slides
... monkey. Several axon collaterals branch off the descending axon near the dendritic tree and in three other clusters (arrows), The clustered collaterals project vertically into several layers at regular intervals, consistent with the sequence of functional columns of cells. B). The horizontal connect ...
... monkey. Several axon collaterals branch off the descending axon near the dendritic tree and in three other clusters (arrows), The clustered collaterals project vertically into several layers at regular intervals, consistent with the sequence of functional columns of cells. B). The horizontal connect ...
Yuste-Banbury-2006 - The Swartz Foundation
... exclusively on voltage-gated Ca2+ channels, almost all of the NMDA-induced Ca2+ influx was via the NMDA ionophore itself, rather than through voltage-gated Ca2+ channels. Glutamate itself altered [Ca2+]i almost exclusively via the NMDA receptor. Furthermore, synaptically induced Ca2+ entry relied al ...
... exclusively on voltage-gated Ca2+ channels, almost all of the NMDA-induced Ca2+ influx was via the NMDA ionophore itself, rather than through voltage-gated Ca2+ channels. Glutamate itself altered [Ca2+]i almost exclusively via the NMDA receptor. Furthermore, synaptically induced Ca2+ entry relied al ...
PDF only
... One of the hallmarks of cerebellar Purkinje cells is their ability to express a characteristic form of activity-dependent synaptic plasticity named long-term depression (LTD) which is essential for motor learning. The cerebellum is the brain region where learned movements are stored and LTD is a key ...
... One of the hallmarks of cerebellar Purkinje cells is their ability to express a characteristic form of activity-dependent synaptic plasticity named long-term depression (LTD) which is essential for motor learning. The cerebellum is the brain region where learned movements are stored and LTD is a key ...
spiking neuron models - Assets - Cambridge
... in the vertebrate brain is a chemical synapse. At a chemical synapse, the axon terminal comes very close to the postsynaptic neuron, leaving only a tiny gap between pre- and postsynaptic cell membranes, called the synaptic cleft. When an action potential arrives at a synapse, it triggers a complex c ...
... in the vertebrate brain is a chemical synapse. At a chemical synapse, the axon terminal comes very close to the postsynaptic neuron, leaving only a tiny gap between pre- and postsynaptic cell membranes, called the synaptic cleft. When an action potential arrives at a synapse, it triggers a complex c ...
Reelin and apolipoprotein E receptor 2 in the embryonic and mature
... 348 N. B. Myant Review. Reelin and apoE receptor 2 It is difficult to envisage a guidance system for cortical layering that does not include signals arising from the extracellular environment, as well as those arising from within the cell itself. 5. REELIN AND APOLIPOPROTEIN E RECEPTOR 2 IN THE ADUL ...
... 348 N. B. Myant Review. Reelin and apoE receptor 2 It is difficult to envisage a guidance system for cortical layering that does not include signals arising from the extracellular environment, as well as those arising from within the cell itself. 5. REELIN AND APOLIPOPROTEIN E RECEPTOR 2 IN THE ADUL ...
File
... ____ 13. Use the graph above to answer the next question. During which indicated period is depolarization occurring? a. A b. B c. C d. D ____ 14. Use the graph above to answer the next question. During which indicated interval do potassium ions rapidly exit the axoplasm? a. A b. B c. C d. D ____ 15 ...
... ____ 13. Use the graph above to answer the next question. During which indicated period is depolarization occurring? a. A b. B c. C d. D ____ 14. Use the graph above to answer the next question. During which indicated interval do potassium ions rapidly exit the axoplasm? a. A b. B c. C d. D ____ 15 ...
BIOGRAPHICAL SKETCH David A. Prince PRINCE
... The major aim is to develop strategies to prevent posttraumatic epilepsy with gabapentin, BDNF activation or other molecules. Role: PI Completed Research Support: 2 P50 NS12151-36 NIH/NINDS Epilepsy Research Program: Project I ...
... The major aim is to develop strategies to prevent posttraumatic epilepsy with gabapentin, BDNF activation or other molecules. Role: PI Completed Research Support: 2 P50 NS12151-36 NIH/NINDS Epilepsy Research Program: Project I ...
More than just synaptic building blocks: scaffolding proteins of the
... facilitating transport of larger macromolecular complexes. Although much remains to be discovered in regards to this novel role, it is now evident that synaptic scaffolding proteins have a much broader role in neuronal biology than previously assumed. In this review, we will summarize the data surro ...
