Standard Physics Mid
... 4. A train is traveling northward with a velocity of 100 km/hr. A child on this train walks southward with a velocity of 5 km/hr. The child’s velocity with respect to he ground is (a) 95 km/hr N (b) 95 km/hr S (c) 105 km/hr N (d) 105 km/hr S 5. A ball is thrown horizontally from the top of a cliff. ...
... 4. A train is traveling northward with a velocity of 100 km/hr. A child on this train walks southward with a velocity of 5 km/hr. The child’s velocity with respect to he ground is (a) 95 km/hr N (b) 95 km/hr S (c) 105 km/hr N (d) 105 km/hr S 5. A ball is thrown horizontally from the top of a cliff. ...
saint patrick`s high school
... frozen pond. The machine fires a 0.40 kg baseball with a speed of 35 m/s in the horizontal direction. What is the recoil speed of the pitching machine? (Assume friction is negligible.) a. 0.14 m/s b. 0.28 m/s c. 0.70 m/s d. 4.4 103 m/s 28. A 3.0 kg object moves to the right at 4.0 m/s. It collides ...
... frozen pond. The machine fires a 0.40 kg baseball with a speed of 35 m/s in the horizontal direction. What is the recoil speed of the pitching machine? (Assume friction is negligible.) a. 0.14 m/s b. 0.28 m/s c. 0.70 m/s d. 4.4 103 m/s 28. A 3.0 kg object moves to the right at 4.0 m/s. It collides ...
Question (1250001) - High Point University
... A 0.4-kg soccer ball is kicked from a location < 8, 0, −8 > m (on the ground) with initial velocity < −9, 14, −4 > m/s. The ball's speed is low enough that air resistance is negligible. Therefore, you can assume that the net force is constant. (Note: the +y direction is de ned to be perpendicular to ...
... A 0.4-kg soccer ball is kicked from a location < 8, 0, −8 > m (on the ground) with initial velocity < −9, 14, −4 > m/s. The ball's speed is low enough that air resistance is negligible. Therefore, you can assume that the net force is constant. (Note: the +y direction is de ned to be perpendicular to ...
Types of Forces with Newton`s Laws
... Gravity Between Objects • The force of gravity between objects increases with greater mass and decreases with greater distance. ...
... Gravity Between Objects • The force of gravity between objects increases with greater mass and decreases with greater distance. ...
Physics Midterm Study Guide
... For addition or subtraction units must be the same. For multiplication and division they can be different. Know how to enter powers of 10 in calculations reliably in your calculator Dependent and independent variables in an experiment are the only ones we want to allow to change Position, x , is the ...
... For addition or subtraction units must be the same. For multiplication and division they can be different. Know how to enter powers of 10 in calculations reliably in your calculator Dependent and independent variables in an experiment are the only ones we want to allow to change Position, x , is the ...
Newton`s Laws and Momentum - science
... There are many misconceptions about Newton’s First Law. Read: "How many ways can you state Newton's First Law?" and "Thoughts on force..."to try and understand how it fits to many situations. Newton’s first law states that an object will remain stationary or continue at a constant velocity unless ac ...
... There are many misconceptions about Newton’s First Law. Read: "How many ways can you state Newton's First Law?" and "Thoughts on force..."to try and understand how it fits to many situations. Newton’s first law states that an object will remain stationary or continue at a constant velocity unless ac ...
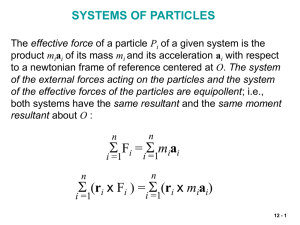
Lec12
... the flow of air through a jet engine. The principle of impulse and momentum is applied to a system S of particles during a time interval Dt, including particles which enter the system at A during that time interval and those (of the same mass Dm) which leave the system at B. The system formed by the ...
... the flow of air through a jet engine. The principle of impulse and momentum is applied to a system S of particles during a time interval Dt, including particles which enter the system at A during that time interval and those (of the same mass Dm) which leave the system at B. The system formed by the ...