Chapter 29 Notes-
... than surrounding regions, and form areas fo the sun that appear darker than their surrounding regions. • These, cooler, darker areas are called sunspots. • Observations of sunspots have shown that the sun rotates. • The numbers and positions of sunspots vary in a cycle that lasts about 11 years. • S ...
... than surrounding regions, and form areas fo the sun that appear darker than their surrounding regions. • These, cooler, darker areas are called sunspots. • Observations of sunspots have shown that the sun rotates. • The numbers and positions of sunspots vary in a cycle that lasts about 11 years. • S ...
Solar System Dynamics Part I: Solar System Dynamics
... M: mass of central body m: mass of orbiting body r: distance of m from M mi: mass of disturbing body “i” ri: distance of mi from M ...
... M: mass of central body m: mass of orbiting body r: distance of m from M mi: mass of disturbing body “i” ri: distance of mi from M ...
Astronomy 160: Frontiers and Controversies in Astrophysics
... stars, which can then be used to determine the distance to progressively further and further away “standard candles.” Hubble’s value was too large by a factor of 7, which means the distances he calculated were too small by a factor of 7. These distance errors could be explained by an error in parall ...
... stars, which can then be used to determine the distance to progressively further and further away “standard candles.” Hubble’s value was too large by a factor of 7, which means the distances he calculated were too small by a factor of 7. These distance errors could be explained by an error in parall ...
Homework #4 Solutions ASTR100: Introduction to Astronomy
... which is approximately 10 billion years. c) Given our solar system is now about 4.6 billion years old, when will we need to start worrying about the Sun running out of hydrogen for fusion? From the above answer, we know that the total life of the Sun in the main sequence is about 10 billion years. I ...
... which is approximately 10 billion years. c) Given our solar system is now about 4.6 billion years old, when will we need to start worrying about the Sun running out of hydrogen for fusion? From the above answer, we know that the total life of the Sun in the main sequence is about 10 billion years. I ...
Lecture4
... a speed that changes in such a way that a line from the planet to the Sun sweeps out equal areas in equal intervals of time. ● Consequence: planets move faster ...
... a speed that changes in such a way that a line from the planet to the Sun sweeps out equal areas in equal intervals of time. ● Consequence: planets move faster ...
“V” points to the area upstream.
... a) Susie pushes a crate with a force of 18N to the left. Jerry pushes the same crate from the other side with a force of 12N to the right. What is the result? ...
... a) Susie pushes a crate with a force of 18N to the left. Jerry pushes the same crate from the other side with a force of 12N to the right. What is the result? ...
Kepler`s Laws
... where r is the average radius for the section of orbit.. Determine 1 by finding the difference in degrees between December 20 and December 30. Measure the radius at a point midway between the two dates. Calculate the area in AUs for this ten-day period. 3. Select two additional ten-day periods of ti ...
... where r is the average radius for the section of orbit.. Determine 1 by finding the difference in degrees between December 20 and December 30. Measure the radius at a point midway between the two dates. Calculate the area in AUs for this ten-day period. 3. Select two additional ten-day periods of ti ...
PYTS/ASTR 206 – Solar System Scales
... The sun is 150,000,000,000 meters away The wavelength of visible light is 0.0000005 meters The solar system is 4,600,000,000 years old The sun is 1.5 x 1011 m away The wavelength of visible light is 5 x 10-7 m The solar system is 4.6 x 109 years old ...
... The sun is 150,000,000,000 meters away The wavelength of visible light is 0.0000005 meters The solar system is 4,600,000,000 years old The sun is 1.5 x 1011 m away The wavelength of visible light is 5 x 10-7 m The solar system is 4.6 x 109 years old ...
Orbit 13 Yes those famous words, “Class, we have a problem.” once
... axis of the Sun and not tilted 24 degrees like our Earth. Thus the intern was able to put all three bodies, the Sun, the Earth and the Moon in the xy-plane. The intern’s equation for the Moon in this system was based on having the Earth a radius R from the Sun, the Moon a radius of 1 from the Earth ...
... axis of the Sun and not tilted 24 degrees like our Earth. Thus the intern was able to put all three bodies, the Sun, the Earth and the Moon in the xy-plane. The intern’s equation for the Moon in this system was based on having the Earth a radius R from the Sun, the Moon a radius of 1 from the Earth ...