... facilitating transport of larger macromolecular complexes. Although much remains to be discovered in regards to this novel role, it is now evident that synaptic scaffolding proteins have a much broader role in neuronal biology than previously assumed. In this review, we will summarize the data surro ...
Ch 48 49 Notes - Dublin City Schools
... • Most neurons are protected, nourished, or insulated by cells called glia – Outnumber neurons by as many as 50 to 1 • Glia have numerous functions – Ependymal cells promote circulation of cerebrospinal fluid – Microglia protect the nervous system from microorganisms – Oligodendrocytes and Schwann c ...
... • Most neurons are protected, nourished, or insulated by cells called glia – Outnumber neurons by as many as 50 to 1 • Glia have numerous functions – Ependymal cells promote circulation of cerebrospinal fluid – Microglia protect the nervous system from microorganisms – Oligodendrocytes and Schwann c ...
Review Mitochondrial movement and positioning in axons
... experimentally induced elongation of axons in the absence The extreme length of axonal processes requires that of an active growth cone, implying that signals from the aerobic ATP production and Ca2+ homeostasis are nonactive growth cone regulate transport. To determine the uniformly organized in th ...
... experimentally induced elongation of axons in the absence The extreme length of axonal processes requires that of an active growth cone, implying that signals from the aerobic ATP production and Ca2+ homeostasis are nonactive growth cone regulate transport. To determine the uniformly organized in th ...
Motor Systems - Neuroanatomy
... The control of voluntary movements is complex. Many different systems across numerous brain areas need to work together to ensure proper motor control. We will start a journey through these areas, beginning at the spinal cord and progressing up the brain stem and eventually reaching the cerebral cor ...
... The control of voluntary movements is complex. Many different systems across numerous brain areas need to work together to ensure proper motor control. We will start a journey through these areas, beginning at the spinal cord and progressing up the brain stem and eventually reaching the cerebral cor ...
Basic functional neuroanatomy
... the brain. The largest choroid plexuses are those of the lateral ventricles. Choroid plexus is a richly vascular tissue in which permeable capillary blood vessels are enclosed in a secretory epithelium. CSF leaves the ventricular system by way of three holes in the roof of the fourth ventricle. The ...
... the brain. The largest choroid plexuses are those of the lateral ventricles. Choroid plexus is a richly vascular tissue in which permeable capillary blood vessels are enclosed in a secretory epithelium. CSF leaves the ventricular system by way of three holes in the roof of the fourth ventricle. The ...
Axons
... • Communication is very rapid, and may be unidirectional or bidirectional • Are important in: • Embryonic nervous tissue ...
... • Communication is very rapid, and may be unidirectional or bidirectional • Are important in: • Embryonic nervous tissue ...
17_QuizShowQuestions
... neuron in the CNS innervates a second neuron located in a peripheral ganglion. b. Visceral motor neurons in the CNS, known as postganglionic neurons, send their axons, known as postganglionic fibers, to synapse on ganglionic neurons. c. The cell bodies of ganglionic neurons are located in autonomic ...
... neuron in the CNS innervates a second neuron located in a peripheral ganglion. b. Visceral motor neurons in the CNS, known as postganglionic neurons, send their axons, known as postganglionic fibers, to synapse on ganglionic neurons. c. The cell bodies of ganglionic neurons are located in autonomic ...
A Functional Role for Intra-Axonal Protein Synthesis during Axonal
... that are conditioned by axonal crush can rapidly extend processes in vitro by regulating the translation of existing mRNAs (Twiss et al., 2000). These regenerating processes contain axonal but not dendritic proteins. Here we show that these axonal processes of adult sensory neurons cultured after co ...
... that are conditioned by axonal crush can rapidly extend processes in vitro by regulating the translation of existing mRNAs (Twiss et al., 2000). These regenerating processes contain axonal but not dendritic proteins. Here we show that these axonal processes of adult sensory neurons cultured after co ...
Got diversity? Wiring the fly brain with Dscam
... These isoforms include 19 008 different ectodomains joined to one of two alternative transmembrane segments. Each ectodomain comprises a unique combination of three variable immunoglobulin domains. Biochemical studies support a model in which each isoform preferentially binds to the same isoform on ...
... These isoforms include 19 008 different ectodomains joined to one of two alternative transmembrane segments. Each ectodomain comprises a unique combination of three variable immunoglobulin domains. Biochemical studies support a model in which each isoform preferentially binds to the same isoform on ...
