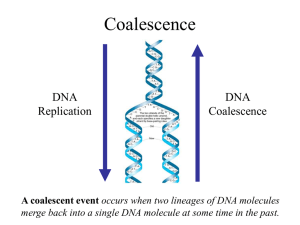
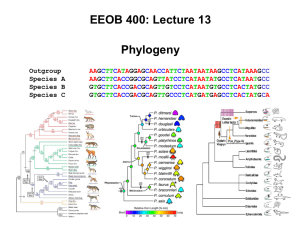
Gene Trees in Species Trees
... Probability of occurrence of gene trees given species trees – from coalescence theory Probability of occurrence of sequences given gene trees – from model of nucleotide evolution Searching ML tree – extremely tedious due to consideration of every species tree for all gene ...
... Probability of occurrence of gene trees given species trees – from coalescence theory Probability of occurrence of sequences given gene trees – from model of nucleotide evolution Searching ML tree – extremely tedious due to consideration of every species tree for all gene ...
A Robust, Non-Parametric Method to Identify Outliers and Improve
... long-tailed distribution receiving radically different treatments, as is appropriate for this kind of distribution. In addition to detecting random defects, the proposed algorithm has been useful in detecting recurring patterns of failing die that were not detectable using test limits alone. Such re ...
... long-tailed distribution receiving radically different treatments, as is appropriate for this kind of distribution. In addition to detecting random defects, the proposed algorithm has been useful in detecting recurring patterns of failing die that were not detectable using test limits alone. Such re ...
Molecular population genetics Magnus Nordborg* and Hideki Innan
... population. The only way to reduce this variance is to collect data from a number of independent (unlinked) loci, and to rely on the fact that the demographic history affects the entire genome in the same way. The conclusions that can be drawn from a single locus (or non-recombining genome, such as ...
... population. The only way to reduce this variance is to collect data from a number of independent (unlinked) loci, and to rely on the fact that the demographic history affects the entire genome in the same way. The conclusions that can be drawn from a single locus (or non-recombining genome, such as ...
Clocks
... The molecular clock hypothesis If proteins evolve at constant rates, then the number of substitutions between two sequences may be used to estimate divergence times. This is analogous to the dating of geological times by radioactive decay. ...
... The molecular clock hypothesis If proteins evolve at constant rates, then the number of substitutions between two sequences may be used to estimate divergence times. This is analogous to the dating of geological times by radioactive decay. ...
Instructions for ICML-98 Authors
... microarrays may be used to identify which genes are involved in causing particular diseases. Currently, discussion of techniques and algorithms of a most approaches to the computational analysis of decision tree learning tool that has been devised taking into consideration the special features of ge ...
... microarrays may be used to identify which genes are involved in causing particular diseases. Currently, discussion of techniques and algorithms of a most approaches to the computational analysis of decision tree learning tool that has been devised taking into consideration the special features of ge ...
Differential Expression Analysis of Microarray Data
... In a signal-to-noise ratio paradigm, we are all familiar with the idea of not wanting to attribute mistaken biology to signals that appear large only by random chance A misleadlingly small estimate of the variance will cause the same problem, and the empirical Bayes adjustment helps address this pro ...
... In a signal-to-noise ratio paradigm, we are all familiar with the idea of not wanting to attribute mistaken biology to signals that appear large only by random chance A misleadlingly small estimate of the variance will cause the same problem, and the empirical Bayes adjustment helps address this pro ...
Printer-friendly Version
... the sequences of the 16S rRNA genes of the 28 bacterial strains collected. This would have allowed them to assess how these strains would have been classified according to the Phylochip, thereby allowing for a stronger comparative analysis. Furthermore, it is unfortunate that the authors made a prel ...
... the sequences of the 16S rRNA genes of the 28 bacterial strains collected. This would have allowed them to assess how these strains would have been classified according to the Phylochip, thereby allowing for a stronger comparative analysis. Furthermore, it is unfortunate that the authors made a prel ...
Accounting for Probe-level Noise in Principal Component Analysis
... downweights noisy values and ensures that the components we extract accurately reflect the structure of the data. The clustering is further improved when performed on the denoised reconstructed profiles, as these are the best estimates of the true profiles. This leads to much tighter and biologicall ...
... downweights noisy values and ensures that the components we extract accurately reflect the structure of the data. The clustering is further improved when performed on the denoised reconstructed profiles, as these are the best estimates of the true profiles. This leads to much tighter and biologicall ...
t - nslc.wustl.edu
... trees or the more traditional species trees of evolutionary biology. • It is common in coalescent theory (and molecular evolution in general) to assume the infinite sites model in which each mutation occurs at a new nucleotide site. • Under this model, there is no homoplasy because no nucleotide sit ...
... trees or the more traditional species trees of evolutionary biology. • It is common in coalescent theory (and molecular evolution in general) to assume the infinite sites model in which each mutation occurs at a new nucleotide site. • Under this model, there is no homoplasy because no nucleotide sit ...
prairieMay05agu
... A stochastic nonparametric technique for space-time disaggregation of streamflows May 27, 2005 2005 Joint Assembly ...
... A stochastic nonparametric technique for space-time disaggregation of streamflows May 27, 2005 2005 Joint Assembly ...
