Nervous System = communication conduit b/w brain
... This allows action potential to jump from node to node, increasing speed of impulse as it travels length of axon. Some neurons have myelin, some do not Neurons with myelin carry impulses associated with sharp pain. Neurons that lack myelin carry impulses associated with dull, throbbing pain. ...
... This allows action potential to jump from node to node, increasing speed of impulse as it travels length of axon. Some neurons have myelin, some do not Neurons with myelin carry impulses associated with sharp pain. Neurons that lack myelin carry impulses associated with dull, throbbing pain. ...
MECHANISMS OF VERTEBRATE SYNAPTOGENESIS
... neuronal circuitry. For example, shortly after neurons differentiate and extend axonal and dendritic processes, many of the genes encoding synaptic proteins are turned on, resulting in the formation, accumulation, and directional trafficking of vesicles carrying pre- and postsynaptic protein complexe ...
... neuronal circuitry. For example, shortly after neurons differentiate and extend axonal and dendritic processes, many of the genes encoding synaptic proteins are turned on, resulting in the formation, accumulation, and directional trafficking of vesicles carrying pre- and postsynaptic protein complexe ...
nervous system 2012 - Junction Hill C
... coordinates many things that happen in your body. It acts as a central command post, collecting and process information and making sure appropriate information gets sent to all parts of the body. ...
... coordinates many things that happen in your body. It acts as a central command post, collecting and process information and making sure appropriate information gets sent to all parts of the body. ...
A. What is a neuron? 1. A neuron is a type of cell that receives and
... (Nitric oxide is an exception to this rule, as neurons do not store nitric oxide for future use). There is also a substantial amount of neurotransmitter outside the vesicles. 2. When an action potential reaches the axon terminal, the depolarization causes voltage-dependent calcium gates to open. As ...
... (Nitric oxide is an exception to this rule, as neurons do not store nitric oxide for future use). There is also a substantial amount of neurotransmitter outside the vesicles. 2. When an action potential reaches the axon terminal, the depolarization causes voltage-dependent calcium gates to open. As ...
Neuron Unit 3A
... • Terminal buttons turns electrical charge into chemical (neurotransmitter) and shoots message to next neuron across the synapse. ...
... • Terminal buttons turns electrical charge into chemical (neurotransmitter) and shoots message to next neuron across the synapse. ...
Slide ()
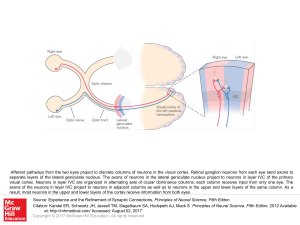
... Afferent pathways from the two eyes project to discrete columns of neurons in the visual cortex. Retinal ganglion neurons from each eye send axons to separate layers of the lateral geniculate nucleus. The axons of neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus project to neurons in layer IVC of the prima ...
... Afferent pathways from the two eyes project to discrete columns of neurons in the visual cortex. Retinal ganglion neurons from each eye send axons to separate layers of the lateral geniculate nucleus. The axons of neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus project to neurons in layer IVC of the prima ...
13. Electrochemical Impulse
... and the action potential moves away from the site of origin. 4. The electrical disturbance moves along the nerve membrane in a wave of depolarization. The membrane is restored, as successive areas once again become more permeable to potassium. The sodium-potassium pump restores and maintains the pol ...
... and the action potential moves away from the site of origin. 4. The electrical disturbance moves along the nerve membrane in a wave of depolarization. The membrane is restored, as successive areas once again become more permeable to potassium. The sodium-potassium pump restores and maintains the pol ...
Nervous Systems - Groupfusion.net
... • Resting potential – membrane potential of unexcited neuron (-70mV) • Neurons become “excited,” when a stimulus opens a gated ion channel and increases the movement of K+ or Na+ across the ...
... • Resting potential – membrane potential of unexcited neuron (-70mV) • Neurons become “excited,” when a stimulus opens a gated ion channel and increases the movement of K+ or Na+ across the ...
A1984SR69800001
... noradrenaline, would have a prominent role in the central nervous system (CNS). Amino acids, with well-identified roles in cellular metabolism, protein synthesis, etc.—and found abundantly throughout the brain—did not fit then current notions about transmitters. By the end of the 1960s, however, in ...
... noradrenaline, would have a prominent role in the central nervous system (CNS). Amino acids, with well-identified roles in cellular metabolism, protein synthesis, etc.—and found abundantly throughout the brain—did not fit then current notions about transmitters. By the end of the 1960s, however, in ...
NERVOUS TISSUE The nervous system consists of all nervous
... outside the CNS. Cranial nerve and dorsal root ganglia (spinal ganglia) are surrounded by a connective tissue capsule, which is continuous with the dorsal root epi- and perineurium. Individual ganglion cells are surrounded by a layer of flattened satellite cells. Neurons in cranial nerve and dorsal ...
... outside the CNS. Cranial nerve and dorsal root ganglia (spinal ganglia) are surrounded by a connective tissue capsule, which is continuous with the dorsal root epi- and perineurium. Individual ganglion cells are surrounded by a layer of flattened satellite cells. Neurons in cranial nerve and dorsal ...
The Nervous System - History with Mr. Bayne
... Transmits messages between the brain and the muscles/glands throughout the body ...
