Student Standards for Social Studies: World History
... Students examine how the agricultural, economic, and industrial revolutions transformed European society and the world economy. WH.4.1 Evaluate the causes and effects of the Industrial Revolution in England, Western Europe, and its spread throughout the world WH.4.2 Describe how the expansion of ind ...
... Students examine how the agricultural, economic, and industrial revolutions transformed European society and the world economy. WH.4.1 Evaluate the causes and effects of the Industrial Revolution in England, Western Europe, and its spread throughout the world WH.4.2 Describe how the expansion of ind ...
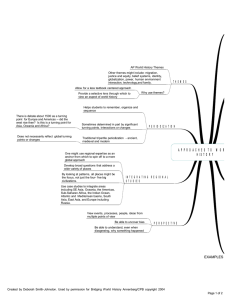
AP World Periodization Periodization Since the history of the world
... Since the history of the world is so large, historians divide world history into specific periods that share a set of common characteristics. These periods begin and end with what historians consider turning points in the world. The dates that historians choose for these turning points are subjectiv ...
... Since the history of the world is so large, historians divide world history into specific periods that share a set of common characteristics. These periods begin and end with what historians consider turning points in the world. The dates that historians choose for these turning points are subjectiv ...
Rigorous Curriculum Design
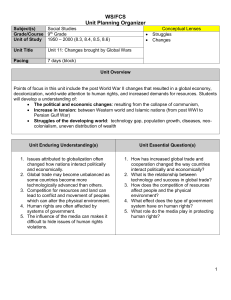
... Points of focus in this unit include the post World War II changes that resulted in a global economy, decolonization, world-wide attention to human rights, and increased demands for resources. Students will develop a understanding of: The political and economic changes: resulting from the collapse ...
... Points of focus in this unit include the post World War II changes that resulted in a global economy, decolonization, world-wide attention to human rights, and increased demands for resources. Students will develop a understanding of: The political and economic changes: resulting from the collapse ...
Modern World History - Dublin City Schools
... The Dublin City Schools K-12 Social Studies educational experience will allow students to see how social studies can be integrated into different disciplines and is relevant to many aspects of life. There is a greater emphasis on problem based/inquiry learning rather than just the memorization of hi ...
... The Dublin City Schools K-12 Social Studies educational experience will allow students to see how social studies can be integrated into different disciplines and is relevant to many aspects of life. There is a greater emphasis on problem based/inquiry learning rather than just the memorization of hi ...
Lab Practice 34 - White Plains Public Schools
... “. . . The wholesale looting and destruction of property and life in Russia during the Mongol invasion of 1237–40 was a staggering blow which left the Russian people stunned, and for a time disrupted the normal course of economic and political life. It is hard to estimate the Russian casualties but ...
... “. . . The wholesale looting and destruction of property and life in Russia during the Mongol invasion of 1237–40 was a staggering blow which left the Russian people stunned, and for a time disrupted the normal course of economic and political life. It is hard to estimate the Russian casualties but ...
Globalization WHAP/Napp “On 9 November 1989, Kristina Matschat
... 5. How did World War II change the patterns of international trade? (A) No countries traded with Germany after the war. (B) The World Trade Organization was created soon after the war ended. (C) The war diminished the European powers’ control over world markets. (D) The USSR began trading more with ...
... 5. How did World War II change the patterns of international trade? (A) No countries traded with Germany after the war. (B) The World Trade Organization was created soon after the war ended. (C) The war diminished the European powers’ control over world markets. (D) The USSR began trading more with ...
File - Social Studies
... The World History is a senior level course that begins with pre-history and concludes in modern era. The emphasis of the course is on world civilizations, political institutions, religions and the transition from the past to the present. Students will utilize different historical methods to interpre ...
... The World History is a senior level course that begins with pre-history and concludes in modern era. The emphasis of the course is on world civilizations, political institutions, religions and the transition from the past to the present. Students will utilize different historical methods to interpre ...
Essential Content #9: Cold War
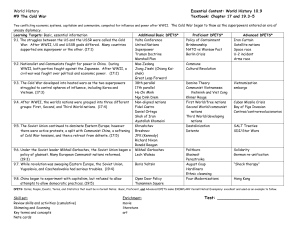
... 9.3. The Cold War developed into heated wars as the two superpowers struggled to control spheres of influence, including Korea and Vietnam. (17:3) 9.4. After WWII, the world’s nations were grouped into three different groups: First, Second, and Third World nations. (17:4) ...
... 9.3. The Cold War developed into heated wars as the two superpowers struggled to control spheres of influence, including Korea and Vietnam. (17:3) 9.4. After WWII, the world’s nations were grouped into three different groups: First, Second, and Third World nations. (17:4) ...
Name - Reeths-Puffer Schools
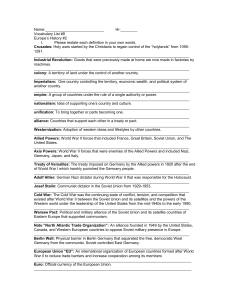
... alliance: Countries that support each other in a treaty or pact. __________________________________________________________________________ Westernization: Adoption of western ideas and lifestyles by other countries. __________________________________________________________________________ Allied P ...
