Astronomy 82 - Problem Set #1
... From Keplerian orbital mechanics, the orbital semimajor axes (a) and velocities (v) of the star and companion depend only on their masses: m* a*=mc a c and m* v *=mc v c . When making radial velocity measurements we can only measure the component of velocity along our line-of-sight. This results in ...
... From Keplerian orbital mechanics, the orbital semimajor axes (a) and velocities (v) of the star and companion depend only on their masses: m* a*=mc a c and m* v *=mc v c . When making radial velocity measurements we can only measure the component of velocity along our line-of-sight. This results in ...
Astronomy vs. Astrology: Uptodate Zodiac Signs and Dates
... is with that of a spinning top, tilted at an angle, which slowly wobbles in a circle while rotating much faster on its axis. Similarly, the Earth’s axis completes the Circle of Precession in 26,000 years, while rotating on its axis in one day or about 24 hours (23h 56 m, to be precise). In addition ...
... is with that of a spinning top, tilted at an angle, which slowly wobbles in a circle while rotating much faster on its axis. Similarly, the Earth’s axis completes the Circle of Precession in 26,000 years, while rotating on its axis in one day or about 24 hours (23h 56 m, to be precise). In addition ...
Kepler`s Laws, Newton`s Laws, and the Search for New Planets
... vector from the Sun to a planet; say the Earth. Then it is shown that the displacement vector lies in a plane, and if the base point is translated to the origin, the endpoint traces out an ellipse. This is said to confirm Kepler’s first law, that the planets orbit the sun in an elliptical path, with ...
... vector from the Sun to a planet; say the Earth. Then it is shown that the displacement vector lies in a plane, and if the base point is translated to the origin, the endpoint traces out an ellipse. This is said to confirm Kepler’s first law, that the planets orbit the sun in an elliptical path, with ...
using a cepheid variable to determine distance
... In this exercise you will use data taken from observations of a Cepheid variable star over a period of 80 days. On each day, the apparent visual magnitude was recorded. Using this data you will be able to plot a light-curve for this Cepheid, and from this light curve, determine the period of the lig ...
... In this exercise you will use data taken from observations of a Cepheid variable star over a period of 80 days. On each day, the apparent visual magnitude was recorded. Using this data you will be able to plot a light-curve for this Cepheid, and from this light curve, determine the period of the lig ...
The Turbulent Sun - Beck-Shop
... magnetic storms and interfering with radio communication. Flares are usually (not always) associated with spot-groups, which means that they are commonest when the Sun is most active. Equipment now is less expensive than it used to be; for example, the serious solar observer will need a telescope de ...
... magnetic storms and interfering with radio communication. Flares are usually (not always) associated with spot-groups, which means that they are commonest when the Sun is most active. Equipment now is less expensive than it used to be; for example, the serious solar observer will need a telescope de ...
Pocket Solar System presentation
... 3. Write the last three Planets on their respective lines, from the SUN: (OK to use Initial) 1. MERCURY = M 2. VENUS = V 3. EARTH = E See next slide ...
... 3. Write the last three Planets on their respective lines, from the SUN: (OK to use Initial) 1. MERCURY = M 2. VENUS = V 3. EARTH = E See next slide ...
constellations
... appear to travel right around the sky and return to exactly due south is 24 hours. This is the Mean Solar Day. Starting from due south, the time taken for a star to appear to travel right around the sky and return to exactly due south is 23 hours, 56 minutes and 4 seconds. This is the Sidereal Day. ...
... appear to travel right around the sky and return to exactly due south is 24 hours. This is the Mean Solar Day. Starting from due south, the time taken for a star to appear to travel right around the sky and return to exactly due south is 23 hours, 56 minutes and 4 seconds. This is the Sidereal Day. ...
Chapter 9: Our Star, the Sun
... • Protects against Solar Flares - violent explosions on the Sun releasing large burst of charged particles into the solar system • Protects against Solar Wind - dangerous stream of charged particles constantly coming from the Sun ...
... • Protects against Solar Flares - violent explosions on the Sun releasing large burst of charged particles into the solar system • Protects against Solar Wind - dangerous stream of charged particles constantly coming from the Sun ...
Journey to the Stars: Activities for Grades 6-8
... Hayden Sphere represents the size of the Sun. Ask students to observe the planets’ relative sizes. Read planet information provided on the accompanying panels, and use that information to complete their worksheets. 2. Investigate Sizes of Stars After students have completed their worksheets, have th ...
... Hayden Sphere represents the size of the Sun. Ask students to observe the planets’ relative sizes. Read planet information provided on the accompanying panels, and use that information to complete their worksheets. 2. Investigate Sizes of Stars After students have completed their worksheets, have th ...
Quiz Maker - Geneva 304
... 13. Right Ascension is measured from 0h to _____ . Sirius has a right ascension of __________ . All stars have a __________ right ascension. 14. The Sun varies in right ascension from ___ h of right ascension, to ___ h of right ascension over the course of a year. The __________ __________ point ma ...
