heart_failure
... NYHA class (ø 0,5-0,8 of class) Quality of life improvement exercise tolerance ...
... NYHA class (ø 0,5-0,8 of class) Quality of life improvement exercise tolerance ...
Dosage of enalapril for congestive heart failure in USA
... LVEF helps distinguish systolic heart failure from heart failure associated with preserved LVF. EF documentation should be included in the medical record. In a survey sponsored by the University Health Systems Consortium evaluating more than 1450 hospitalized patients with heart failure, disease sev ...
... LVEF helps distinguish systolic heart failure from heart failure associated with preserved LVF. EF documentation should be included in the medical record. In a survey sponsored by the University Health Systems Consortium evaluating more than 1450 hospitalized patients with heart failure, disease sev ...
Popular Links
... year survival of 68%. In May 2008, Prucz et al published a retrospective case-control study with 120 patients that reported a 50% reduction in hospitalizations and a statistically significant improvement in NYHA HF classification but similar 4 year survival and LVEF in patients that had CABG +/- SVR ...
... year survival of 68%. In May 2008, Prucz et al published a retrospective case-control study with 120 patients that reported a 50% reduction in hospitalizations and a statistically significant improvement in NYHA HF classification but similar 4 year survival and LVEF in patients that had CABG +/- SVR ...
CR 10: Myocarditis mimicking an acute coronary syndrome
... acute coronary syndrome was considered. • The patient received anti-ischemic treatment. ...
... acute coronary syndrome was considered. • The patient received anti-ischemic treatment. ...
CARDIAC ARREST DURING ELECTIVE ORTHOPEDIC SURGERY DUE TO MODERATE HYPOKALEMIA m
... compressions were performed immediately. The first defibrillation had no effect, whereas the second resulted in asystole. After total administration of 2 mg adrenaline (aliquots of 1 mg each), return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) was evident by palpable pulses of both carotid arteries and the EC ...
... compressions were performed immediately. The first defibrillation had no effect, whereas the second resulted in asystole. After total administration of 2 mg adrenaline (aliquots of 1 mg each), return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) was evident by palpable pulses of both carotid arteries and the EC ...
File
... Hispanic patients have a higher rate of systolic dysfunction than other communities. It is important for nurses to educate on the importance of sodium intake, fluid buildup, medication adherence, and self-management of symptoms in minority communities because of the disproportionate burden from hear ...
... Hispanic patients have a higher rate of systolic dysfunction than other communities. It is important for nurses to educate on the importance of sodium intake, fluid buildup, medication adherence, and self-management of symptoms in minority communities because of the disproportionate burden from hear ...
Physiology of the Cardiovascular System
... G. Once the ventricles are completely repolarized it is back to the baseline ECG ...
... G. Once the ventricles are completely repolarized it is back to the baseline ECG ...
Acute heart failure: vasoactive agents – does it matter?
... to dobutamine develops after a few days of therapy, and malignant ventricular tachyarrhythmias can be observed at any dose. Increased myocardial oxygen consumption promotes cardiac ischemia, thus the usage of this agent can be associated with excess mortality. Chronic therapy may also cause an eosin ...
... to dobutamine develops after a few days of therapy, and malignant ventricular tachyarrhythmias can be observed at any dose. Increased myocardial oxygen consumption promotes cardiac ischemia, thus the usage of this agent can be associated with excess mortality. Chronic therapy may also cause an eosin ...
Outline the control of the heart beat in terms of myogenic muscle
... the heart usually beats about 50 to 70 times each minute, and the heart rate may increase 2- to 3-fold during stress or exercise. If the heart beats too slowly, the brain and body do not get enough blood flow and a variety of symptoms may result. ...
... the heart usually beats about 50 to 70 times each minute, and the heart rate may increase 2- to 3-fold during stress or exercise. If the heart beats too slowly, the brain and body do not get enough blood flow and a variety of symptoms may result. ...
