1. Describe the cardiac conduction system and an ECG. Tell how an
... there, the signal travels to the AV node, through the bundle of HIS, down the bundle branches, and through the Purkinje fibers, causing the ventricles to contract. This signal creates an electrical current that can be seen on a graph called an Electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG). Doctors use an ECG to mo ...
... there, the signal travels to the AV node, through the bundle of HIS, down the bundle branches, and through the Purkinje fibers, causing the ventricles to contract. This signal creates an electrical current that can be seen on a graph called an Electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG). Doctors use an ECG to mo ...
Update on Percutaneous Mitral Valve Therapy
... “The MitraClip Clip Delivery System is indicated for the percutaneous reduction of significant symptomatic mitral regurgitation (MR ≥ 3+) due to primary abnormality of the mitral apparatus [degenerative MR] in patients who have been determined to be at prohibitive risk for mitral valve surgery by a ...
... “The MitraClip Clip Delivery System is indicated for the percutaneous reduction of significant symptomatic mitral regurgitation (MR ≥ 3+) due to primary abnormality of the mitral apparatus [degenerative MR] in patients who have been determined to be at prohibitive risk for mitral valve surgery by a ...
Maggie Smith Sudden Cardiac Death in Athletes. The concerns on
... a. Shortness of breath and fatigue while exercise are among these signs and symptoms for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. ...
... a. Shortness of breath and fatigue while exercise are among these signs and symptoms for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. ...
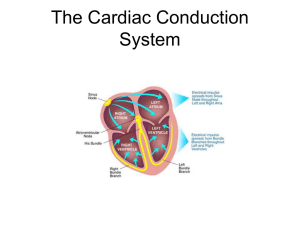
The Cardiac Conduction System
... Definition: Specialized cardiac muscle tissue with fibers that initiate and distribute impulses throughout the myocardium. (muscle layer of the heart) ...
... Definition: Specialized cardiac muscle tissue with fibers that initiate and distribute impulses throughout the myocardium. (muscle layer of the heart) ...
VAD Strategies and Outcomes in Congenital Heart Disease
... Bridge-to-transplant therapy in the setting of progressive heart failure, usually after previous cardiac surgery. Rarely, long term “Destination” therapy ...
... Bridge-to-transplant therapy in the setting of progressive heart failure, usually after previous cardiac surgery. Rarely, long term “Destination” therapy ...
Direct Access Echocardiogram
... Report to GP within 1 week. Patient booked into Cardiology clinic at CUH ...
... Report to GP within 1 week. Patient booked into Cardiology clinic at CUH ...
Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy
... improved quality of life, exercise capacity & ventricular function Trials with CRT +/- ICD (COMPANION) showed that with CRT alone the decrease in risk of death was insignificant Meta-analysis are inconclusive This trial was designed to assess the effect of CRT on mortality in patients with severe HF ...
... improved quality of life, exercise capacity & ventricular function Trials with CRT +/- ICD (COMPANION) showed that with CRT alone the decrease in risk of death was insignificant Meta-analysis are inconclusive This trial was designed to assess the effect of CRT on mortality in patients with severe HF ...
drivers
... chronic MR patients can remain asymptomatic for a long time, depending on the severity of the regurgitation and on the left ventricle function. Syncope is not primarily a MR symptom. Yearly linearized risk of sudden cardiac death of NYHA I, II and III and IV patients are respectively 1%, 3.1% and 7. ...
... chronic MR patients can remain asymptomatic for a long time, depending on the severity of the regurgitation and on the left ventricle function. Syncope is not primarily a MR symptom. Yearly linearized risk of sudden cardiac death of NYHA I, II and III and IV patients are respectively 1%, 3.1% and 7. ...
Note the Atrioventricular valves are ALWAYS attached/associated
... Initially there is bilateral subarterial consus present at around one month of development. Normally, the subaortic conus and subpulmonary conus are present in the first month of gestation as the great arteries are positioned superior to the right ventricle. Next, the subaortic conus is resorbed at ...
... Initially there is bilateral subarterial consus present at around one month of development. Normally, the subaortic conus and subpulmonary conus are present in the first month of gestation as the great arteries are positioned superior to the right ventricle. Next, the subaortic conus is resorbed at ...
Adult Congenital Heart Disease
... discipline. The ability to make appropriate diagnostic and management decisions that have important consequences for patients will be assessed. The exam may require recognition of common as well as rare clinical problems for which patients may consult an adult congenital heart disease specialist. Ex ...
