure, separated by the white matter of the internal capsule. Like th ...
... into two parts: the pars reticulata (SNpr) and pars compacta (SNpc). The SNpr bears a strong structural and functional resemblance to the internal part of the globus pallidus. The two are sometimes considered parts of the same structure, separated by the white matter of the internal capsule. Like th ...
CHAPTER 10: NERVOUS SYSTEM I
... Summation = many subthreshold stimuli received one after another may allow threshold potential to be reached, and trigger an AP, which in turn begins an impulse on a neuron. a. +15 mV = threshold = AP = impulse b. +5, +5, +5, = +15 mV = threshold = AP = impulse. ...
... Summation = many subthreshold stimuli received one after another may allow threshold potential to be reached, and trigger an AP, which in turn begins an impulse on a neuron. a. +15 mV = threshold = AP = impulse b. +5, +5, +5, = +15 mV = threshold = AP = impulse. ...
NETMORPH: A Framework for the Stochastic
... Sporns et al. 2004) that emerge during development will depend on the specific characteristics of axonal and dendritic arbors, such as their length, number of segments, branching structure and coverage of space. In general, however, it is not well understood how these details of neuronal morphology ...
... Sporns et al. 2004) that emerge during development will depend on the specific characteristics of axonal and dendritic arbors, such as their length, number of segments, branching structure and coverage of space. In general, however, it is not well understood how these details of neuronal morphology ...
chapter 43 The Nervous System
... pulling K+ ions back inside the cell. The balance between diffusional force -and the electrical force produces ""equilibrium potential (table 43.1). By relating the work cby each type of force, we can derive a quantitative expressz for this equilibrium potential called the Nernst equation. :2._ assu ...
... pulling K+ ions back inside the cell. The balance between diffusional force -and the electrical force produces ""equilibrium potential (table 43.1). By relating the work cby each type of force, we can derive a quantitative expressz for this equilibrium potential called the Nernst equation. :2._ assu ...
Appendix 4 Mathematical properties of the state-action
... The heart of the ANNABELL model is the state-action association system, which is responsible for all decision processes, as described in Sect. “Global organization of the model”. This system is implemented as a neural network (state-action association neural network, abbreviated as SAANN) with input ...
... The heart of the ANNABELL model is the state-action association system, which is responsible for all decision processes, as described in Sect. “Global organization of the model”. This system is implemented as a neural network (state-action association neural network, abbreviated as SAANN) with input ...
Nerve Cells, Neural Circuitry, and Behavior
... specificity are the basis of the modern connectionist approach to studying the brain. Ramón y Cajal was also among the first to realize that the feature that most distinguishes one type of neuron from another is form, specifically the number of the processes arising from the cell body. Neurons are t ...
... specificity are the basis of the modern connectionist approach to studying the brain. Ramón y Cajal was also among the first to realize that the feature that most distinguishes one type of neuron from another is form, specifically the number of the processes arising from the cell body. Neurons are t ...
Chapter 4
... Neurotransmitter – chemical stored in the synaptic vesicles that when released transmits messages to other neurons, muscles, or blood vessels Synaptic transmission occurs when neurotransmitter molecules pass across the synaptic cleft and depolarize or hyperpolarize the postsynaptic membrane. Hyperpo ...
... Neurotransmitter – chemical stored in the synaptic vesicles that when released transmits messages to other neurons, muscles, or blood vessels Synaptic transmission occurs when neurotransmitter molecules pass across the synaptic cleft and depolarize or hyperpolarize the postsynaptic membrane. Hyperpo ...
mechanisms of neurotransmitter receptor biogenesis and trafficking
... chaperones can play a crucial role in facilitating the process. Finding out how proteins are folded into their proper conformation is an important ...
... chaperones can play a crucial role in facilitating the process. Finding out how proteins are folded into their proper conformation is an important ...
10-1
... 25. This neurotransmitter is produced in quite a few areas of the brain, including the substantia nigra and the ventral tegmental area. It is also a neurohormone released by the hypothalamus. Its principle hormonal role is to inhibit the release of prolactin from the anterior lobe of the pituitary. ...
