Chapter 4. Rotation and Conservation of Angular Momentum
... We previously derived equation (4.16) for the linear velocity of a rotating rigid body. We could think, for example, of a solid, rotating disk and focus on the trajectory of a point on its surface. Since this point, which at a given instant has the velocity v , does not move linearly but rotates, th ...
... We previously derived equation (4.16) for the linear velocity of a rotating rigid body. We could think, for example, of a solid, rotating disk and focus on the trajectory of a point on its surface. Since this point, which at a given instant has the velocity v , does not move linearly but rotates, th ...
Preview for Makeup and Final Exam
... b. Preview of Calculus 1. Solve the derivative of a polynomial 2. Solve the derivative of a sine or cosine function 3. Determine if the derivative of a point on a curve is positive, negative or zero 4. Solve the derivative of a vector c. Mathematics in Physics 1. List the units and dimensions for th ...
... b. Preview of Calculus 1. Solve the derivative of a polynomial 2. Solve the derivative of a sine or cosine function 3. Determine if the derivative of a point on a curve is positive, negative or zero 4. Solve the derivative of a vector c. Mathematics in Physics 1. List the units and dimensions for th ...
03 - Northern Highlands
... gravity exerts a force on the book (Figure 3.1)? “Force” is a good answer to this question and the third law is the key to understanding why. ...
... gravity exerts a force on the book (Figure 3.1)? “Force” is a good answer to this question and the third law is the key to understanding why. ...
Unit Plan Motion and Forces - Mrs. Olivas 8th Grade Science
... 08.04.02.03. Describe and explain forces that produce motion in objects. 08.04.02.03.01. Know that there are fundamental forces in nature (e.g., gravity, electromagnetic forces, nuclear forces). 08.04.02.03.02. Know that a force has both magnitude and direction. 08.04.02.03.03. Analyze the separate ...
... 08.04.02.03. Describe and explain forces that produce motion in objects. 08.04.02.03.01. Know that there are fundamental forces in nature (e.g., gravity, electromagnetic forces, nuclear forces). 08.04.02.03.02. Know that a force has both magnitude and direction. 08.04.02.03.03. Analyze the separate ...
TOWNSHIP OF UNION PUBLIC SCHOOLS
... recognize in what time intervals the other two are positive, negative, or zero, and can identify or sketch a graph of each as a function of time. Use the standard kinematics equations to solve problems involving one-dimensional motion with constant acceleration. ...
... recognize in what time intervals the other two are positive, negative, or zero, and can identify or sketch a graph of each as a function of time. Use the standard kinematics equations to solve problems involving one-dimensional motion with constant acceleration. ...
Physics_1996_Paper_I_+_ANS
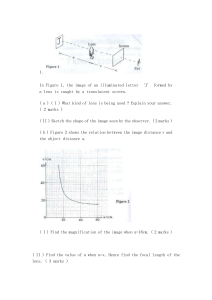
... (ii) the source with half-life 5 years should be used Because * The source will decay slowly (OR The activity of the source will be very stable) and can be used for a long time. The source with half-life 10 minutes will decay rapidly and the registered count rate is unstable even when no bottles are ...
... (ii) the source with half-life 5 years should be used Because * The source will decay slowly (OR The activity of the source will be very stable) and can be used for a long time. The source with half-life 10 minutes will decay rapidly and the registered count rate is unstable even when no bottles are ...
Phy CH 06 momentum - Milton-Union Exempted Village Schools
... word we use every day in a variety of situations. In physics this word has a specific meaning. The linear momentum of an object of mass m moving with a velocity v is defined as the product of the mass and the velocity. Momentum is represented by the symbol p. MOMENTUM ...
... word we use every day in a variety of situations. In physics this word has a specific meaning. The linear momentum of an object of mass m moving with a velocity v is defined as the product of the mass and the velocity. Momentum is represented by the symbol p. MOMENTUM ...