Social Consciousness
... scientists can extract in their studies everything from themselves except their scientific knowledge. In varying degrees, it is possible for them to do this, and they can assert the existence of external objects. Both of these steps, however—steps that are at the core of science and are pervasive wi ...
... scientists can extract in their studies everything from themselves except their scientific knowledge. In varying degrees, it is possible for them to do this, and they can assert the existence of external objects. Both of these steps, however—steps that are at the core of science and are pervasive wi ...
PASS Criteria - IHMC Public Cmaps (2)
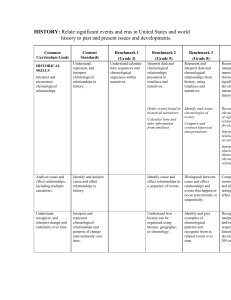
... lasting influence of individuals, issues, events, people, and developments in U.S. history. ...
... lasting influence of individuals, issues, events, people, and developments in U.S. history. ...
English
... falsehoods, and to retain, once again, the scientific truths.’ This, however, would be too naïve. For the problem lies precisely in determining which of the true statements about the world are the scientific ones and which are not. But even were we to solve this problem, the naïve response would sti ...
... falsehoods, and to retain, once again, the scientific truths.’ This, however, would be too naïve. For the problem lies precisely in determining which of the true statements about the world are the scientific ones and which are not. But even were we to solve this problem, the naïve response would sti ...
Sixth Grade Social Studies v. 2016
... customs, beliefs, and art of a group of people; Domesticate- to tame wild animals or plants; Vocabulary: Excavation site- place where archaeologists dig up artifacts; Geography- the study of the relationship between physical features, climate and people; Migrate- to move from one area to another; Pr ...
... customs, beliefs, and art of a group of people; Domesticate- to tame wild animals or plants; Vocabulary: Excavation site- place where archaeologists dig up artifacts; Geography- the study of the relationship between physical features, climate and people; Migrate- to move from one area to another; Pr ...
what are belief systems
... system, and as such, they may play an unusual role which is not typically to be found in the concepts of straight knowledge systems. 9) Belief systems often include representations of alternative worlds, typically the world as it is and the world as it should be. Revolutionary or Utopian belief sys ...
... system, and as such, they may play an unusual role which is not typically to be found in the concepts of straight knowledge systems. 9) Belief systems often include representations of alternative worlds, typically the world as it is and the world as it should be. Revolutionary or Utopian belief sys ...
MODERN WORLD HISTORY 1
... in a frequently violent course that involved conflicts, negotiations, and adaptations. This yearlong course aims at providing a broad overview of these five hundred years along two organizational lines. First, it will discuss the major processes that shaped the modern world such as the development o ...
... in a frequently violent course that involved conflicts, negotiations, and adaptations. This yearlong course aims at providing a broad overview of these five hundred years along two organizational lines. First, it will discuss the major processes that shaped the modern world such as the development o ...
Section 1
... The Restoration and the Glorious Revolution Political parties develop – Charles tried to increase toleration for Catholicism; Tories supported Anglican Church, Whigs opposed having Catholic ruler The Glorious Revolution – bloodless transfer of power in English monarchy; religious attitudes led t ...
... The Restoration and the Glorious Revolution Political parties develop – Charles tried to increase toleration for Catholicism; Tories supported Anglican Church, Whigs opposed having Catholic ruler The Glorious Revolution – bloodless transfer of power in English monarchy; religious attitudes led t ...
Amartya Sen`s Concept of Human Rights: Agency`s Vital Role
... that social actors’ actions are partly self-determined, my question is: Is there any real possibility that an adherence to the empowerment of agents would mean vast differences in the current human rights concepts? Methodologically, his human agency’s freedom is both a constituent component of human ...
... that social actors’ actions are partly self-determined, my question is: Is there any real possibility that an adherence to the empowerment of agents would mean vast differences in the current human rights concepts? Methodologically, his human agency’s freedom is both a constituent component of human ...
