Introduction to Antibacterial Therapy
... Can’t do MIC without culture (at reference lab only) FQ resistance 13% in 2011 – FQ not recommended for empiric Rx since 2007 ...
... Can’t do MIC without culture (at reference lab only) FQ resistance 13% in 2011 – FQ not recommended for empiric Rx since 2007 ...
Specimen and Collection Transport - IP Col-lab
... Collect a sufficient volume of specimen to ensure that all tests requested may be performed. Inadequate amounts of specimen may yield false-negative results. • Label specimens properly with patient’s name and identification number, source, specific site, date, time of collection, and initials of co ...
... Collect a sufficient volume of specimen to ensure that all tests requested may be performed. Inadequate amounts of specimen may yield false-negative results. • Label specimens properly with patient’s name and identification number, source, specific site, date, time of collection, and initials of co ...
Problems caused by biofilms
... Biofilms will form on critical locations in processing plants in the food and beverage industries, where nutrients are available and where cleaning and disinfection are inadequate. Formation of biofilms can lead to a number of problems such as product spoilage, food safety problems, and loss of prod ...
... Biofilms will form on critical locations in processing plants in the food and beverage industries, where nutrients are available and where cleaning and disinfection are inadequate. Formation of biofilms can lead to a number of problems such as product spoilage, food safety problems, and loss of prod ...
Some effects of Fluoride on the IgA Protease of the Oral Bacterium
... Streptucuccus sanguis is quantitatively one of the most important bacteria of the tooth surface environment. The 1gA protease activity of this organism is believed to reduce susceptibility to the host mucosal defence mechanisms and may also benefit other bacteria colonising the same local microenvir ...
... Streptucuccus sanguis is quantitatively one of the most important bacteria of the tooth surface environment. The 1gA protease activity of this organism is believed to reduce susceptibility to the host mucosal defence mechanisms and may also benefit other bacteria colonising the same local microenvir ...
O A RIGINAL RTICLE
... bacteriostatic effects of essential oil and solvent extracts compounds of the plants under study on Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria Pseudomonas aeroginosa, Klebsiella pneumonia, Proteus vulgaris, Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus are presented in Table 1. Effectively The ethyl acetate ...
... bacteriostatic effects of essential oil and solvent extracts compounds of the plants under study on Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria Pseudomonas aeroginosa, Klebsiella pneumonia, Proteus vulgaris, Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus are presented in Table 1. Effectively The ethyl acetate ...
Nitrogen fixation in microbial biotechnology
... Nitrogen fixation in cereal crops http://www.producer.com/2014/04/the-search-for-the -holy-grail-nitrogen-fixation-in-cereal-crops/ This article discusses efforts to effectively use microbial nitrogen fixation to boost the growth of cereal crops ...
... Nitrogen fixation in cereal crops http://www.producer.com/2014/04/the-search-for-the -holy-grail-nitrogen-fixation-in-cereal-crops/ This article discusses efforts to effectively use microbial nitrogen fixation to boost the growth of cereal crops ...
Intervention, integration and translation in obesity research: Genetic
... tissue both subcutaneously and around organs, with differential health effects [2]. Obesity is a difficult term to define. It refers to excessive and unhealthy amounts of fat (rather than body weight per se), and is measured by a variety of means, all of which have practical and theoretical problems ...
... tissue both subcutaneously and around organs, with differential health effects [2]. Obesity is a difficult term to define. It refers to excessive and unhealthy amounts of fat (rather than body weight per se), and is measured by a variety of means, all of which have practical and theoretical problems ...