Addendum to Lab 9:
... effects of several inotropes (factors which affect the strength of cardiac contraction)and chronotropes. (factors that affect the rate of cardiac contraction). Although the frog heart is anatomically different from the human heart, the conduction and contraction characteristics are similar to those ...
... effects of several inotropes (factors which affect the strength of cardiac contraction)and chronotropes. (factors that affect the rate of cardiac contraction). Although the frog heart is anatomically different from the human heart, the conduction and contraction characteristics are similar to those ...
AED + CPR Save Lives
... without warning. The heart is no longer able to pump blood to the rest of the body. Often confused with a What is Defibrillation? heart attack (blockages in the heart’s Defibrillation is a process in blood vessels), SCA is essentially an which an electronic device electrical problem that creates an ...
... without warning. The heart is no longer able to pump blood to the rest of the body. Often confused with a What is Defibrillation? heart attack (blockages in the heart’s Defibrillation is a process in blood vessels), SCA is essentially an which an electronic device electrical problem that creates an ...
Lesson 10 Effect of exercise on the CVS
... may increase to 70-170 beats per min and SV from 70 ml to 120 ml per beat. These changes are caused by: ...
... may increase to 70-170 beats per min and SV from 70 ml to 120 ml per beat. These changes are caused by: ...
Ivabradine and Outcomes in Chronic Heart Failure (SHIFT)
... reduction for improvement of clinical outcomes. Discussion: Strengths of this study include that it was a well-designed study. Limitations include generalizability (limited NYHA class IV patients, limited number of elderly patients, and did not include any patients from the US – limited minority pat ...
... reduction for improvement of clinical outcomes. Discussion: Strengths of this study include that it was a well-designed study. Limitations include generalizability (limited NYHA class IV patients, limited number of elderly patients, and did not include any patients from the US – limited minority pat ...
3U 5.6 The Cardiac Cycle PDF
... Ventricles contract fully, forcing the SL valves open and ejecting blood into arteries. ...
... Ventricles contract fully, forcing the SL valves open and ejecting blood into arteries. ...
CARDIAC RESYNCHRONISATION THERAPY IN HEART FAILURE
... Recent data suggest that also patients with narrow QRS (< 120 ms), but with echocardiographic evidence of mechanical dyssynchrony may benefit from CRT. Nevertheless, CRT should not be extended to this group before results of prospective randomised trials will be available. The important issue raised ...
... Recent data suggest that also patients with narrow QRS (< 120 ms), but with echocardiographic evidence of mechanical dyssynchrony may benefit from CRT. Nevertheless, CRT should not be extended to this group before results of prospective randomised trials will be available. The important issue raised ...
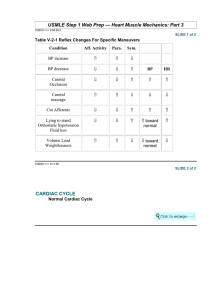
USMLE Step 1 Web Prep — Heart Muscle Mechanics: Part 3
... The correct answer is E. The various points on the volume-pressure diagram correspond to specific events of the cardiac cycle as follows: Choice A: Marks the beginning of systole. The mitral valve closes and S1 can be heard. The end diastolic pressure (5 mmHg) and end diastolic volume (125 mL) can b ...
... The correct answer is E. The various points on the volume-pressure diagram correspond to specific events of the cardiac cycle as follows: Choice A: Marks the beginning of systole. The mitral valve closes and S1 can be heard. The end diastolic pressure (5 mmHg) and end diastolic volume (125 mL) can b ...
An Investigation of Cardiac Dynamics and Substrate Metabolism in
... • Allows for measurement of myocardial function and metabolism under defined loading conditions • Ex Vivo - Independent of neurohormonal influence • Desirable – easy genetic modification, rapid reproductive cycle, similarity to human physiology ...
