IOSR Journal of Economics and Finance (IOSR-JEF)
... have present value similar to the initial tax cut. The demand for goods is based on expected present value of the future taxes. The assumption in the Ricardian theory is that government expenditure must be financed by taxes either now or sometimes in future, i.e. budget deficit is simply described a ...
... have present value similar to the initial tax cut. The demand for goods is based on expected present value of the future taxes. The assumption in the Ricardian theory is that government expenditure must be financed by taxes either now or sometimes in future, i.e. budget deficit is simply described a ...
After Virtue chapter guide
... another, and thus such a decision has the appearance of being personal and non-rational; Second, that despite the necessity of some personal and non-rational choice, the arguments all purport to be impersonal and rational, in that they "presuppose ... the existence, independently of the preferences ...
... another, and thus such a decision has the appearance of being personal and non-rational; Second, that despite the necessity of some personal and non-rational choice, the arguments all purport to be impersonal and rational, in that they "presuppose ... the existence, independently of the preferences ...
Greece`s Golden and Hellenistic Ages
... Detail how Philip II of Macedon paved the way for cultural change. Examine what Alexander the Great accomplished. Identify the factors that contributed to the breakup of Alexander’s empire. ...
... Detail how Philip II of Macedon paved the way for cultural change. Examine what Alexander the Great accomplished. Identify the factors that contributed to the breakup of Alexander’s empire. ...
Weber Italy
... in his discussion of ideal types faced the problem of normativity in almost the same form, since he was compelled to distinguish the explanatory from the “dogmatic” uses of the same concept, and to explain that the unique ideal of rationality was abstract and therefore ideal in the sense of ideation ...
... in his discussion of ideal types faced the problem of normativity in almost the same form, since he was compelled to distinguish the explanatory from the “dogmatic” uses of the same concept, and to explain that the unique ideal of rationality was abstract and therefore ideal in the sense of ideation ...
Methodological Conclusions and Other Definitions of Coyuntura
... made the basic text of this edition possible. From his document we try to be loyal to the methodological process he plants in a difficult theme, but essential for those who carry out a labor of education and accompaniment to social processes and the reality of our country. These materials are aimed ...
... made the basic text of this edition possible. From his document we try to be loyal to the methodological process he plants in a difficult theme, but essential for those who carry out a labor of education and accompaniment to social processes and the reality of our country. These materials are aimed ...
AP World History : Sample Syllabus 1
... maps, images, quantitative data (charts, graphs, tables), works of art, and other types of sources. Students will develop and enhance their skills at interpreting, summarizing, and analyzing primary source material including documents, maps, charts & graphs, and visuals through weekly examination of ...
... maps, images, quantitative data (charts, graphs, tables), works of art, and other types of sources. Students will develop and enhance their skills at interpreting, summarizing, and analyzing primary source material including documents, maps, charts & graphs, and visuals through weekly examination of ...
Reconciling behavioural and neoclassical economics - Hal-SHS
... interest. Further exploring how markets and market experience influence behavior represents an important line of future inquiry.” (Levitt and List, 2008, 910) ...
... interest. Further exploring how markets and market experience influence behavior represents an important line of future inquiry.” (Levitt and List, 2008, 910) ...
AP World History : Sample Syllabus 1
... maps, images, quantitative data (charts, graphs, tables), works of art, and other types of sources. Students will develop and enhance their skills at interpreting, summarizing, and analyzing primary source material including documents, maps, charts & graphs, and visuals through weekly examination of ...
... maps, images, quantitative data (charts, graphs, tables), works of art, and other types of sources. Students will develop and enhance their skills at interpreting, summarizing, and analyzing primary source material including documents, maps, charts & graphs, and visuals through weekly examination of ...
World Civilizations Dr. Rick Sherrod
... maps, images, quantitative data (charts, graphs, tables), works of art, and other types of sources. Students will develop and enhance their skills at interpreting, summarizing, and analyzing primary source material including documents, maps, charts & graphs, and visuals through weekly examination of ...