Lab 1: The Celestial Sphere
... turning the knob at the bottom of the globe. Please don’t turn it counterclockwise, since that will disassemble the globe. One full clockwise turn represents one day. (If you wished to, you could hold the Earth still and turn the celestial sphere. Hence, the daily rotation of the Earth and the appar ...
... turning the knob at the bottom of the globe. Please don’t turn it counterclockwise, since that will disassemble the globe. One full clockwise turn represents one day. (If you wished to, you could hold the Earth still and turn the celestial sphere. Hence, the daily rotation of the Earth and the appar ...
section 16 powerpoint
... caused by hot bubbles of gas at the Sun’s surface. Spicule. A spikey jet of hot gas from the solar chromosphere erupting into the solar corona. Prominence. Huge gaseous eruptions of arching clouds of ionized particles streaming between sunspots of opposite polarity through the corona. Filament. The ...
... caused by hot bubbles of gas at the Sun’s surface. Spicule. A spikey jet of hot gas from the solar chromosphere erupting into the solar corona. Prominence. Huge gaseous eruptions of arching clouds of ionized particles streaming between sunspots of opposite polarity through the corona. Filament. The ...
The Milky Way - Computer Science Technology
... •How do Earth’s motions affect the appearance of the sky? •What causes the seasons? •How can astronomical cycles affect Earth’s climate? As you study the sky and its motions, you will be thinking of Earth as a planet rotating on its axis and moving in an orbit. ...
... •How do Earth’s motions affect the appearance of the sky? •What causes the seasons? •How can astronomical cycles affect Earth’s climate? As you study the sky and its motions, you will be thinking of Earth as a planet rotating on its axis and moving in an orbit. ...
Chapter 2 User`s Guide to the Sky
... •How do Earth’s motions affect the appearance of the sky? •What causes the seasons? •How can astronomical cycles affect Earth’s climate? As you study the sky and its motions, you will be thinking of Earth as a planet rotating on its axis and moving in an orbit. ...
... •How do Earth’s motions affect the appearance of the sky? •What causes the seasons? •How can astronomical cycles affect Earth’s climate? As you study the sky and its motions, you will be thinking of Earth as a planet rotating on its axis and moving in an orbit. ...
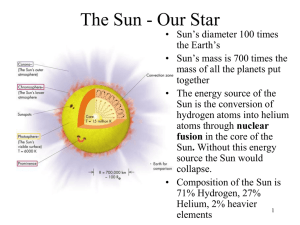
The Sun - Our Star - Academic Computer Center
... The Sun’s Energy Source • The Sun is not burning. If it were burning fuel like coal it would have exhausted its fuel long ago. • The slow collapse of the Sun was once thought to be the energy source but that wouldn’t have lasted more than a few million years. • It wasn’t until the 20th century that ...
... The Sun’s Energy Source • The Sun is not burning. If it were burning fuel like coal it would have exhausted its fuel long ago. • The slow collapse of the Sun was once thought to be the energy source but that wouldn’t have lasted more than a few million years. • It wasn’t until the 20th century that ...
Time
... Century years (or those ending in '00') should only be leap years if divisible by 400. This eliminates three leap years in every four centuries and neatly solves the problem. The result, in the centuries since the reform, is that 1600 and 2000 are normal leap years, but the intervening 1700, 1800 an ...
... Century years (or those ending in '00') should only be leap years if divisible by 400. This eliminates three leap years in every four centuries and neatly solves the problem. The result, in the centuries since the reform, is that 1600 and 2000 are normal leap years, but the intervening 1700, 1800 an ...
Keplerian Motion
... at aphelion • But in same amount of time, same amount of area is covered • This is the law of equal areas • For a circular orbit, the planet would have to move at constant speed at all times ...
... at aphelion • But in same amount of time, same amount of area is covered • This is the law of equal areas • For a circular orbit, the planet would have to move at constant speed at all times ...
Quiz 3
... • If a set of measurements has very high bias, can the set of measurements have a very high accuracy? 1. No. If there is a high bias, then the average of the measurements is far away from the true value. In order to have high accuracy, you need to have all measurements very close to the true value. ...