Critical Political Economy of Communication and
... partially reified: Culture can be understood by understanding its historically specific “economic” production. Signification is completely eliminated from consideration. “The economic,” is then an “evasion” (Williams 1977, 93; Garnham 2006/1986, 207). Ultimately, Garnham’s position is insightful but ...
... partially reified: Culture can be understood by understanding its historically specific “economic” production. Signification is completely eliminated from consideration. “The economic,” is then an “evasion” (Williams 1977, 93; Garnham 2006/1986, 207). Ultimately, Garnham’s position is insightful but ...
1 Structuration Theory and Self-Organization Christian Fuchs1
... “History does nothing, it “possesses no immense wealth”, it “wages no battles”. It is man, real, living man who does all that, who possesses and fights; “history” is not, as it were, a person apart, using man as a means to achieve its own aims; history is nothing but the activity of man pursuing his ...
... “History does nothing, it “possesses no immense wealth”, it “wages no battles”. It is man, real, living man who does all that, who possesses and fights; “history” is not, as it were, a person apart, using man as a means to achieve its own aims; history is nothing but the activity of man pursuing his ...
AP World History Course Syllabus
... Welcome to AP World History! I am very excited about this class and the opportunity to study World History together. I hope that we will successfully accomplish three main goals this year. First of all, each student will gain a meaningful education in the history of the world and understand its sign ...
... Welcome to AP World History! I am very excited about this class and the opportunity to study World History together. I hope that we will successfully accomplish three main goals this year. First of all, each student will gain a meaningful education in the history of the world and understand its sign ...
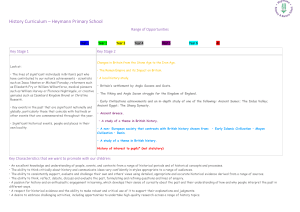
History Curriculum – Heymann Primary School
... • Ask questions such as: What was it like for people? What happened? How long ago? • Use artefacts, pictures, stories, online sources and databases to find out about the past. • Identify some of the different ways the past has been represented. ...
... • Ask questions such as: What was it like for people? What happened? How long ago? • Use artefacts, pictures, stories, online sources and databases to find out about the past. • Identify some of the different ways the past has been represented. ...
The Theory of Capital Markets
... • Labor demand rises,, but labor supply is not available at the lower real wage. • Firms offer higher nominal wages, causing the short-run aggregate supply curve to shift left. • Output remains at Y1 with an efficiency wage of w2/P3 equal to w1/P1. ...
... • Labor demand rises,, but labor supply is not available at the lower real wage. • Firms offer higher nominal wages, causing the short-run aggregate supply curve to shift left. • Output remains at Y1 with an efficiency wage of w2/P3 equal to w1/P1. ...
Measuring human development in Botswana
... development in any society therefore cannot be underestimated. The development of any society should be measurable to make possible the monitoring of strategies put in place to develop the people. Information on the available resources (inputs) and the products (outputs) should guide any human devel ...
... development in any society therefore cannot be underestimated. The development of any society should be measurable to make possible the monitoring of strategies put in place to develop the people. Information on the available resources (inputs) and the products (outputs) should guide any human devel ...
Using CMM - Pearce Associates
... up trying to talk in the language of positivist social science, having learned that it is impossible to say what CMM says in that language (and thanks to Jim McCroskey for help in making that discovery). We've learned to speak in ways informed by anthropology (there's a lot of Clifford Geertz in CMM ...
... up trying to talk in the language of positivist social science, having learned that it is impossible to say what CMM says in that language (and thanks to Jim McCroskey for help in making that discovery). We've learned to speak in ways informed by anthropology (there's a lot of Clifford Geertz in CMM ...
Structuration Theory and Self-Organization
... thought. “History does nothing; it “possesses no immense wealth”; it “wages no battles.” It is man, real, living man who does all that, who possesses and fights; “history” is not, as it were, a person apart, using man as a means to achieve its own aims; history is nothing but the activity of man pur ...
... thought. “History does nothing; it “possesses no immense wealth”; it “wages no battles.” It is man, real, living man who does all that, who possesses and fights; “history” is not, as it were, a person apart, using man as a means to achieve its own aims; history is nothing but the activity of man pur ...