... maps, images, quantitative data (charts, graphs, tables), works of art, and other types of sources. Students will develop and enhance their skills at interpreting, summarizing, and analyzing primary source material including documents, maps, charts & graphs, and visuals through weekly examination of ...
AP World History : Sample Syllabus 1
... maps, images, quantitative data (charts, graphs, tables), works of art, and other types of sources. Students will develop and enhance their skills at interpreting, summarizing, and analyzing primary source material including documents, maps, charts & graphs, and visuals through weekly examination of ...
... maps, images, quantitative data (charts, graphs, tables), works of art, and other types of sources. Students will develop and enhance their skills at interpreting, summarizing, and analyzing primary source material including documents, maps, charts & graphs, and visuals through weekly examination of ...
AP World History : Sample Syllabus 1
... maps, images, quantitative data (charts, graphs, tables), works of art, and other types of sources. Students will develop and enhance their skills at interpreting, summarizing, and analyzing primary source material including documents, maps, charts & graphs, and visuals through weekly examination of ...
... maps, images, quantitative data (charts, graphs, tables), works of art, and other types of sources. Students will develop and enhance their skills at interpreting, summarizing, and analyzing primary source material including documents, maps, charts & graphs, and visuals through weekly examination of ...
Ogres and Omnivores: Early American Historians and Climate
... Your use of the JSTOR archive indicates your acceptance of the Terms & Conditions of Use, available at http://www.jstor.org/page/ ...
... Your use of the JSTOR archive indicates your acceptance of the Terms & Conditions of Use, available at http://www.jstor.org/page/ ...
Buford High School – AP World History – Summer Assignment 2017
... AP World History goes well beyond facts and memorization. It is centered around ‘thinking like a historian’. A major part of that is analyzing sources, at the same time taking into account the historical content that is being covered. The Neolithic Revolution is considered one of the seminal events ...
... AP World History goes well beyond facts and memorization. It is centered around ‘thinking like a historian’. A major part of that is analyzing sources, at the same time taking into account the historical content that is being covered. The Neolithic Revolution is considered one of the seminal events ...
So, you are interested in taking Pre-A
... historians use to categorize events into discrete blocks and to identify turning points, recognizing that the choice of specific dates privileges one narrative, region or group over another narrative, region or group; therefore, changing the periodization can change a historical narrative. Moreover, ...
... historians use to categorize events into discrete blocks and to identify turning points, recognizing that the choice of specific dates privileges one narrative, region or group over another narrative, region or group; therefore, changing the periodization can change a historical narrative. Moreover, ...
quantitative and qualitative - BU Blogs
... a higher-order concept – e.g., fruit – according to which apples and oranges are similar. This common-sense meaning of comparability is widely understood and agreed upon. But what does it mean for items to be comparable within the context of social science research? Surely, it is more than shared me ...
... a higher-order concept – e.g., fruit – according to which apples and oranges are similar. This common-sense meaning of comparability is widely understood and agreed upon. But what does it mean for items to be comparable within the context of social science research? Surely, it is more than shared me ...
Challenging Transformation`s Clichés
... threats are sometimes inflated, and even if the stockpiles of such weapons actually have declined overall.9 The threat of infectious diseases also remains valid.10 Naturally, each report tends to portray its particular threat, or set of threats, as the most urgent. Policymakers are then left to asse ...
... threats are sometimes inflated, and even if the stockpiles of such weapons actually have declined overall.9 The threat of infectious diseases also remains valid.10 Naturally, each report tends to portray its particular threat, or set of threats, as the most urgent. Policymakers are then left to asse ...
The debate about utopias from a sociological perspective
... existentialist philosophy: the transhistorical validity of a utopia, they write, is the result of its closeness to some aspect of the ‘human condition’ as such (Manuel & Manuel:20). In the analysis of Thomas More’s Utopia of 1516, specifically, the Manuels are aware that this work in particular has ...