... • Allows for measurement of myocardial function and metabolism under defined loading conditions • Ex Vivo - Independent of neurohormonal influence • Desirable – easy genetic modification, rapid reproductive cycle, similarity to human physiology ...
Congestive Heart Failure in Dogs
... pump enough blood throughout the body to keep the circulatory system from “backing up.” Not only does this lead to a condition whereby fluid accumulates upstream of the failing chambers of the (right sided heart failure affects the animal differently than left sided heart failure), it means less blo ...
... pump enough blood throughout the body to keep the circulatory system from “backing up.” Not only does this lead to a condition whereby fluid accumulates upstream of the failing chambers of the (right sided heart failure affects the animal differently than left sided heart failure), it means less blo ...
Cardiac output
... increased), cardiac output is increased by increasing in both heart rate and stroke ...
... increased), cardiac output is increased by increasing in both heart rate and stroke ...
6.2 Blood continued
... Sinoatrial node (SA) in the right atrium. Natural pacemaker, ‘sends out’ electrical signals every 0.8 sec. Contracts both atria. Atrioventricular node (AV) also in the right atrium. Receives signal, sends a second signal 0.1 sec. later. Contracts ventricles. The medulla area in the brainstem, sends ...
... Sinoatrial node (SA) in the right atrium. Natural pacemaker, ‘sends out’ electrical signals every 0.8 sec. Contracts both atria. Atrioventricular node (AV) also in the right atrium. Receives signal, sends a second signal 0.1 sec. later. Contracts ventricles. The medulla area in the brainstem, sends ...
The Heart Chapter 18 Part 1
... – Serves as a point of insertion for cardiac muscle and as an electrical insulator. ...
... – Serves as a point of insertion for cardiac muscle and as an electrical insulator. ...
Lead I
... The electrocardiogram (ECG) is a representation of the electrical events of the cardiac cycle. Each event has a distinctive waveform, the study of which can lead to greater insight into a patient’s cardiac pathophysiology. ...
... The electrocardiogram (ECG) is a representation of the electrical events of the cardiac cycle. Each event has a distinctive waveform, the study of which can lead to greater insight into a patient’s cardiac pathophysiology. ...
Cardiac contractility modulation
.jpg?width=300)
Cardiac contractility modulation (CCM) is a treatment for patients with moderate to severe left ventricular systolic heart failure (NYHA class II–IV). The short- and long-term use of this therapy enhances both the strength of ventricular contraction and the heart’s pumping capacity. The CCM mechanism is based on stimulation of the cardiac muscle by non-excitatory electrical signals (NES). CCM treatment is delivered by a pacemaker-like device that applies the NES, adjusted to and synchronized with the electrical action in the cardiac cycle.In CCM therapy, electrical stimulation is applied to the cardiac muscle during the absolute refractory period. In this phase of the cardiac cycle, electrical signals cannot trigger new cardiac muscle contractions, hence this type of stimulation is known as a non-excitatory stimulation. However, the electrical CCM signals increase the influx of calcium ions into the cardiac muscle cells (cardiomyocytes). In contrast to other electrical stimulation treatments for heart failure, such as pacemaker therapy or implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICD), CCM does not affect the cardiac rhythm directly. Rather, the aim is to enhance the heart’s natural contraction (the native cardiac contractility) sustainably over long periods of time. Furthermore, unlike most interventions that increase cardiac contractility, CCM is not associated with an unfavorable increase in oxygen demand by the heart (measured in terms of Myocardial Oxygen Consumption or MVO2). This may be explained by the beneficial effect CCM has in improving cardiac efficiency. A meta-analysis in 2014 and an overview of device-based treatment options in heart failure in 2013 concluded that CCM treatment is safe, that it is generally beneficial to patients and that CCM treatment increases the exercise tolerance (ET) and quality of life (QoL) of patients. Furthermore, preliminary long-term survival data shows that CCM is associated with lower long-term mortality in heart failure patients when compared with expected rates among similar patients not treated with CCM.