... 25. This neurotransmitter is produced in quite a few areas of the brain, including the substantia nigra and the ventral tegmental area. It is also a neurohormone released by the hypothalamus. Its principle hormonal role is to inhibit the release of prolactin from the anterior lobe of the pituitary. ...
A17 - Viktor`s Notes for the Neurosurgery Resident
... - sensation modality / quality evoked by impulses depends upon specific part of brain they ultimately activate; i.e. sensation evoked is that for which receptor is specialized no matter how or where along pathway activity is initiated. e.g. if sensory nerve from pacinian corpuscle in hand is stimula ...
... - sensation modality / quality evoked by impulses depends upon specific part of brain they ultimately activate; i.e. sensation evoked is that for which receptor is specialized no matter how or where along pathway activity is initiated. e.g. if sensory nerve from pacinian corpuscle in hand is stimula ...
Summary of Results and Discussion
... Previous studies by Josephson and Meier reported no alterations of Nogo-A expression at 24 hours after KA injection, and no alterations or strong upregulation after 7-5 days (Table 1.1; Josephson et al., 2001; Meier et al., 2003). The doses used in the three studies were similar (10 mg/kg Josephson ...
... Previous studies by Josephson and Meier reported no alterations of Nogo-A expression at 24 hours after KA injection, and no alterations or strong upregulation after 7-5 days (Table 1.1; Josephson et al., 2001; Meier et al., 2003). The doses used in the three studies were similar (10 mg/kg Josephson ...
Local functions for FMRP in axon growth cone motility and activity
... knockout mice (Irwin et al., 2000, 2001; Greenough et al., 2001). In Golgi-stained sections from FMR1 KO mice, there also appears to be an increase in total spine density in vivo (Irwin et al., 2002); however, this phenotype was only transient during postnatal development in a subsequent study (Nimc ...
... knockout mice (Irwin et al., 2000, 2001; Greenough et al., 2001). In Golgi-stained sections from FMR1 KO mice, there also appears to be an increase in total spine density in vivo (Irwin et al., 2002); however, this phenotype was only transient during postnatal development in a subsequent study (Nimc ...
Olfactory cortex as a model for telencephalic processing
... generate cluster responses in cortex, thereby unmasking the remainder of the bulb’s activity. That remainder becomes the subsequent input to the cortex on the next activity cycle, whereupon the same cortical operations are performed. The result is that the second cortical response (one fourth to one ...
... generate cluster responses in cortex, thereby unmasking the remainder of the bulb’s activity. That remainder becomes the subsequent input to the cortex on the next activity cycle, whereupon the same cortical operations are performed. The result is that the second cortical response (one fourth to one ...
Unit 12 ~ Learning Guide Name
... BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 = reflex arcs signal independent of the brain to ensure the fastest possible reaction time and are generally associated with involuntary reflexes that prevent us from harm such as blinking, pulling limbs away from sharp or hot objects ...
... BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 = reflex arcs signal independent of the brain to ensure the fastest possible reaction time and are generally associated with involuntary reflexes that prevent us from harm such as blinking, pulling limbs away from sharp or hot objects ...
Skeletal System
... Also changes in brain wave patterns Its function is to provide the optimal conditions for an appropriate response to some threat (run / see / think) ...
... Also changes in brain wave patterns Its function is to provide the optimal conditions for an appropriate response to some threat (run / see / think) ...
Fifty years of CPGs: two neuroethological papers that shaped BEHAVIORAL NEUROSCIENCE
... to explain how these properties emerge from the system’s cellular and synaptic organization (Smarandache et al., 2009). Wilson and Weis-Fogh (1962) described the skeletal mechanics, musculature, and motor innervation of the locust flight system, and carefully demonstrated the timing of firing in dif ...
... to explain how these properties emerge from the system’s cellular and synaptic organization (Smarandache et al., 2009). Wilson and Weis-Fogh (1962) described the skeletal mechanics, musculature, and motor innervation of the locust flight system, and carefully demonstrated the timing of firing in dif ...
HISTAMINE AND RESTLESS LEGS SYNDROME
... individuals with RLS.8 The subjects were given either the antihistamine medication diphenhydramine, or as a control they were given a non-histamine sedative to induce drowsiness, which is a common effect of antihistamine use. They found that the RLS subjects who had taken the antihistamine drug had ...
