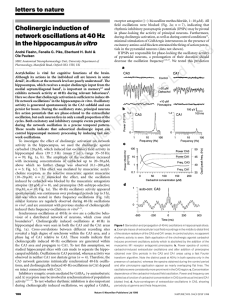
Cholinergic induction of network oscillations at 40 Hz in the
... We next determined whether glutamatergic excitatory mechanisms are necessary for the emergent population oscillation. Metabotropic glutamate receptors are not necessary, because the receptor antagonist (S)-a-methyl-4-carboxyphenylglycine (MCPG, 200– 500 mM; n ¼ 6; Fig. 2c) failed to block carbachol- ...
... We next determined whether glutamatergic excitatory mechanisms are necessary for the emergent population oscillation. Metabotropic glutamate receptors are not necessary, because the receptor antagonist (S)-a-methyl-4-carboxyphenylglycine (MCPG, 200– 500 mM; n ¼ 6; Fig. 2c) failed to block carbachol- ...
PDF
... fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), which is an intermediate filament (IF) protein belonging to the type III subclass of IF proteins, reacts with a single band of 52 kDa on immunoblotting [19]. The antibody used here showed a typical immunostaing pattern for astroglial cells, comparable to that descri ...
... fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), which is an intermediate filament (IF) protein belonging to the type III subclass of IF proteins, reacts with a single band of 52 kDa on immunoblotting [19]. The antibody used here showed a typical immunostaing pattern for astroglial cells, comparable to that descri ...
Case Study 29 - University of Pittsburgh
... Axonal swellings can also be seen in metabolic disorders (e.g. Nieman-Pick disease) and nutritional deficiencies (vitamin E deficiency) ...
... Axonal swellings can also be seen in metabolic disorders (e.g. Nieman-Pick disease) and nutritional deficiencies (vitamin E deficiency) ...
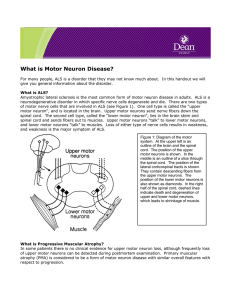
What is Motor Neuron
... not develop. PLS has a slower course of progression. What is Progressive Bulbar Palsy? Progressive bulbar palsy refers to patients who initially have only upper motor weakness that affect speech and swallowing. However, these patients almost always progress to have ALS with with weakness of limb mus ...
... not develop. PLS has a slower course of progression. What is Progressive Bulbar Palsy? Progressive bulbar palsy refers to patients who initially have only upper motor weakness that affect speech and swallowing. However, these patients almost always progress to have ALS with with weakness of limb mus ...
08 Electrophysiology of muscles
... In cardiac muscle cells some (10 -20%) of extracellular calcium is required for contraction. This calcium enters through voltage dependent calcium channels known as L (Long lasting) channels or sometimes referred to as slow calcium channels. The 10 -20% of calcium coming from the outside of the cell ...
... In cardiac muscle cells some (10 -20%) of extracellular calcium is required for contraction. This calcium enters through voltage dependent calcium channels known as L (Long lasting) channels or sometimes referred to as slow calcium channels. The 10 -20% of calcium coming from the outside of the cell ...
Neurotransmitters - AC Reynolds High
... The nervous system originates from the neural tube and neural crest The neural tube becomes the CNS There is a three-phase process of differentiation: Proliferation of cells needed for development ...
... The nervous system originates from the neural tube and neural crest The neural tube becomes the CNS There is a three-phase process of differentiation: Proliferation of cells needed for development ...
Cellular-synaptic generation of EEG activity
... extracellular space. Until recently, synaptic activity has been viewed as the exclusive source of extracellular current flow or EEG. As will be discussed below, however, synaptic activity is only one of the several membrane voltage changes that contributes to the measured field potential. Progress d ...
... extracellular space. Until recently, synaptic activity has been viewed as the exclusive source of extracellular current flow or EEG. As will be discussed below, however, synaptic activity is only one of the several membrane voltage changes that contributes to the measured field potential. Progress d ...
Structure of the central nervous system of a juvenile acoel
... using immunochemical tools, suggest that the nervous system in Acoela is organized as a commissural brain that bears little resemblance to the central, ganglionic type brain of other flatworms, and bilaterians in general. Others, who used histological staining on paraffin sections, conclude that it ...
... using immunochemical tools, suggest that the nervous system in Acoela is organized as a commissural brain that bears little resemblance to the central, ganglionic type brain of other flatworms, and bilaterians in general. Others, who used histological staining on paraffin sections, conclude that it ...