Posterior Pituitary
... Posterior Pituitary The posterior pituitary is significantly different in structure and function from the anterior pituitary. As its name implies, the posterior pituitary is behind the anterior pituitary (toward the back). It contains mostly axons of secretory neurons and neuroglia cells; the cell b ...
... Posterior Pituitary The posterior pituitary is significantly different in structure and function from the anterior pituitary. As its name implies, the posterior pituitary is behind the anterior pituitary (toward the back). It contains mostly axons of secretory neurons and neuroglia cells; the cell b ...
Ascending tracts
... Each column (funiculus) contains either Ascending (sensory) Descending (motor) ...
... Each column (funiculus) contains either Ascending (sensory) Descending (motor) ...
[10] P. Paul, J de Belleroche, The role of D-amino acids in
... essential for operation of the NMDA receptor and differentially regulate receptor function. It ...
... essential for operation of the NMDA receptor and differentially regulate receptor function. It ...
Redalyc.Normal neuronal migration
... to form the first cortical layer or preplate. The subsequent developing cortical plate is formed within the preplate and divides this layer and its neuronal population into a superficial zone, named the marginal zone, and a deep, lower zone called the subplate. 4 As additional waves migrating neuron ...
... to form the first cortical layer or preplate. The subsequent developing cortical plate is formed within the preplate and divides this layer and its neuronal population into a superficial zone, named the marginal zone, and a deep, lower zone called the subplate. 4 As additional waves migrating neuron ...
Spinal Cord and reflexes lab
... Thoracic Nerves • Not associated with a plexus. • Many exit through the intervertebral foramina of the vertebral column and innervate the ribs, muscles and other structures of the thoracic wall ...
... Thoracic Nerves • Not associated with a plexus. • Many exit through the intervertebral foramina of the vertebral column and innervate the ribs, muscles and other structures of the thoracic wall ...
Copyrighted Material
... of regeneration. This process proceeds through a sequence of changes involving the distal axon, ensheathing glial cells and the blood nerve barrier. Initially there is a period during which the distal stump survives and maintains relatively normal structural, transport, and conduction properties. Th ...
... of regeneration. This process proceeds through a sequence of changes involving the distal axon, ensheathing glial cells and the blood nerve barrier. Initially there is a period during which the distal stump survives and maintains relatively normal structural, transport, and conduction properties. Th ...
Changes in spinal cord
... *leads to initial flaccid paralysis *later patients will develop spastic paralysis & inappropriate reflexes -damage to ventral tracts does not usu. present as severely, have some loss of function from level of damage down- ipsilateral AND contralateral *why does this not have as much effect as later ...
... *leads to initial flaccid paralysis *later patients will develop spastic paralysis & inappropriate reflexes -damage to ventral tracts does not usu. present as severely, have some loss of function from level of damage down- ipsilateral AND contralateral *why does this not have as much effect as later ...
PDF file - University of Kentucky
... Monitoring the force skeletal muscles exert is an intricate and complicated task as there are unique morphological arrangements, such as, various pinnate and fusiform structures of muscle fibers. Also, muscles in different developmental stages generate various force and some are capable of producing ...
... Monitoring the force skeletal muscles exert is an intricate and complicated task as there are unique morphological arrangements, such as, various pinnate and fusiform structures of muscle fibers. Also, muscles in different developmental stages generate various force and some are capable of producing ...
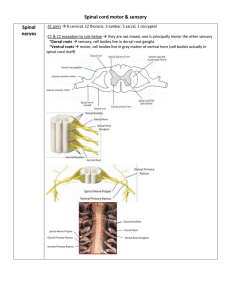
1 Principles of structure and functioning of nervous system
... preservation of the brain motor systems is an important term of accidental moves of a person. Motor system abnormalities happen in the damage of nervous system by many different factors and represent great importance for the diagnostics of the nosologic form of a disease. Motor abnormalities represe ...
... preservation of the brain motor systems is an important term of accidental moves of a person. Motor system abnormalities happen in the damage of nervous system by many different factors and represent great importance for the diagnostics of the nosologic form of a disease. Motor abnormalities represe ...
















![[10] P. Paul, J de Belleroche, The role of D-amino acids in](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/022394228_1-c70b74890df8cd7f8a841431fb6562f6-300x300.png)