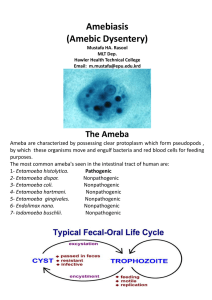
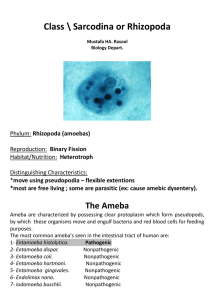
Entamoeba histolytica
... cyst which contaminated food, drinks and also by hand to mouth contact. Then pass through the stomach , as the cyst wall is resistant to gastric juice. - In the intestine excystation takes place. - Trophozoit being actively motile invade the tissue of the submucous layer of ...
... cyst which contaminated food, drinks and also by hand to mouth contact. Then pass through the stomach , as the cyst wall is resistant to gastric juice. - In the intestine excystation takes place. - Trophozoit being actively motile invade the tissue of the submucous layer of ...
Bacterial rheotaxis
... where the shear rate S was varied between 0 and 36 s−1. Celltracking software yielded the bacteria’s drift velocity, V, perpendicular to the flow gradient plane (i.e., along z; Fig. 1C and Materials and Methods). Experiments revealed a large and highly reproducible drift velocity along –z (Fig. 2A), ...
... where the shear rate S was varied between 0 and 36 s−1. Celltracking software yielded the bacteria’s drift velocity, V, perpendicular to the flow gradient plane (i.e., along z; Fig. 1C and Materials and Methods). Experiments revealed a large and highly reproducible drift velocity along –z (Fig. 2A), ...
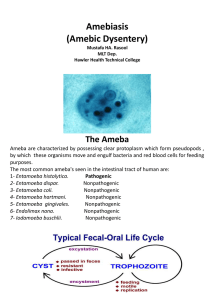
Entamoeba histolytica
... Life cycle of E. histolytica (Noninvasive form) Intestinal infection occur through the ingestion of a mature quadrinucleate infective cyst which contaminated food, drinks and also by hand to mouth contact. Then pass through the stomach , as the cyst wall is resistant to gastric juice. - In the intes ...
... Life cycle of E. histolytica (Noninvasive form) Intestinal infection occur through the ingestion of a mature quadrinucleate infective cyst which contaminated food, drinks and also by hand to mouth contact. Then pass through the stomach , as the cyst wall is resistant to gastric juice. - In the intes ...
Nasal vaccination using live bacterial vectors
... addition, mucosal anti-TTFC IgA responses were monitored in fresh fecal pellets. Fifteen days after immunization, the oral route led to a high but very transient response, whereas the nasal route provided a more sustained IgA level at least up to 41 days after immunization. Even though serum antibod ...
... addition, mucosal anti-TTFC IgA responses were monitored in fresh fecal pellets. Fifteen days after immunization, the oral route led to a high but very transient response, whereas the nasal route provided a more sustained IgA level at least up to 41 days after immunization. Even though serum antibod ...
HALOMONAS HYDROTHERMALIS PRODUCING A CLASS-A β-LACTAMASE, ISOLATED FROM KUMTA COAST Research Article
... Environmental microbes that are either non-pathogenic or opportunistic pathogens have also been found to be more drug resistant in comparison to the bacteria typically associated with disease and therefore the role of these organisms as potential reservoirs of resistance genes is becoming a focus of ...
... Environmental microbes that are either non-pathogenic or opportunistic pathogens have also been found to be more drug resistant in comparison to the bacteria typically associated with disease and therefore the role of these organisms as potential reservoirs of resistance genes is becoming a focus of ...
COMPLEMENT ACTIVATION AND REGULATION IN MUCOSAL
... proteins acquired from the host. Oral and gastric mucosa are not sterile. In health, harmony exists between the "normal" flora and the immune system. The number of microbes is kept under control and their invasion to deeper tissues is prevented by mechanisms that provoke inflammation only minimally. ...
... proteins acquired from the host. Oral and gastric mucosa are not sterile. In health, harmony exists between the "normal" flora and the immune system. The number of microbes is kept under control and their invasion to deeper tissues is prevented by mechanisms that provoke inflammation only minimally. ...