... • If a set of measurements has very high bias, can the set of measurements have a very high accuracy? 1. No. If there is a high bias, then the average of the measurements is far away from the true value. In order to have high accuracy, you need to have all measurements very close to the true value. ...
celestial clock - the sun, the moon, and the stars
... different spot 0.26° North2 and 1.0° West3 of its starting point the previous day. When it reaches the Tropic of Cancer it reverses its motion and moves 0.26° South but continues advancing 1.0° West. The Sun is only directly overhead at most once a year any place on earth. Outside the band of the Tr ...
... different spot 0.26° North2 and 1.0° West3 of its starting point the previous day. When it reaches the Tropic of Cancer it reverses its motion and moves 0.26° South but continues advancing 1.0° West. The Sun is only directly overhead at most once a year any place on earth. Outside the band of the Tr ...
instructor notes: week 5
... caused by hot bubbles of gas at the Sun’s surface. Spicule. A spikey jet of hot gas from the solar chromosphere erupting into the solar corona. Prominence. Huge gaseous eruptions of arching clouds of ionized particles streaming between sunspots of opposite polarity through the corona. Filament. The ...
... caused by hot bubbles of gas at the Sun’s surface. Spicule. A spikey jet of hot gas from the solar chromosphere erupting into the solar corona. Prominence. Huge gaseous eruptions of arching clouds of ionized particles streaming between sunspots of opposite polarity through the corona. Filament. The ...
Application of Perturbation theory in Classical
... It addresses long-period oscillations in planetary orbits, with a history of more than 200 years. Many of the fundamental questions in celestial mechanics have been answered, some interesting ones remain just beyond the scope of basic secular theory. The recent burst of extrasolar planetary system d ...
... It addresses long-period oscillations in planetary orbits, with a history of more than 200 years. Many of the fundamental questions in celestial mechanics have been answered, some interesting ones remain just beyond the scope of basic secular theory. The recent burst of extrasolar planetary system d ...
Our Sun - LWC Earth Science
... How much of the solar system makes up the sun? – The sun contains 99.8% of the solar systems mass. ...
... How much of the solar system makes up the sun? – The sun contains 99.8% of the solar systems mass. ...
Sun - Midlandstech
... explore the universe in space and time. That quick preview only sets the stage for the drama to come. Now it is time to return to Earth and look closely at the sky. To understand what you are in the universe, you must know where you are. As you look at the sky, you can answer three essential questio ...
... explore the universe in space and time. That quick preview only sets the stage for the drama to come. Now it is time to return to Earth and look closely at the sky. To understand what you are in the universe, you must know where you are. As you look at the sky, you can answer three essential questio ...
The Sun Times
... wind, and solar prominences. Sunspots are magnetic storms on the photosphere which appear as dark areas. Sunspots regularly appear and disappear in eleven year cycles. Sunspots appear darker because they are cooler than the rest of the sun’s surface. Solar flares are spectacular discharges of magnet ...
... wind, and solar prominences. Sunspots are magnetic storms on the photosphere which appear as dark areas. Sunspots regularly appear and disappear in eleven year cycles. Sunspots appear darker because they are cooler than the rest of the sun’s surface. Solar flares are spectacular discharges of magnet ...
Sun - Blackboard
... • How does the sky appear to move as Earth rotates? • What causes the seasons? • How can astronomical cycles affect Earth’s climate? As you study the sky and its motions, you will be learning to think of Earth as a planet rotating on its axis. The next chapter will introduce you to some of the most ...
... • How does the sky appear to move as Earth rotates? • What causes the seasons? • How can astronomical cycles affect Earth’s climate? As you study the sky and its motions, you will be learning to think of Earth as a planet rotating on its axis. The next chapter will introduce you to some of the most ...
Equation of time
The equation of time describes the discrepancy between two kinds of solar time. These are apparent solar time, which directly tracks the motion of the sun, and mean solar time, which tracks a fictitious ""mean"" sun with noons 24 hours apart. Apparent (or true) solar time can be obtained by measurement of the current position (hour angle) of the Sun, or indicated (with limited accuracy) by a sundial. Mean solar time, for the same place, would be the time indicated by a steady clock set so that over the year its differences from apparent solar time average to zero.The equation of time is the east or west component of the analemma, a curve representing the angular offset of the Sun from its mean position on the celestial sphere as viewed from Earth. The equation of time values for each day of the year, compiled by astronomical observatories, were widely listed in almanacs and ephemerides.