Mining Multi-label Data by Grigorios Tsoumakas, Ioannis Katakis
... • “A large body of research in supervised learning deals with the analysis of single label data, where training examples are associated with a single label l from a set of disjoint labels L. However, training examples in several application domains are often associated with a set of labels Y (union) ...
... • “A large body of research in supervised learning deals with the analysis of single label data, where training examples are associated with a single label l from a set of disjoint labels L. However, training examples in several application domains are often associated with a set of labels Y (union) ...
Slides 5 - University of Florida
... • Find a particular (usually) short sequence in a database of sequences (or one huge sequence). • Problem is identical to local sequence alignment, but on a much larger scale. • We must also have some idea of the significance of a database hit. – Databases always return some kind of hit, how much at ...
... • Find a particular (usually) short sequence in a database of sequences (or one huge sequence). • Problem is identical to local sequence alignment, but on a much larger scale. • We must also have some idea of the significance of a database hit. – Databases always return some kind of hit, how much at ...
Virtual Lab
... Background: Mutations involve a physical change to genetic material that results in the abnormal encoding of protein sequences. The impact of these changes can be insignificant or devastating. In this lab, you will complete mRNA and protein sequences based on the information provided. You will be gi ...
... Background: Mutations involve a physical change to genetic material that results in the abnormal encoding of protein sequences. The impact of these changes can be insignificant or devastating. In this lab, you will complete mRNA and protein sequences based on the information provided. You will be gi ...
doc - Lonely Joe Parker
... sister tips’ MRCA). It is therefore important to ensure appropriate phylogenetic contrasts are made. We may therefore refine this technique by using an ancestral reconstruction technique to infer ancestral nucleotide and/or amino-acid sequences, typically by maximum-likelihood. Reconstructing the an ...
... sister tips’ MRCA). It is therefore important to ensure appropriate phylogenetic contrasts are made. We may therefore refine this technique by using an ancestral reconstruction technique to infer ancestral nucleotide and/or amino-acid sequences, typically by maximum-likelihood. Reconstructing the an ...
view
... To use GP to evolve NN architecture, the GP is constrained in such a way that it uses standard GP operators but retains the typical structure of feed-forward NN. The flexibility of the GPNN allows optimal network architecture to be generated for a given data set. (view figure #2) While GPNN is effec ...
... To use GP to evolve NN architecture, the GP is constrained in such a way that it uses standard GP operators but retains the typical structure of feed-forward NN. The flexibility of the GPNN allows optimal network architecture to be generated for a given data set. (view figure #2) While GPNN is effec ...
News Coverage - Reptilian
... evo-devo candidates are cichlid fish (7). Hundreds of extremely young and genetically almost identical, though phenotypically diverse, species offer a kind of “natural experiment” and can be seen as “natural mutants”. Work on the development and evolution of colorational differences, that play an im ...
... evo-devo candidates are cichlid fish (7). Hundreds of extremely young and genetically almost identical, though phenotypically diverse, species offer a kind of “natural experiment” and can be seen as “natural mutants”. Work on the development and evolution of colorational differences, that play an im ...
week7
... When species do this they tend to produce more offspring than the environment can support. The lack of resources to nourish these individuals places pressure on the size of the species population, and the lack of resources means increased competition and as a consequence, some organisms will not sur ...
... When species do this they tend to produce more offspring than the environment can support. The lack of resources to nourish these individuals places pressure on the size of the species population, and the lack of resources means increased competition and as a consequence, some organisms will not sur ...
The Clegg Collection - UC Agriculture and Natural Resources
... useful for breeding purposes. The environmental component is the “noise” that misleads breeders and, regrettably, often has a large influence on agriculturally relevant traits. Since 2003 the Clegg trees have been put to good use. First, a quantitative genetic study was initiated to address the mism ...
... useful for breeding purposes. The environmental component is the “noise” that misleads breeders and, regrettably, often has a large influence on agriculturally relevant traits. Since 2003 the Clegg trees have been put to good use. First, a quantitative genetic study was initiated to address the mism ...
An Overview of Clustering Methods
... • Run minimum-weight cutset algorithm twice on graph from previous example to produce good clustering (assuming the weight of each edge is 1): ...
... • Run minimum-weight cutset algorithm twice on graph from previous example to produce good clustering (assuming the weight of each edge is 1): ...
An Overview of Clustering Methods
... • Run minimum-weight cutset algorithm twice on graph from previous example to produce good clustering (assuming the weight of each edge is 1): ...
... • Run minimum-weight cutset algorithm twice on graph from previous example to produce good clustering (assuming the weight of each edge is 1): ...
Data Structures - Exercises
... smaller, we can go to the left. If its larger, we need to get the count of the left elements and go to the right. If we find the element, we will return the count of elements, smaller than it. ...
... smaller, we can go to the left. If its larger, we need to get the count of the left elements and go to the right. If we find the element, we will return the count of elements, smaller than it. ...
characters
... Reptilia exclusive of birds These are not synapomorphies for “reptiles”, they are ancestral traits Feathers, two legs, and endothermy are apomorphic in birds Other characters reflect synapomorphy and recover the true relationships But in many cases it is more difficult to resolve character conflict ...
... Reptilia exclusive of birds These are not synapomorphies for “reptiles”, they are ancestral traits Feathers, two legs, and endothermy are apomorphic in birds Other characters reflect synapomorphy and recover the true relationships But in many cases it is more difficult to resolve character conflict ...