... discipline. The ability to make appropriate diagnostic and management decisions that have important consequences for patients will be assessed. The exam may require recognition of common as well as rare clinical problems for which patients may consult an adult congenital heart disease specialist. Ex ...
Heart Rhythm Refresher Course 2014 Module 1: Epidemiology
... Athlete screening in the Veneto region of Italy is part of a national program (with 12lead ECG) that has reported the detection of previously undiagnosed hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and a decrease in the cardiovascular death rate in young athletes. In this study, over time periods of similar length, ...
... Athlete screening in the Veneto region of Italy is part of a national program (with 12lead ECG) that has reported the detection of previously undiagnosed hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and a decrease in the cardiovascular death rate in young athletes. In this study, over time periods of similar length, ...
S 2
... In newborn and infants 4. intercostal space/midclavicular line In older children and adults 5. intercostal space/midclavicular line ...
... In newborn and infants 4. intercostal space/midclavicular line In older children and adults 5. intercostal space/midclavicular line ...
12.04.28 Genetic Testing for Predisposition to Inherited Hypertrophic
... HCM is a very heterogeneous disorder. Manifestations range from subclinical, asymptomatic disease to severe life-threatening disease. Wide phenotypic variability exists among individuals, even when an identical variant is present, including among affected family members.2 This variability in clinica ...
... HCM is a very heterogeneous disorder. Manifestations range from subclinical, asymptomatic disease to severe life-threatening disease. Wide phenotypic variability exists among individuals, even when an identical variant is present, including among affected family members.2 This variability in clinica ...
A ventricular septal defect (VSD) - University of Maryland School of
... What is a ventricular septal defect? A ventricular septal defect (VSD) is the most common type of congenital heart defect. The wall between the two pumping chambers (ventricles), or ventricular septum, does not form correctly, leaving a hole, or ventricular septal defect (VSD). The hole can be in di ...
... What is a ventricular septal defect? A ventricular septal defect (VSD) is the most common type of congenital heart defect. The wall between the two pumping chambers (ventricles), or ventricular septum, does not form correctly, leaving a hole, or ventricular septal defect (VSD). The hole can be in di ...
Issues in Heart Failure
... ACE-inhibitors, spironolactone: may cause regression of hypertrophy cautious use of diuretics digoxin unhelpful ...
... ACE-inhibitors, spironolactone: may cause regression of hypertrophy cautious use of diuretics digoxin unhelpful ...
Regulation of the Heart`s Functions
... of normal function and control. Primary derangements of various cardiovascular control mechanisms represent an important and perplexing group of disease entities confronting the physician in his daily practice. The various types of regulating mechanisms being discussed in this symposium constitute a ...
... of normal function and control. Primary derangements of various cardiovascular control mechanisms represent an important and perplexing group of disease entities confronting the physician in his daily practice. The various types of regulating mechanisms being discussed in this symposium constitute a ...
When a Family Member Dies Suddenly
... 3. If tissue is saved, cardiac tissue is usually preferred. This should also be frozen at -80 degrees C immediately after collection. For both sources of DNA, standard freezers are OK if -80 degree C freezers are not available. 4. Counsel the family to have all surviving first degree relatives (pare ...
... 3. If tissue is saved, cardiac tissue is usually preferred. This should also be frozen at -80 degrees C immediately after collection. For both sources of DNA, standard freezers are OK if -80 degree C freezers are not available. 4. Counsel the family to have all surviving first degree relatives (pare ...
Muscularisation of the chordae tendineae: an
... many variations that some remain unbranched or branching into three cords before insertion into the leaflet (3-6). The LV usually has two papillary muscles (PM) (posteromedial and anterolateral), both arise from the LV free wall, unlike the right ventricle (RV), without any papillary muscles arising ...
... many variations that some remain unbranched or branching into three cords before insertion into the leaflet (3-6). The LV usually has two papillary muscles (PM) (posteromedial and anterolateral), both arise from the LV free wall, unlike the right ventricle (RV), without any papillary muscles arising ...
The Long QT Syndrome
... genetic cause. For example, beta-blockers are generally extremely protective in type 1 LQTS (LQT1) but may not afford sufficient protection in type 3 LQTS (LQT3). Left cardiac sympathetic denervation (LCSD) surgery is available in a few LQTS centers providing another important treatment option for t ...
... genetic cause. For example, beta-blockers are generally extremely protective in type 1 LQTS (LQT1) but may not afford sufficient protection in type 3 LQTS (LQT3). Left cardiac sympathetic denervation (LCSD) surgery is available in a few LQTS centers providing another important treatment option for t ...