Microbial Detection and Elimination
... hyorhinis, M. fermentans and M. arginini, and Acheloplasma laidlawii. These species are responsible for most mycoplasma contaminations in cell culture. At the concentrations recommended for use, no cytotoxic effects have been found, and the treatment can be performed within 12 days. ...
... hyorhinis, M. fermentans and M. arginini, and Acheloplasma laidlawii. These species are responsible for most mycoplasma contaminations in cell culture. At the concentrations recommended for use, no cytotoxic effects have been found, and the treatment can be performed within 12 days. ...
Exam questions to microbiology, virology and immunology course
... 59.Humoral factors of the non-specific defense: complement, lysozyme, β-lysins, leukins, properdine. 60.Antigens as inducers of immune response. The structure of antigen. Complete antigens and haptens, their characteristics. 61.Antigenic structure of bacterial cells. Protective antigens. Antigenic s ...
... 59.Humoral factors of the non-specific defense: complement, lysozyme, β-lysins, leukins, properdine. 60.Antigens as inducers of immune response. The structure of antigen. Complete antigens and haptens, their characteristics. 61.Antigenic structure of bacterial cells. Protective antigens. Antigenic s ...
Entamoeba histolytica
... cyst which contaminated food, drinks and also by hand to mouth contact. Then pass through the stomach , as the cyst wall is resistant to gastric juice. - In the intestine excystation takes place. - Trophozoit being actively motile invade the tissue of the submucous layer of ...
... cyst which contaminated food, drinks and also by hand to mouth contact. Then pass through the stomach , as the cyst wall is resistant to gastric juice. - In the intestine excystation takes place. - Trophozoit being actively motile invade the tissue of the submucous layer of ...
Document
... • Prokaryotes thrive almost everywhere, including places too acidic, salty, cold, or hot for most other organisms • Most prokaryotes are microscopic, but what they lack in size they make up for in numbers • There are more in a handful of fertile soil than the number of people who have ever lived • ...
... • Prokaryotes thrive almost everywhere, including places too acidic, salty, cold, or hot for most other organisms • Most prokaryotes are microscopic, but what they lack in size they make up for in numbers • There are more in a handful of fertile soil than the number of people who have ever lived • ...
InterFase®: Specialized Enzymes Disrupt Biofilm Matrix that
... luminal particulate matter. Among the more important species involved in gastrointestinal biofilm formation are Bacteroides, Bifidobacterium, and Fusobacterium. Fusobacterium species appear to play a key role in formation and maintenance of healthy biofilm by forming coaggregation and coadhesion bri ...
... luminal particulate matter. Among the more important species involved in gastrointestinal biofilm formation are Bacteroides, Bifidobacterium, and Fusobacterium. Fusobacterium species appear to play a key role in formation and maintenance of healthy biofilm by forming coaggregation and coadhesion bri ...
- International Journal of MEDICAL DENTISTRY
... the hematogene way, following anachoresis. Minute studies on the method of collecting, transport and cultivation showed that the most frequently occurring strains are the ones normally present in the oral cavity, where other bacteria from the outside environment are quite rare (1). The role played b ...
... the hematogene way, following anachoresis. Minute studies on the method of collecting, transport and cultivation showed that the most frequently occurring strains are the ones normally present in the oral cavity, where other bacteria from the outside environment are quite rare (1). The role played b ...
Pathogenic E.coli - SHS
... of the gut, and can benefit their hosts by producing vitamin K2,[3] and by preventing the establishment of pathogenic bacteria within the intestine.[4][5] ...
... of the gut, and can benefit their hosts by producing vitamin K2,[3] and by preventing the establishment of pathogenic bacteria within the intestine.[4][5] ...
Chapter Web Links
... termasuk dinding sel yang tidak mempunyai peptidoglika dan sel dengan nukleoid yang diselimuti membran; membelah dengan bertunas dan membentuk tonjolan (appendages) yang disebut stalks 2. Chlamydiae - phylum terdiri dari patogen intraseluler obligat yang mempunyai siklus hidup unik; patogen ini tida ...
