Biological of Behavior
... The neuron that sends a signal across the gap is called the presynaptic neuron. The neuron that receives the signal is called the postsynaptic neuron. ...
... The neuron that sends a signal across the gap is called the presynaptic neuron. The neuron that receives the signal is called the postsynaptic neuron. ...
Autonomic_notes
... by by alpha-1 receptors, whose activation causes blood vessel constriction in skin and viscera (but not in skeletal muscle, which has few alpha receptors). Beta-1 receptors on heart make it beat faster/stronger during same stimuli. Beta-2 receptors cause dilation of bronchioles (helps with increased ...
... by by alpha-1 receptors, whose activation causes blood vessel constriction in skin and viscera (but not in skeletal muscle, which has few alpha receptors). Beta-1 receptors on heart make it beat faster/stronger during same stimuli. Beta-2 receptors cause dilation of bronchioles (helps with increased ...
Prelab 3 Nerve
... trabecular processes. (Hence, name arachnoid, spider). CSF circulates in the spaces between the trabeculae (subarachnoid space). The inner surface of the pia forms a firm interface with a special layer of brain glial cells to form a pial-glial (external limiting) membrane. The large blood vessels of ...
... trabecular processes. (Hence, name arachnoid, spider). CSF circulates in the spaces between the trabeculae (subarachnoid space). The inner surface of the pia forms a firm interface with a special layer of brain glial cells to form a pial-glial (external limiting) membrane. The large blood vessels of ...
מצגת של PowerPoint
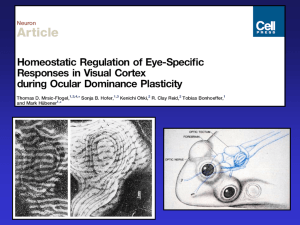
... - The proportion of monocular, deprived-eye neurons, in deprived animals was no different to the proportion of these neurons in controls (supporting prediction ‘a’). - The entire deprived-eye response range of neurons responding predominantly or exclusively to the deprived eye (OD score 0–0.25) was ...
... - The proportion of monocular, deprived-eye neurons, in deprived animals was no different to the proportion of these neurons in controls (supporting prediction ‘a’). - The entire deprived-eye response range of neurons responding predominantly or exclusively to the deprived eye (OD score 0–0.25) was ...
Exam - McLoon Lab
... A. spinal cord ventral horn B. spinal cord dorsal horn C. hypothalamus D. sympathetic ganglion E. More than one of the above are correct. 29. What is the fewest number of synapses possible between a neuron in motor cortex and a ...
... A. spinal cord ventral horn B. spinal cord dorsal horn C. hypothalamus D. sympathetic ganglion E. More than one of the above are correct. 29. What is the fewest number of synapses possible between a neuron in motor cortex and a ...
Anatomy Lecture 3 Descending Motor Tracts In the last lecture the
... alpha and gamma motor neurons below the level of damage (or cut). - Although the lateral corticospinal tract mainly affects the distal muscles, it also could affect the proximal one but less commonly. Suppose we have 1000 fibers in the corticospinal tract, then: - 55% will synapse in the cervical re ...
... alpha and gamma motor neurons below the level of damage (or cut). - Although the lateral corticospinal tract mainly affects the distal muscles, it also could affect the proximal one but less commonly. Suppose we have 1000 fibers in the corticospinal tract, then: - 55% will synapse in the cervical re ...
Scoring Rubric
... Neurons transmit electrical impulses. The myelination of nerve fibers allows for salutatory conduction. Neurons pump sodium and potassium ions across their membranes to generate a resting potential. An action potential consists of depolarization and repolarization of the neuron. Nerve impulses are a ...
... Neurons transmit electrical impulses. The myelination of nerve fibers allows for salutatory conduction. Neurons pump sodium and potassium ions across their membranes to generate a resting potential. An action potential consists of depolarization and repolarization of the neuron. Nerve impulses are a ...