Slide 1
... • 1st order neuron axons terminate at the base of post gray column (nucleus dorsalis) • the majority of axons of 2nd order neurons cross to opposite side and ascend as anterior spinocerebellar tract in the contralateral white column the minority of axons ascend as anterior spinocerebellar tract in ...
... • 1st order neuron axons terminate at the base of post gray column (nucleus dorsalis) • the majority of axons of 2nd order neurons cross to opposite side and ascend as anterior spinocerebellar tract in the contralateral white column the minority of axons ascend as anterior spinocerebellar tract in ...
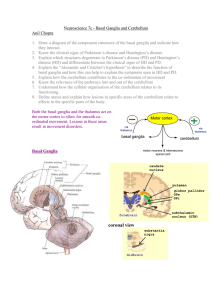
Neuroscience 7c – Basal Ganglia and Cerebellum
... thought you were going to do (according to the motor cortex) with what you are actually about to do (according to proprioceptive feedback). The Basic Circuit is the same in all parts of the cerebellum and has 3 parts to it: » Direct path – input projects directly to motor systems via deep cerebellar ...
... thought you were going to do (according to the motor cortex) with what you are actually about to do (according to proprioceptive feedback). The Basic Circuit is the same in all parts of the cerebellum and has 3 parts to it: » Direct path – input projects directly to motor systems via deep cerebellar ...
Module 4 SG - HallquistCPHS.com
... (positively /negatively) charged ions, while the fluid outside has mostly _ (positively /negatively) charged ions. This polarization, called the _ , occurs because the cell membrane is ~~~~~~~ ...
... (positively /negatively) charged ions, while the fluid outside has mostly _ (positively /negatively) charged ions. This polarization, called the _ , occurs because the cell membrane is ~~~~~~~ ...
Molecular mechanisms of growth cone guidance
... cone discriminate between target and non-target cells? What are the receptors on the growth cone membrane responsible for the recognition of environmental signals, Correspondence to: E.T. Stoeckli (Tel.: +41 61 267 3490; Fax: +41 61 267 3457; E-mail: [email protected])&/fn-block: ...
... cone discriminate between target and non-target cells? What are the receptors on the growth cone membrane responsible for the recognition of environmental signals, Correspondence to: E.T. Stoeckli (Tel.: +41 61 267 3490; Fax: +41 61 267 3457; E-mail: [email protected])&/fn-block: ...
Can regenerating axons recapitulate developmental
... the neural pathway1,2. Basic fibroblast growth factors (bFGFs) and WNT proteins stimulate differentiation into anterior neural structures, whereas retinoids stimulate posterior neural fates 3–6. In the developing spinal cord, the floor plate and nearby notochord secrete sonic hedgehog (SHH), which s ...
... the neural pathway1,2. Basic fibroblast growth factors (bFGFs) and WNT proteins stimulate differentiation into anterior neural structures, whereas retinoids stimulate posterior neural fates 3–6. In the developing spinal cord, the floor plate and nearby notochord secrete sonic hedgehog (SHH), which s ...
Presentation materials - Brain Dynamics Laboratory
... ISIs form the first mode while quiescent periods correspond to the longer ISIs of the second mode. • This is true for intrinsic or forced (stimulus driven and network-induced) bursting. Furthermore, the trough between the two modes may correspond to the refractory period of an intrinsic burst or the ...
... ISIs form the first mode while quiescent periods correspond to the longer ISIs of the second mode. • This is true for intrinsic or forced (stimulus driven and network-induced) bursting. Furthermore, the trough between the two modes may correspond to the refractory period of an intrinsic burst or the ...
Spike Timing-Dependent Plasticity: From Synapse to Perception
... efficiency of the spike-timing protocol in long-term modification of excitatory synapses in hippocampal cultures (13) and midbrain slices (60). The NMDARs are largely blocked by Mg2⫹ at hyperpolarized membrane potentials, but the block can be relieved by depolarization (69, 83), leading to the idea ...
... efficiency of the spike-timing protocol in long-term modification of excitatory synapses in hippocampal cultures (13) and midbrain slices (60). The NMDARs are largely blocked by Mg2⫹ at hyperpolarized membrane potentials, but the block can be relieved by depolarization (69, 83), leading to the idea ...
P2 Receptor Antagonist Trinitrophenyl-Adenosine
... Both P2X and P2Y receptors are ubiquitously expressed in the CNS and PNS (Kucher and Neary, 2005). In particular, the P2X1 receptor is present on astrocytes of juvenile rats (Kukley et al., 2001), on rat cerebellar granule neurons (Amadio et al., 2002), and on purified synaptosome from rat hippocamp ...
