Word document
... example, the rotational analog of force is torque () with units of [Nm]. 3. Know the moments of inertia about a center of mass of axis for a disk, thick ring, thin ring (hoop), and sphere. Use the parallel axis theorem to find the moment of inertia about any axis parallel to the CM axis. 4. Find t ...
... example, the rotational analog of force is torque () with units of [Nm]. 3. Know the moments of inertia about a center of mass of axis for a disk, thick ring, thin ring (hoop), and sphere. Use the parallel axis theorem to find the moment of inertia about any axis parallel to the CM axis. 4. Find t ...
Notes
... – Angular displacement, angular velocity, and angular acceleration are all vectors • Given that they are vectors, they need to point in a direction • The issue is that these vectors are associated with something that is rotating – By its very definition, a rotating object changes its direction const ...
... – Angular displacement, angular velocity, and angular acceleration are all vectors • Given that they are vectors, they need to point in a direction • The issue is that these vectors are associated with something that is rotating – By its very definition, a rotating object changes its direction const ...
AQAA2_ch7 Linear Motion
... therefore have to have a direction connected to them as well as value or size. For example, a force could be 100 newtons downward (the downward specifies the direction), an acceleration could be 10 metres per second squared forwards (the forwards specifies the direction). ...
... therefore have to have a direction connected to them as well as value or size. For example, a force could be 100 newtons downward (the downward specifies the direction), an acceleration could be 10 metres per second squared forwards (the forwards specifies the direction). ...
Lecture – 4 Torque and Levers The Mechanics of Rigid Bodies
... The parallel axis theorem (Steinerscher Satz) • The moment of inertia of a rigid body depends on the distribution of mass around the axis of rotation Problem we have infinitely many axes of rotation ! For example, I could take this mechanical linkage and have it rotate around an axis through its ...
... The parallel axis theorem (Steinerscher Satz) • The moment of inertia of a rigid body depends on the distribution of mass around the axis of rotation Problem we have infinitely many axes of rotation ! For example, I could take this mechanical linkage and have it rotate around an axis through its ...
here
... The average acceleration aav of an object as it moves from x1 (at time t1 ) to x2 (at time t2 ) is a vector quantity whose x component is the ratio of the change in the x component of velocity, ∆vx = v2x − v1x , to the time ...
... The average acceleration aav of an object as it moves from x1 (at time t1 ) to x2 (at time t2 ) is a vector quantity whose x component is the ratio of the change in the x component of velocity, ∆vx = v2x − v1x , to the time ...
ys1 yt1 - Stewart Calculus
... sandth of a second. Here we calculate the average force on the bat during this collision by first computing the change in the ball’s momentum. The momentum p of an object is the product of its mass m and its velocity v, that is, p 苷 mv. Suppose an object, moving along a straight line, is acted on by ...
... sandth of a second. Here we calculate the average force on the bat during this collision by first computing the change in the ball’s momentum. The momentum p of an object is the product of its mass m and its velocity v, that is, p 苷 mv. Suppose an object, moving along a straight line, is acted on by ...
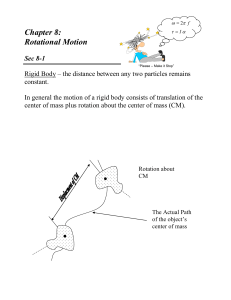
Chapter 8: Rotational Motion
... How to “think” about Torque 1. Torque must be specified about a pivot point 2. Torque is a product quantity made up of distance and force. 3. Torque causes angular acceleration, , in the same way that forces cause linear accelerations. 4. The Moment of Inertia, I, is a measure of resistance to rota ...
... How to “think” about Torque 1. Torque must be specified about a pivot point 2. Torque is a product quantity made up of distance and force. 3. Torque causes angular acceleration, , in the same way that forces cause linear accelerations. 4. The Moment of Inertia, I, is a measure of resistance to rota ...