Jared Diamond, “Yali`s Question” (Prologue to Guns
... immediate cause of the modern world's inequalities. Empires with steel weapons were able to conquer or exterminate tribes with weapons of stone and wood. How, though, did the world get to be the way it was in A.D. 1500? Once again, we can easily push this question back one step further, by drawing o ...
... immediate cause of the modern world's inequalities. Empires with steel weapons were able to conquer or exterminate tribes with weapons of stone and wood. How, though, did the world get to be the way it was in A.D. 1500? Once again, we can easily push this question back one step further, by drawing o ...
The IDEA of a Social Science
... rule, in its application to the use of language, and to apply that discussion to human behaviour much more generally. That still seems to me a good strategy: not least because it is a central feature of what Wittgenstein writes about language that this can only be seen for what it is if looked at in ...
... rule, in its application to the use of language, and to apply that discussion to human behaviour much more generally. That still seems to me a good strategy: not least because it is a central feature of what Wittgenstein writes about language that this can only be seen for what it is if looked at in ...
YALI`S QUESTION
... Today, segments of Western society publicly repudiate racism. Yet many (perhaps most!) Westerners continue to accept racist explanations privately or subconsciously. In Japan and many other countries, such explanations are still advanced publicly and without apology. Even educated white Americans, E ...
... Today, segments of Western society publicly repudiate racism. Yet many (perhaps most!) Westerners continue to accept racist explanations privately or subconsciously. In Japan and many other countries, such explanations are still advanced publicly and without apology. Even educated white Americans, E ...
HST 101 L - University of Southern Maine
... course is structured according to the pedagogical approach of ‘big history’. Traditional history, as with most academic disciplines, looks in detail at particular subjects, events, processes, themes, and other phenomena. Whilst focusing on the minutiae of the physical and metaphysical allows us to g ...
... course is structured according to the pedagogical approach of ‘big history’. Traditional history, as with most academic disciplines, looks in detail at particular subjects, events, processes, themes, and other phenomena. Whilst focusing on the minutiae of the physical and metaphysical allows us to g ...
WSN 37 (2016) 114-152
... and deductive ambitions of Homans the solution that he proposes in this situation may surprise : "methodological liberalism" tantamount to ... the absence of rules in this area. Homans appears to be saying: ―Anything goes‖; any method of choice of "action units" is appropriate, on condition that it ...
... and deductive ambitions of Homans the solution that he proposes in this situation may surprise : "methodological liberalism" tantamount to ... the absence of rules in this area. Homans appears to be saying: ―Anything goes‖; any method of choice of "action units" is appropriate, on condition that it ...
Guidance notes for institutional analysis in rural development
... and the improved outcomes that they aspire to achieve, constitute the central concern of an institutional analysis. Whatever improved institutional process that the analysis generates should aim at helping poor people to achieve these aspirations and satisfy basic standards of living and well-being. ...
... and the improved outcomes that they aspire to achieve, constitute the central concern of an institutional analysis. Whatever improved institutional process that the analysis generates should aim at helping poor people to achieve these aspirations and satisfy basic standards of living and well-being. ...
How Historians Work (HAA)
... The Process of History Writing Historians typically begin their work with a question they hope to answer. One example might be, How did the ancient Silk Road trade routes help spread religious ideas across Asia? The first step in answering that question is to gather evidence [evidence: information i ...
... The Process of History Writing Historians typically begin their work with a question they hope to answer. One example might be, How did the ancient Silk Road trade routes help spread religious ideas across Asia? The first step in answering that question is to gather evidence [evidence: information i ...
historical materialism k
... adventuring into an explanation of its causes have left us with an image of “history without subject”. If the imperative of thinking about social institutions—sovereignty—in dynamic terms necessitates that we abandon any attempt to fix meanings into rigid definitions, as suggested by Walker, we have ...
... adventuring into an explanation of its causes have left us with an image of “history without subject”. If the imperative of thinking about social institutions—sovereignty—in dynamic terms necessitates that we abandon any attempt to fix meanings into rigid definitions, as suggested by Walker, we have ...