Newton`s Three Laws: Answer the questions below using pages 389
... Figure 17 don’t cancel in the left picture but do in the right picture. ...
... Figure 17 don’t cancel in the left picture but do in the right picture. ...
doc
... Normally Newton’s second law is written as F=ma which means the force on an object is equal to the object’s mass times its acceleration, where bold indicates a vector. Consider gravity. The acceleration of gravity is independent of the object being pulled. The force of gravity is proportional to the ...
... Normally Newton’s second law is written as F=ma which means the force on an object is equal to the object’s mass times its acceleration, where bold indicates a vector. Consider gravity. The acceleration of gravity is independent of the object being pulled. The force of gravity is proportional to the ...
Forces Physical Science Chapter 2
... Fig 1 - shows the magnitude & direction of the 2 vectors we are adding Fig 2 – we move the beginning of vector B to the end of Vector A, making sure to keep the magnitude & direction exactly the same Fig 3 – Connect the beginning of Vector A to the end of Vector B, this is your “Resultant” C. ...
... Fig 1 - shows the magnitude & direction of the 2 vectors we are adding Fig 2 – we move the beginning of vector B to the end of Vector A, making sure to keep the magnitude & direction exactly the same Fig 3 – Connect the beginning of Vector A to the end of Vector B, this is your “Resultant” C. ...
Document
... ______ 7. .Newton’s first law of motion applies to a. moving objects. b. objects that are not moving. c. objects that are accelerating. d. Both (a) and (b) _____ 8. To accelerate two objects at the same rate, the force used to push the object that has more mass should be a. smaller than the force us ...
... ______ 7. .Newton’s first law of motion applies to a. moving objects. b. objects that are not moving. c. objects that are accelerating. d. Both (a) and (b) _____ 8. To accelerate two objects at the same rate, the force used to push the object that has more mass should be a. smaller than the force us ...
Conservation of Momentum
... – Two objects colliding experience equal force for equal time, thus the magnitude of impulse, or change in momentum, must be the same for both objects – When there are no external influences, momentum gained by one object must equal the momentum lost by another and the total momentum of the system i ...
... – Two objects colliding experience equal force for equal time, thus the magnitude of impulse, or change in momentum, must be the same for both objects – When there are no external influences, momentum gained by one object must equal the momentum lost by another and the total momentum of the system i ...
dynamics - Mulberry Education Centre
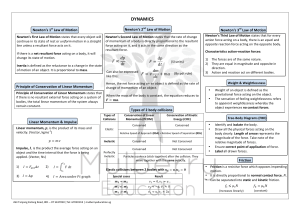
... Newton’s First Law of Motion states that every object will continue in its state of rest or uniform motion in a straight line unless a resultant force acts on it. If there is a net resultant ...
... Newton’s First Law of Motion states that every object will continue in its state of rest or uniform motion in a straight line unless a resultant force acts on it. If there is a net resultant ...