June 20_Neurodevelopment
... These neural precursor cells thicken into the neural plate. The neural plate folds inward to create the neural tube (brain & spinal cord). Neuroblasts will continue to become neurons. The dorsal end of the neural tube contains neural crest cells. The ventral end of the neural tube contains the floor ...
... These neural precursor cells thicken into the neural plate. The neural plate folds inward to create the neural tube (brain & spinal cord). Neuroblasts will continue to become neurons. The dorsal end of the neural tube contains neural crest cells. The ventral end of the neural tube contains the floor ...
Neuroscience01_Introduction
... system, which consists of a nerve cell body, dendrites, and an axon. ...
... system, which consists of a nerve cell body, dendrites, and an axon. ...
Neural Pathways and Transmission
... Ion channels specific for sodium open within the cell membrane, allowing sodium to move into the neuron This causes a very temporary reversal in charges, in which the interior is now positively charged, and the exterior is negatively charged Internal environment is, on average, 30 mV at this state T ...
... Ion channels specific for sodium open within the cell membrane, allowing sodium to move into the neuron This causes a very temporary reversal in charges, in which the interior is now positively charged, and the exterior is negatively charged Internal environment is, on average, 30 mV at this state T ...
Iliopsoas Muscle Injury
... Your pet has been examined for an acute or chronic lameness of the rear leg and an injury to the iliopsoas muscle is a possible diagnosis based upon physical examination findings. Muscle strains in dogs, like people, can be graded from mild sprains (grade I), grade II with hematoma (blood clot) form ...
... Your pet has been examined for an acute or chronic lameness of the rear leg and an injury to the iliopsoas muscle is a possible diagnosis based upon physical examination findings. Muscle strains in dogs, like people, can be graded from mild sprains (grade I), grade II with hematoma (blood clot) form ...
Prenatal Central Nervous System Development
... Prenatal CNS Development To help conceptualize fetal CNS development, Nowakowski and Hayes (1999) metaphorically link the development of the CNS to the construction of a house. In the same way that a blueprint guides house construction, an individual’s genome serves as a blueprint for the brain. Som ...
... Prenatal CNS Development To help conceptualize fetal CNS development, Nowakowski and Hayes (1999) metaphorically link the development of the CNS to the construction of a house. In the same way that a blueprint guides house construction, an individual’s genome serves as a blueprint for the brain. Som ...
Chapter_15_Teacher_Notes
... a) Periosteum – tough, tight fitting membrane that covers a bone’s surface b) Compact Bone c) Spongy Bone d) Marrow in cavities of long bones 2. Cartilage – a smooth, slippery, thick layer at the ends of bones that acts as a ...
... a) Periosteum – tough, tight fitting membrane that covers a bone’s surface b) Compact Bone c) Spongy Bone d) Marrow in cavities of long bones 2. Cartilage – a smooth, slippery, thick layer at the ends of bones that acts as a ...
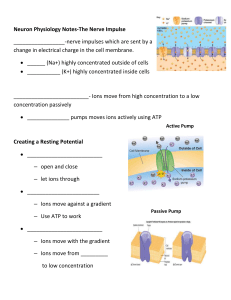
Neuron Physiology Notes
... _________________________- Ions move from high concentration to a low concentration passively ______________ pumps moves ions actively using ATP Active Pump ...
... _________________________- Ions move from high concentration to a low concentration passively ______________ pumps moves ions actively using ATP Active Pump ...
Anatomy and Physiology of the Retina
... Inner plexiform layer (IPL): contains the synapses made between bipolar, amacrine and ganglion cells. The thickness of this layer varies considerably across species, where "simpler" organisms (such as frogs, pigeons and squirrels, for example) possess thicker IPL's than "higher" organisms like prima ...
... Inner plexiform layer (IPL): contains the synapses made between bipolar, amacrine and ganglion cells. The thickness of this layer varies considerably across species, where "simpler" organisms (such as frogs, pigeons and squirrels, for example) possess thicker IPL's than "higher" organisms like prima ...