... alliance: Countries that support each other in a treaty or pact. __________________________________________________________________________ Westernization: Adoption of western ideas and lifestyles by other countries. __________________________________________________________________________ Allied P ...
World History Connections to Today
... Most were unable to sustain democratic rule. As problems multiplied, military or authoritarian leaders often took control. They imposed order by building one-party dictatorships. Despite setbacks, in the 1980s and 1990s democracy did make progress in some African, Asian, and Latin American nations. ...
... Most were unable to sustain democratic rule. As problems multiplied, military or authoritarian leaders often took control. They imposed order by building one-party dictatorships. Despite setbacks, in the 1980s and 1990s democracy did make progress in some African, Asian, and Latin American nations. ...
Document
... – ex. Most Western European nations (UK, France, Spain, Germany, etc.), the United States, but only a few non-Western countries like Japan ...
... – ex. Most Western European nations (UK, France, Spain, Germany, etc.), the United States, but only a few non-Western countries like Japan ...
approaches to world history
... west rise then? Is this is a turning point for Asia, Oceania and Africa? ...
... west rise then? Is this is a turning point for Asia, Oceania and Africa? ...
AP World History
... AP World History is a rigorous program designed to help students gain college credit while still in high school. This class approaches history in a nontraditional way in that it looks at the common thread of humanity over time---trade, religion, politics, society, and technology--- and it investigat ...
... AP World History is a rigorous program designed to help students gain college credit while still in high school. This class approaches history in a nontraditional way in that it looks at the common thread of humanity over time---trade, religion, politics, society, and technology--- and it investigat ...
Putting American History into World History
... China and the Wealth of the Americas Foundation of Manila by the Spanish in 1571 Global Connections reveal that historical change and historical explanations operate across space as well as through time space as well as through time ...
... China and the Wealth of the Americas Foundation of Manila by the Spanish in 1571 Global Connections reveal that historical change and historical explanations operate across space as well as through time space as well as through time ...
From World War I through the Cold War
... But also: cooperating with each other to keep their power Each needed the other as “The Other” But both wanted to survive ...
... But also: cooperating with each other to keep their power Each needed the other as “The Other” But both wanted to survive ...
ADVANCED PLACEMENT WORLD HISTORY
... Political revolutions and independence movements and new political ideas Latin American independence movements Revolutions (United States, France, Haiti, Mexico, China) Rise of nationalism, nation-states, and movements of political reform Overlaps between nations and empires Rise of democracy and it ...
... Political revolutions and independence movements and new political ideas Latin American independence movements Revolutions (United States, France, Haiti, Mexico, China) Rise of nationalism, nation-states, and movements of political reform Overlaps between nations and empires Rise of democracy and it ...
War in Afghanistan
... • An army of Muslim fighters of Jihad defending Islam • Made up of Muslims from around the world (including Osama Bin Laden) • Assisted by the United State’s CIA to remove the Soviet Union ($, weapons, training) ...
... • An army of Muslim fighters of Jihad defending Islam • Made up of Muslims from around the world (including Osama Bin Laden) • Assisted by the United State’s CIA to remove the Soviet Union ($, weapons, training) ...
Introduction to AP World History
... AP® World History is for the exceptionally studious high school junior who wishes to earn college credit through a rigorous academic program. This class approaches history in a non-traditional way in that it looks at the common threads of humanity over time: trade, religion, politics, society and te ...
... AP® World History is for the exceptionally studious high school junior who wishes to earn college credit through a rigorous academic program. This class approaches history in a non-traditional way in that it looks at the common threads of humanity over time: trade, religion, politics, society and te ...
Name: Date: ______ Hour: ______ World History and Geography B
... 22. How were the following events a major turning point of World War II? a. the Battle of Britain: b. the attack on Pearl Harbor: c. the Battle of Midway d. the Battle of Stalingrad ...
... 22. How were the following events a major turning point of World War II? a. the Battle of Britain: b. the attack on Pearl Harbor: c. the Battle of Midway d. the Battle of Stalingrad ...
Historical Periodization SEMESTER ONE
... UNIT TOPICS, LENGTH OF TEACHING, AND WEIGHT ON AP EXAM 1. Technological and Environmental Transformations to c. 600 B.C.E. 5% 2. Organization and Reorganization of Human Societies c. 600 B.C.E. to c. 600C.E. 15% INTRO TO WORLD HISTORY & FOUNDATIONS (8000 BCE – 600 AD) 7.5 weeks Understanding world ...
... UNIT TOPICS, LENGTH OF TEACHING, AND WEIGHT ON AP EXAM 1. Technological and Environmental Transformations to c. 600 B.C.E. 5% 2. Organization and Reorganization of Human Societies c. 600 B.C.E. to c. 600C.E. 15% INTRO TO WORLD HISTORY & FOUNDATIONS (8000 BCE – 600 AD) 7.5 weeks Understanding world ...