... individuals with RLS.8 The subjects were given either the antihistamine medication diphenhydramine, or as a control they were given a non-histamine sedative to induce drowsiness, which is a common effect of antihistamine use. They found that the RLS subjects who had taken the antihistamine drug had ...
Chapter 11 Efferent Division: Autonomic and Somatic Motor Control
... They differ in their affinity for catecholamines: – Beta-1 receptors respond equally strongly to both epinephrine and norepinephrine – Beta-2 receptors are more sensitive to epinephrine than to norepinephrine • Beta-2 receptors are not innervated • This limits their exposure to norepinephrine becau ...
... They differ in their affinity for catecholamines: – Beta-1 receptors respond equally strongly to both epinephrine and norepinephrine – Beta-2 receptors are more sensitive to epinephrine than to norepinephrine • Beta-2 receptors are not innervated • This limits their exposure to norepinephrine becau ...
peripheral nervous system
... smooth muscle of blood vessels, together with the cardiac muscle, and further divided into sympathetic nerve and parasympathetic nerve. ...
... smooth muscle of blood vessels, together with the cardiac muscle, and further divided into sympathetic nerve and parasympathetic nerve. ...
Chapter 54: The Nervous System
... Alligators are among the most interesting of animals for a biologist to study. Their ecology is closely tied to the environment, and their reptilian biology offers an interesting contrast to that of mammals like ourselves. Studies of alligator development offer powerful general lessons well worthy o ...
... Alligators are among the most interesting of animals for a biologist to study. Their ecology is closely tied to the environment, and their reptilian biology offers an interesting contrast to that of mammals like ourselves. Studies of alligator development offer powerful general lessons well worthy o ...
Biology 231
... membrane and less ATP (energy) is used to pump them back Synapses Between Neurons presynaptic neuron – sending neuron (axon synaptic end bulb) postsynaptic neuron – receiving neuron (dendrite) synaptic cleft – small space between 2 communicating neurons an action potential in the presynaptic neuron ...
... membrane and less ATP (energy) is used to pump them back Synapses Between Neurons presynaptic neuron – sending neuron (axon synaptic end bulb) postsynaptic neuron – receiving neuron (dendrite) synaptic cleft – small space between 2 communicating neurons an action potential in the presynaptic neuron ...
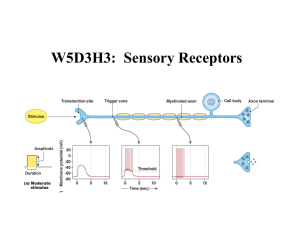
W5D3H3: Sensory Receptors
... In the somatosensory system, various different sensory receptors capture different stimuli and convey them to the sensory cortex. Each type of receptor is specialised, that is, receives the stimulus to which it is predetermined to receive. Immediately as it is stimulated, the receptor sends a signal ...
... In the somatosensory system, various different sensory receptors capture different stimuli and convey them to the sensory cortex. Each type of receptor is specialised, that is, receives the stimulus to which it is predetermined to receive. Immediately as it is stimulated, the receptor sends a signal ...
pituiter_gland23.63 MB
... effect) by enhancing protein and RNA synthesis. Negative feedback by cortisol occurs at both the hypothalamic and pituitary levels: Fast feedback alters the release of CRH and CRH_mediated ACTH secretion, slow feedback results from reduced synthesis of CRH plus supression of POMC gene transcriptio ...
... effect) by enhancing protein and RNA synthesis. Negative feedback by cortisol occurs at both the hypothalamic and pituitary levels: Fast feedback alters the release of CRH and CRH_mediated ACTH secretion, slow feedback results from reduced synthesis of CRH plus supression of POMC gene transcriptio ...
Zeitschrift für Naturforschung / C / 31 (1976) - Max-Planck
... branches of the last four cells are curved in a lateral direction (type C). Fig. l c shows the photographic montage of a type A vertical cell. Signals recorded from vertical cells show a strong similarity to those recorded from horizontal cells i. e. characteristic patterns of synaptic activity and ...
... branches of the last four cells are curved in a lateral direction (type C). Fig. l c shows the photographic montage of a type A vertical cell. Signals recorded from vertical cells show a strong similarity to those recorded from horizontal cells i. e. characteristic patterns of synaptic activity and ...