Anti-SLC30A3 antibody ab102611 Product datasheet 1 Abreviews 1 Image
... Replacement or refund for products not performing as stated on the datasheet Valid for 12 months from date of delivery Response to your inquiry within 24 hours We provide support in Chinese, English, French, German, Japanese and Spanish Extensive multi-media technical resources to help you We invest ...
... Replacement or refund for products not performing as stated on the datasheet Valid for 12 months from date of delivery Response to your inquiry within 24 hours We provide support in Chinese, English, French, German, Japanese and Spanish Extensive multi-media technical resources to help you We invest ...
Unit 1: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium (II) The Nervous System
... Neurons are the structural and functional unit of the nervous system. Neurons are cells that send and receive electro-chemical signals to and from the brain and nervous system. There are about 100 billion neurons in the brain. Unlike most other cells, neurons cannot regrow after damage. Fortunately, ...
... Neurons are the structural and functional unit of the nervous system. Neurons are cells that send and receive electro-chemical signals to and from the brain and nervous system. There are about 100 billion neurons in the brain. Unlike most other cells, neurons cannot regrow after damage. Fortunately, ...
Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
... – Stimuli originating either inside or outside of the body must be detected by sensory receptors and converted into action potentials, which are propagated to the CNS by nerves. – Within the CNS, nerve tracts convey action potentials to the cerebral cortex and to other areas of the CNS. – Action pot ...
... – Stimuli originating either inside or outside of the body must be detected by sensory receptors and converted into action potentials, which are propagated to the CNS by nerves. – Within the CNS, nerve tracts convey action potentials to the cerebral cortex and to other areas of the CNS. – Action pot ...
Self Assessment Chapter 11 - CM
... • Pseudounipolar neurons – have only one fused axon that extends from cell body and divides into two processes: one process carries sensory information from sensory receptors to cell body; other process carries sensory information from cell body to spinal cord; sensory neurons that carry information ...
... • Pseudounipolar neurons – have only one fused axon that extends from cell body and divides into two processes: one process carries sensory information from sensory receptors to cell body; other process carries sensory information from cell body to spinal cord; sensory neurons that carry information ...
Nervous System Lecture- Part II
... Each region of the sensory cortex corresponds to a body regions. The amount of cortical space dedicated to that body region is proportional to the number of sensory receptors located in that body region. This is the sensory homunculus Motor Homunculus Corticospinal pathway provides voluntary control ...
... Each region of the sensory cortex corresponds to a body regions. The amount of cortical space dedicated to that body region is proportional to the number of sensory receptors located in that body region. This is the sensory homunculus Motor Homunculus Corticospinal pathway provides voluntary control ...
Nerves, Muscles and how they work
... • They are efferent/afferent neurons which control voluntary muscle. • Voluntary muscle is also known as……muscle and looks………under the microscope. • Is a motor neuron a fast or slow transmitter? ...
... • They are efferent/afferent neurons which control voluntary muscle. • Voluntary muscle is also known as……muscle and looks………under the microscope. • Is a motor neuron a fast or slow transmitter? ...
Upper and Lower Motor Neuron Lesions
... • Result from spontaneous generation of action potential (injury potentials) in distal segment of the injured axon ...
... • Result from spontaneous generation of action potential (injury potentials) in distal segment of the injured axon ...
Lecture6 - Part 1 ANS student (2012).
... exit the CNS from the thoracic + lumbar segments of the spinal cord Therefore , the sympathetic system is also called : “ Thoraco-lumbar Outflow “ Preganglionic Parasympathetic nerves exit the CNS from the Cranium ( skull ) +sacral segments of the spinal cord Therefore , the Parasympathetic syst ...
... exit the CNS from the thoracic + lumbar segments of the spinal cord Therefore , the sympathetic system is also called : “ Thoraco-lumbar Outflow “ Preganglionic Parasympathetic nerves exit the CNS from the Cranium ( skull ) +sacral segments of the spinal cord Therefore , the Parasympathetic syst ...