... Both P2X and P2Y receptors are ubiquitously expressed in the CNS and PNS (Kucher and Neary, 2005). In particular, the P2X1 receptor is present on astrocytes of juvenile rats (Kukley et al., 2001), on rat cerebellar granule neurons (Amadio et al., 2002), and on purified synaptosome from rat hippocamp ...
Nerves and Special Senses
... • If the action potential (nerve impulse) starts, it is propagated over the entire axon • Potassium ions rush out of the neuron after sodium ions rush in, which repolarizes the membrane • The sodium-potassium pump restores the original configuration – This action requires ATP ...
... • If the action potential (nerve impulse) starts, it is propagated over the entire axon • Potassium ions rush out of the neuron after sodium ions rush in, which repolarizes the membrane • The sodium-potassium pump restores the original configuration – This action requires ATP ...
A channel to neurodegeneration
... lives or dies. The work may also open the door neurons triggers cell death. This finding runs for new therapeutic strategies aimed at slowing counter to prevailing notions that neurodegeneration is associated with hyper- rather the progression of Parkinson disease. If KATP channels govern differenti ...
... lives or dies. The work may also open the door neurons triggers cell death. This finding runs for new therapeutic strategies aimed at slowing counter to prevailing notions that neurodegeneration is associated with hyper- rather the progression of Parkinson disease. If KATP channels govern differenti ...
Introductory Psychology Concepts
... System (CNS) • Composed of the brain and spinal cord. • Spinal cord is the primary means for transmitting messages between the brain and the rest of the body. © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. ...
... System (CNS) • Composed of the brain and spinal cord. • Spinal cord is the primary means for transmitting messages between the brain and the rest of the body. © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. ...
Where is the proprioception first processed? Thalamus vs. Cerebellum
... • They are highly sensitive to the small perturbation after steady position (or after adaptation period). (neurons with sustained response in MCN, which encodes muscle extension, do not project to cerebellum.) ...
... • They are highly sensitive to the small perturbation after steady position (or after adaptation period). (neurons with sustained response in MCN, which encodes muscle extension, do not project to cerebellum.) ...
Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal
... • Describe the two major groups of receptors and their subtypes (and their usual ligands.) • Distinguish between receptor stimulation and cell stimulation. ...
... • Describe the two major groups of receptors and their subtypes (and their usual ligands.) • Distinguish between receptor stimulation and cell stimulation. ...
Lab Activity 14 - Portland Community College
... 1. Receptor – site of stimulus 2. Sensory neuron – transmits the afferent impulse to the CNS 3. Integration center – either monosynaptic or polysynaptic region within the CNS 4. Motor neuron – conducts efferent impulses from the integration center to an effector 5. Effector – muscle fiber or gland t ...
... 1. Receptor – site of stimulus 2. Sensory neuron – transmits the afferent impulse to the CNS 3. Integration center – either monosynaptic or polysynaptic region within the CNS 4. Motor neuron – conducts efferent impulses from the integration center to an effector 5. Effector – muscle fiber or gland t ...
Perception Spike Timing-Dependent Plasticity: From Synapse to
... described by a small number of parameters, and the dependence of synaptic modification on these parameters (e.g., pre/post spike interval) can be easily determined. For neural circuits in vivo, however, spiking in both preand postsynaptic cells is likely to be irregular (98), with occasional high-fr ...
... described by a small number of parameters, and the dependence of synaptic modification on these parameters (e.g., pre/post spike interval) can be easily determined. For neural circuits in vivo, however, spiking in both preand postsynaptic cells is likely to be irregular (98), with occasional high-fr ...
A part of the cholinergic fibers in mouse superior cervical ganglia
... GABAergic boutons only. We found that about half of the GABA-immunopositive fibers were also immunopositive for nNOS (Fig. 2). Although the majority of the GAD65-immunopositive boutons encircled large NPY-immunonegative postganglionic neurons (Fig. 3a), as previously reported in a rat study using th ...
... GABAergic boutons only. We found that about half of the GABA-immunopositive fibers were also immunopositive for nNOS (Fig. 2). Although the majority of the GAD65-immunopositive boutons encircled large NPY-immunonegative postganglionic neurons (Fig. 3a), as previously reported in a rat study using th ...
Introduction to Psychology - Shoreline School District
... Reflex a simple, automatic, inborn response to a sensory stimulus Brain Sensory neuron (incoming information) ...
... Reflex a simple, automatic, inborn response to a sensory stimulus Brain Sensory neuron (incoming information) ...