... 13. Right Ascension is measured from 0h to _____ . Sirius has a right ascension of __________ . All stars have a __________ right ascension. 14. The Sun varies in right ascension from ___ h of right ascension, to ___ h of right ascension over the course of a year. The __________ __________ point ma ...
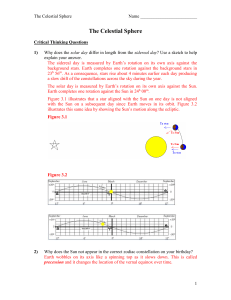
The Celestial Sphere
... The 2000 Olympics were held in Sydney, Australia in late September and early October. This is about 6 – 8 weeks later than the normal July – August period when the summer games are held. Why did the International Olympic Committee schedule the 2000 games around the equinox rather than closer to the ...
... The 2000 Olympics were held in Sydney, Australia in late September and early October. This is about 6 – 8 weeks later than the normal July – August period when the summer games are held. Why did the International Olympic Committee schedule the 2000 games around the equinox rather than closer to the ...
THE ROTATION OF THE SUN
... The slides presented here are from J. -P. Rosenstiehl and prepared by the French association CLEA (Comité de Liaison Enseignants et Astronomes) under the designation D7. First of all, let us examine a set of slides presenting the evolution of the solar features during several days. These documents a ...
... The slides presented here are from J. -P. Rosenstiehl and prepared by the French association CLEA (Comité de Liaison Enseignants et Astronomes) under the designation D7. First of all, let us examine a set of slides presenting the evolution of the solar features during several days. These documents a ...
Star/Sun/Spectral Analysis - ppt
... Chromosphere is the layer above the photosphere. •It is a very thin layer that appears reddish in color • Temperatures ranging from 6,000 °C (at lower altitudes) to 50,000 °C (at higher altitudes). •This layer is a few thousand miles thick. ...
... Chromosphere is the layer above the photosphere. •It is a very thin layer that appears reddish in color • Temperatures ranging from 6,000 °C (at lower altitudes) to 50,000 °C (at higher altitudes). •This layer is a few thousand miles thick. ...
The Celestial Sphere
... 0h when the vernal equinox γ (position of Sun on March 21) is on the meridian. So ST = 0h at noon on March 21, and 12h at noon on September 21. Hour angle HA is the angular measure in h,m,s from the meridian westward along the celestial equator to the foot of the hour circle (like longitude circle) ...
... 0h when the vernal equinox γ (position of Sun on March 21) is on the meridian. So ST = 0h at noon on March 21, and 12h at noon on September 21. Hour angle HA is the angular measure in h,m,s from the meridian westward along the celestial equator to the foot of the hour circle (like longitude circle) ...
The sun is a star. It is a huge, spinning, glowing sphere of hot gas
... The average sunspot is about the size of the entire planet Earth! However, sunspots come in a variety of sizes ranging from hundreds to tens of thousands of miles across (many times larger that Earth). Scientists measure the total size (area) of all of the sunspots seen on the sun every day to get a ...
... The average sunspot is about the size of the entire planet Earth! However, sunspots come in a variety of sizes ranging from hundreds to tens of thousands of miles across (many times larger that Earth). Scientists measure the total size (area) of all of the sunspots seen on the sun every day to get a ...
Introduction to Celestial Motions
... • fixed with respect to the background stars for a given epoch (precession affects) • tilted by colatitude wrt horizon (angle of rising & setting of celestial objects) • can determine how long a celestial body is visible in the sky Abstract Spherical Coordinate Systems • fundamental reference great c ...
... • fixed with respect to the background stars for a given epoch (precession affects) • tilted by colatitude wrt horizon (angle of rising & setting of celestial objects) • can determine how long a celestial body is visible in the sky Abstract Spherical Coordinate Systems • fundamental reference great c ...
Greek geocentric model
... • Found that planetary orbits were heliocentric and elliptical (not circular) Heliocentric = centered around the SUN ...
... • Found that planetary orbits were heliocentric and elliptical (not circular) Heliocentric = centered around the SUN ...
Lecture 2: The Sun and the Heliophysics
... radiation as photons Matter in a radiation zone is so dense that photons can travel only a short distance before they are absorbed or scattered by another particle T drops from 15 million K to 1.5 million K it takes an average of 171,000 years for gamma rays from the core of the Sun to leave the rad ...
... radiation as photons Matter in a radiation zone is so dense that photons can travel only a short distance before they are absorbed or scattered by another particle T drops from 15 million K to 1.5 million K it takes an average of 171,000 years for gamma rays from the core of the Sun to leave the rad ...
lecture 1 - University of Florida Astronomy
... Annual Motion of Sun • The sun moves along a repeatable path on the celestial sphere throughout the year. This path is called the ECLIPTIC – Sun moves east ward relative to stars on celestial sphere – It moves 360 degrees in a year about 1 degree per day – The constellations through which we see th ...