... Transmits messages between the brain and the muscles/glands throughout the body ...
Nerve
... 2. Connective Tissue- provides stability to peripheral nerve 3. Satellite Cells- cuboidal cells that provides peripheral insulation, but does not make myelin 4. Schwann Cells- forms myelin sheath that insulates axon and makes myelin 5. Histocytes- macrophages of the PNS ...
... 2. Connective Tissue- provides stability to peripheral nerve 3. Satellite Cells- cuboidal cells that provides peripheral insulation, but does not make myelin 4. Schwann Cells- forms myelin sheath that insulates axon and makes myelin 5. Histocytes- macrophages of the PNS ...
D. Vertebrate Nervous Systems
... Gated Na+ channels open Na+ diffuses into the cell the membrane potential becomes less negative. The Action Potential: All or Nothing Depolarization. If graded potentials sum to -55mV a threshold potential is achieved. This triggers an action potential. Axons only. In the resting state ...
... Gated Na+ channels open Na+ diffuses into the cell the membrane potential becomes less negative. The Action Potential: All or Nothing Depolarization. If graded potentials sum to -55mV a threshold potential is achieved. This triggers an action potential. Axons only. In the resting state ...
Nervous Systems
... Neurons • Function - conduct messages to help communication between parts of nervous system. • Neurons are helped by numerous supporting cells, which provide structural support, protection, and insulation of neurons. ...
... Neurons • Function - conduct messages to help communication between parts of nervous system. • Neurons are helped by numerous supporting cells, which provide structural support, protection, and insulation of neurons. ...
Drug and Alcohol Abuse
... • We will not talk about electrical properties of neurons too much – What is important is that a cell is “excited” or “inhibited”. – Excited: causes the neighbor neuron to release neurotransmitter to another neuron • When excited, neurons produce “action potentials” • Action potential: electricity, ...
... • We will not talk about electrical properties of neurons too much – What is important is that a cell is “excited” or “inhibited”. – Excited: causes the neighbor neuron to release neurotransmitter to another neuron • When excited, neurons produce “action potentials” • Action potential: electricity, ...
Neurons - Cloudfront.net
... Types of Neurons Different neurons have different functions, and might ...
... Types of Neurons Different neurons have different functions, and might ...
Neurons - Holterman
... 19. Presynaptic is the neuron before the gap, carrying the message. Postsynaptic is the neuron after the gap, receiving and possibly carrying on the message. 20. The dendrite contains vesicles full of chemicals called neurotransmitters. When the action potential (wave of depolarization) reaches the ...
... 19. Presynaptic is the neuron before the gap, carrying the message. Postsynaptic is the neuron after the gap, receiving and possibly carrying on the message. 20. The dendrite contains vesicles full of chemicals called neurotransmitters. When the action potential (wave of depolarization) reaches the ...
Chapter 3 Biological Aspects of Psychology
... Structure of the neuron. Neurons are the communication links of the nervous system. This diagram highlights the key parts of a neuron, including specialized receptor areas (dendrites), the cell body (soma), the fiber along which impulses are transmitted (axon), and the junctions across which chemica ...
... Structure of the neuron. Neurons are the communication links of the nervous system. This diagram highlights the key parts of a neuron, including specialized receptor areas (dendrites), the cell body (soma), the fiber along which impulses are transmitted (axon), and the junctions across which chemica ...
The Nervous System
... the membrane (returns to resting). A neuron cannot conduct another impulse until repolarization occurs. ...
... the membrane (returns to resting). A neuron cannot conduct another impulse until repolarization occurs. ...
SENSORY AND MOTOR SYSTEMS: REFLEXES
... DETECTOR(SENSORY FIBERS) • TYPE Ia NERVE FIBERS: TRANSMIT INFORMATION ABOUT LENGTH AND VELOCITY TO THE CNS • TYPE II NERVE FIBERS:TRANSMIT ...
... DETECTOR(SENSORY FIBERS) • TYPE Ia NERVE FIBERS: TRANSMIT INFORMATION ABOUT LENGTH AND VELOCITY TO THE CNS • TYPE II NERVE FIBERS:TRANSMIT ...
Slide 1
... 1. Neurons are electrically active; They have a resting voltage, and can undergo electrical changes ...
... 1. Neurons are electrically active; They have a resting voltage, and can undergo electrical changes ...
Ocular Dominance Columns
... Early experience and neural development Overview of neuronal development Neuronal survival vs. apoptosis Competition for cortical space The critical period Cortical plasticity in the adult ...
... Early experience and neural development Overview of neuronal development Neuronal survival vs. apoptosis Competition for cortical space The critical period Cortical plasticity in the adult ...
The Nervous System
... • The myelin sheath is made by Oligodendrocytes in the CNS and by Schwann cells in the PNS. • This wrapping is never complete. Interspersed along the axon are gaps where there is no myelin – these are nodes of Ranvier. • In the PNS, the exterior of the Schwann cell surrounding an axon is the neurile ...
... • The myelin sheath is made by Oligodendrocytes in the CNS and by Schwann cells in the PNS. • This wrapping is never complete. Interspersed along the axon are gaps where there is no myelin – these are nodes of Ranvier. • In the PNS, the exterior of the Schwann cell surrounding an axon is the neurile ...