Ventricular hypertrophy icd 10
... Pulmonary heart disease; Right ventricular hypertrophy: Classification and external resources; Specialty: Pulmonology: ICD-10: I26, I27: ICD-9-CM: 415.0: MedlinePlus What is Concentric left ventricular hypertrophy? I was feeling discomfort and breathlessness after meals and consulted a doctor. He as ...
... Pulmonary heart disease; Right ventricular hypertrophy: Classification and external resources; Specialty: Pulmonology: ICD-10: I26, I27: ICD-9-CM: 415.0: MedlinePlus What is Concentric left ventricular hypertrophy? I was feeling discomfort and breathlessness after meals and consulted a doctor. He as ...
Emergencies in adults with congenital heart disease: a guide for the
... • Treat the haemodynamic lesion – may need valve replacement • May need EP studies (VStim) to risk stratify • If symptoms infrequent could consider ILR (Reveal) ...
... • Treat the haemodynamic lesion – may need valve replacement • May need EP studies (VStim) to risk stratify • If symptoms infrequent could consider ILR (Reveal) ...
amyloidosis
... Urine: specimen of urine 24 h: 9,57 g of protein, 0,462 g of creatinine Cardiac ultrasonographic examination: left ventricle - marked concentric hypertrophy; estimated ejection franction, 65 %; mitral valve - calcification of the annulus, papillary-muscle displacement; aortic valve – cusp thickening ...
... Urine: specimen of urine 24 h: 9,57 g of protein, 0,462 g of creatinine Cardiac ultrasonographic examination: left ventricle - marked concentric hypertrophy; estimated ejection franction, 65 %; mitral valve - calcification of the annulus, papillary-muscle displacement; aortic valve – cusp thickening ...
Bonita MB Porter, B.Sc., Phm., B.Sc., MD, CCFP Chief Coroner for
... Sudden unexpected cardiac death of persons under the age of 40 is not rare. The incidence is estimated at 3.5 to 5.5 per million population per year, with significant loss of years of potential life. Many causes of death can be ascertained following scene investigation and complete autopsy, as well ...
... Sudden unexpected cardiac death of persons under the age of 40 is not rare. The incidence is estimated at 3.5 to 5.5 per million population per year, with significant loss of years of potential life. Many causes of death can be ascertained following scene investigation and complete autopsy, as well ...
Bio 449 Lecture 3 Outline Aug. 30, 2008
... Electrical events of the heartbeat Mechanical events of the heartbeat Cardiac output Heart rate Stroke volume Control of cardiac output Blood flow Vessel size, blood velocity and pressure Control of blood distribution Poiseuille's Law Local vs. systemic effects of vasoconstriction Regulation of arte ...
... Electrical events of the heartbeat Mechanical events of the heartbeat Cardiac output Heart rate Stroke volume Control of cardiac output Blood flow Vessel size, blood velocity and pressure Control of blood distribution Poiseuille's Law Local vs. systemic effects of vasoconstriction Regulation of arte ...
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy

Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a primary disease of the myocardium (the muscle of the heart) in which a portion of the myocardium is hypertrophied (thickened) without any obvious cause, creating functional impairment of the cardiac muscle. It is a leading cause of sudden cardiac death in young athletes.The occurrence of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is a significant cause of sudden unexpected cardiac death in any age group and as a cause of disabling cardiac symptoms. Younger people are likely to have a more severe form of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.HCM is frequently asymptomatic until sudden cardiac death, and for this reason some suggest routinely screening certain populations for this disease.A cardiomyopathy is a disease that affects the muscle of the heart. With HCM, the myocytes (cardiac contractile cells) in the heart increase in size, which results in the thickening of the heart muscle. In addition, the normal alignment of muscle cells is disrupted, a phenomenon known as myocardial disarray. HCM also causes disruptions of the electrical functions of the heart. HCM is most commonly due to a mutation in one of nine sarcomeric genes that results in a mutated protein in the sarcomere, the primary component of the myocyte (the muscle cell of the heart). These are predominantly single-point missense mutations in the genes for beta-myosin heavy chain (MHC), myosin-binding protein C, cardiac troponinT, or tropomyosin. These mutations cause myofibril and myocyte structural abnormalities and possible deficiencies in force generation. Not to be confused with dilated cardiomyopathy or any other cardiomyopathy.While most literature so far focuses on European, American, and Japanese populations, HCM appears in all ethnic groups. The prevalence of HCM is about 0.2% to 0.5% of the general population.