... existentialist philosophy: the transhistorical validity of a utopia, they write, is the result of its closeness to some aspect of the ‘human condition’ as such (Manuel & Manuel:20). In the analysis of Thomas More’s Utopia of 1516, specifically, the Manuels are aware that this work in particular has ...
Social Studies
... 1. how race, culture, gender, and disability may influence beliefs, actions, and world view; 2. how the same data can be interpreted differently depending upon perspectives, goals, attitudes, personal history, culture, or other factors; 3. issues, topics, or concepts around which disagreement or amb ...
... 1. how race, culture, gender, and disability may influence beliefs, actions, and world view; 2. how the same data can be interpreted differently depending upon perspectives, goals, attitudes, personal history, culture, or other factors; 3. issues, topics, or concepts around which disagreement or amb ...
Geography Policy - Norfolk Community Primary School
... changing landscape and environmental issues leads children to ask questions about the evolution of the planet. We encourage the children to reflect on the impact of mankind on our world and we introduce the concept of ‘stewardship’ in relation to sustainable development. Through teaching about contr ...
... changing landscape and environmental issues leads children to ask questions about the evolution of the planet. We encourage the children to reflect on the impact of mankind on our world and we introduce the concept of ‘stewardship’ in relation to sustainable development. Through teaching about contr ...
AHR Forum The End of Prehistory? An Africanist
... and history, philosophy and mythology, and memory and history. The totality of change between these divides is impossible when the goal is to make sense of human experience in all its ramifications.10 History shares with archaeology a primary interest in understanding human and social actions within ...
... and history, philosophy and mythology, and memory and history. The totality of change between these divides is impossible when the goal is to make sense of human experience in all its ramifications.10 History shares with archaeology a primary interest in understanding human and social actions within ...
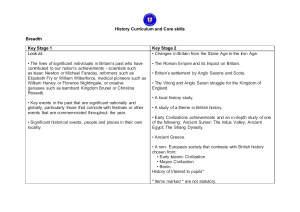
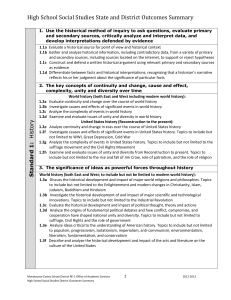
High School Social Studies State and District Outcomes Summary
... 1.1d Differentiate between facts and historical interpretations, recognizing that a historian’s narrative reflects his or her judgment about the significance of particular facts 2. The key concepts of continuity and change, cause and effect, complexity, unity and diversity over time World history (b ...
... 1.1d Differentiate between facts and historical interpretations, recognizing that a historian’s narrative reflects his or her judgment about the significance of particular facts 2. The key concepts of continuity and change, cause and effect, complexity, unity and diversity over time World history (b ...
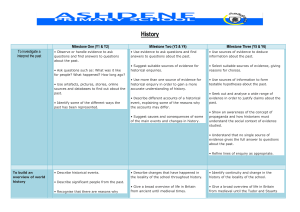
History - Ashdene Primary School
... history that consolidates and extends pupils’ chronological knowledge from before 1066. • At least one study of a significant society or issue in world history and its interconnections with other world developments. ...
... history that consolidates and extends pupils’ chronological knowledge from before 1066. • At least one study of a significant society or issue in world history and its interconnections with other world developments. ...
From Who am I to When am I?: Framing the Time and Shape of the
... So we are struggling to find out what futures studies is, given the fact that so many people still want to be able to predict and control the future. If futures studies can know nothing about the future, what use is it?l If this ...
... So we are struggling to find out what futures studies is, given the fact that so many people still want to be able to predict and control the future. If futures studies can know nothing about the future, what use is it?l If this ...
History
... production of narrative and analysis of past events relating to the human race.[14] The modern discipline of history is dedicated to the institutional production of this discourse. All events that are remembered and preserved in some authentic form constitute the historical record.[15] The task of h ...
... production of narrative and analysis of past events relating to the human race.[14] The modern discipline of history is dedicated to the institutional production of this discourse. All events that are remembered and preserved in some authentic form constitute the historical record.[15] The task of h ...