... termasuk dinding sel yang tidak mempunyai peptidoglika dan sel dengan nukleoid yang diselimuti membran; membelah dengan bertunas dan membentuk tonjolan (appendages) yang disebut stalks 2. Chlamydiae - phylum terdiri dari patogen intraseluler obligat yang mempunyai siklus hidup unik; patogen ini tida ...
II. PENGGOLONGAN MIKROBA Taksonomi Mikroba
... termasuk dinding sel yang tidak mempunyai peptidoglika dan sel dengan nukleoid yang diselimuti membran; membelah dengan bertunas dan membentuk tonjolan (appendages) yang disebut stalks 2. Chlamydiae - phylum terdiri dari patogen intraseluler obligat yang mempunyai siklus hidup unik; patogen ini tida ...
... termasuk dinding sel yang tidak mempunyai peptidoglika dan sel dengan nukleoid yang diselimuti membran; membelah dengan bertunas dan membentuk tonjolan (appendages) yang disebut stalks 2. Chlamydiae - phylum terdiri dari patogen intraseluler obligat yang mempunyai siklus hidup unik; patogen ini tida ...
Mid-term PowerPoint Presentation
... inside a grid on the microscope ~ every other day and use the Hypothesis Test to determine whether there is a significant difference between the bacteria growing inside vesicles compared to those free-floating in the environment. I will create graphs to more clearly illustrate my results. ...
... inside a grid on the microscope ~ every other day and use the Hypothesis Test to determine whether there is a significant difference between the bacteria growing inside vesicles compared to those free-floating in the environment. I will create graphs to more clearly illustrate my results. ...
Staphylococci and Streptococci
... • Cultivation on blood and chocolate agar: - haemolysis • Separate from S. pneumoniae S: normal flora optochin R • clinical picture: In oral cavity: colonisation on the teeth dental plaque formation dental caries • If Streptococcus viridans enter the circulation cause subacute endocarditis ...
... • Cultivation on blood and chocolate agar: - haemolysis • Separate from S. pneumoniae S: normal flora optochin R • clinical picture: In oral cavity: colonisation on the teeth dental plaque formation dental caries • If Streptococcus viridans enter the circulation cause subacute endocarditis ...
Human microbiota

The human microbiota is the aggregate of microorganisms, a microbiome that resides on the surface and in deep layers of skin (including in mammary glands), in the saliva and oral mucosa, in the conjunctiva, and in the gastrointestinal tracts. They include bacteria, fungi, and archaea. Micro-animals which live on the human body are excluded. The human microbiome refer to their genomes.One study indicated they outnumber human cells 10 to 1. Some of these organisms perform tasks that are useful for the human host. However, the majority have been too poorly researched for us to understand the role they play, however communities of microflora have been shown to change their behavior in diseased individuals. Those that are expected to be present, and that under normal circumstances do not cause disease, but instead participate in maintaining health, are deemed members of the normal flora. Though widely known as microflora, this is a misnomer in technical terms, since the word root flora pertains to plants, and biota refers to the total collection of organisms in a particular ecosystem. Recently, the more appropriate term microbiota is applied, though its use has not eclipsed the entrenched use and recognition of flora with regard to bacteria and other microorganisms. Both terms are being used in different literature.Studies in 2009 questioned whether the decline in biota (including microfauna) as a result of human intervention might impede human health.Most of the microbes associated with humans appear to be not harmful at all, but rather assist in maintaining processes necessary for a healthy body. A surprising finding was that at specific sites on the body, a different set of microbes may perform the same function for different people. For example, on the tongues of two people, two entirely different sets of organisms will break down sugars in the same way. This suggests that medical science may be forced to abandon the ""one only"" microbe model of infectious disease, and rather pay attention to functions of groups of microbes that have somehow gone awry.