... Annual Motion of Sun • The sun moves along a repeatable path on the celestial sphere throughout the year. This path is called the ECLIPTIC – Sun moves east ward relative to stars on celestial sphere – It moves 360 degrees in a year about 1 degree per day – The constellations through which we see th ...
Week two: The Sun (pdf, 3.9 MB)
... radiation as photons Matter in a radiation zone is so dense that photons can travel only a short distance before they are absorbed or scattered by another particle T drops from 15 million K to 1.5 million K it takes an average of 171,000 years for gamma rays from the core of the Sun to leave the rad ...
... radiation as photons Matter in a radiation zone is so dense that photons can travel only a short distance before they are absorbed or scattered by another particle T drops from 15 million K to 1.5 million K it takes an average of 171,000 years for gamma rays from the core of the Sun to leave the rad ...
March 2013 - Joliet Junior College
... The Vernal Equinox (start of spring) is on March 20th at 6:02 am. Since the first day of winter, the sun has been crossing the sky slightly higher every day. On the equinox the sun is directly above the Earth’s equator and will begin shining above the northern hemisphere until next September. On the ...
... The Vernal Equinox (start of spring) is on March 20th at 6:02 am. Since the first day of winter, the sun has been crossing the sky slightly higher every day. On the equinox the sun is directly above the Earth’s equator and will begin shining above the northern hemisphere until next September. On the ...
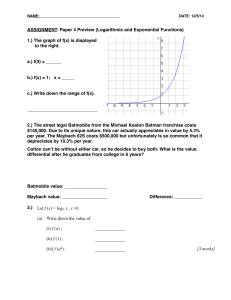
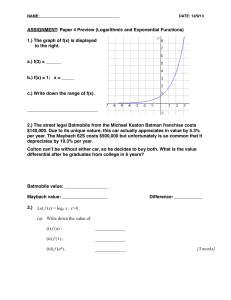
Let f (x) = log x , Let f (x) = loga x , x>0 . (a) Write down the value of (i
... the number of parsecs from earth. 1 parsec = 3.26 light years. Rho Ophiuchi is a nebulous cloud of dust that helps in star formation. Rho Ophiuchi has an apparent magnitude of 5.0 and an absolute magnitude of –0.4. How many light years is Rho Ophiuchi from Earth? ***You must show work to receive cre ...
... the number of parsecs from earth. 1 parsec = 3.26 light years. Rho Ophiuchi is a nebulous cloud of dust that helps in star formation. Rho Ophiuchi has an apparent magnitude of 5.0 and an absolute magnitude of –0.4. How many light years is Rho Ophiuchi from Earth? ***You must show work to receive cre ...
Let f (x) = log x , Let f (x) = loga x , x>0 . (a) Write down the value of (i
... the number of parsecs from earth. 1 parsec = 3.26 light years. Rho Ophiuchi is a nebulous cloud of dust that helps in star formation. Rho Ophiuchi has an apparent magnitude of 5.0 and an absolute magnitude of –0.4. How many light years is Rho Ophiuchi from Earth? ***You must show work to receive cre ...
... the number of parsecs from earth. 1 parsec = 3.26 light years. Rho Ophiuchi is a nebulous cloud of dust that helps in star formation. Rho Ophiuchi has an apparent magnitude of 5.0 and an absolute magnitude of –0.4. How many light years is Rho Ophiuchi from Earth? ***You must show work to receive cre ...
ecliptic. - Valhalla High School
... h R.A., and 1° = 4 min R.A. Right ascension increases from west to east (note that we are looking at the exterior of the celestial sphere in the above picture). ...
... h R.A., and 1° = 4 min R.A. Right ascension increases from west to east (note that we are looking at the exterior of the celestial sphere in the above picture). ...
The Celestial Sphere
... The Moon moves westto-east in the sky (like the Sun), and takes about a month to circle the Earth (hence the word month). But once again, there’s a difference between the Moon’s sidereal period with respect to the stars (27 days), and the synodic period with respect to the Sun (29 days). ...
... The Moon moves westto-east in the sky (like the Sun), and takes about a month to circle the Earth (hence the word month). But once again, there’s a difference between the Moon’s sidereal period with respect to the stars (27 days), and the synodic period with respect to the Sun (29 days). ...
Equation of time
The equation of time describes the discrepancy between two kinds of solar time. These are apparent solar time, which directly tracks the motion of the sun, and mean solar time, which tracks a fictitious ""mean"" sun with noons 24 hours apart. Apparent (or true) solar time can be obtained by measurement of the current position (hour angle) of the Sun, or indicated (with limited accuracy) by a sundial. Mean solar time, for the same place, would be the time indicated by a steady clock set so that over the year its differences from apparent solar time average to zero.The equation of time is the east or west component of the analemma, a curve representing the angular offset of the Sun from its mean position on the celestial sphere as viewed from Earth. The equation of time values for each day of the year, compiled by astronomical observatories, were widely listed in almanacs and ephemerides.