ML Forces Newton Laws from Prentice Hall
... greater force. (When forces are shown in this book, the strength. of a force will usually be shown by the width of an arrow.) When forces act in opposite directions, they also add together. However, you must pay attention to the direction of each force. Adding a force acting in one direction to a fo ...
... greater force. (When forces are shown in this book, the strength. of a force will usually be shown by the width of an arrow.) When forces act in opposite directions, they also add together. However, you must pay attention to the direction of each force. Adding a force acting in one direction to a fo ...
The Lorentz transformation
... when the units of distance and time (and all other units that depend on them) are chosen appropriately. For example, one could work with seconds for time, and light-seconds for distance. (One light-second is equal to 299792458 metres). The only problem with this approach is that you must apply it co ...
... when the units of distance and time (and all other units that depend on them) are chosen appropriately. For example, one could work with seconds for time, and light-seconds for distance. (One light-second is equal to 299792458 metres). The only problem with this approach is that you must apply it co ...
Physics 207: Lecture 2 Notes
... provided by the applied force about the rotation axis biggest? In both cases the magnitude and direction of the applied force is the same. Remember torque requires F, r and sin f or the tangential force component times perpendicular distance ...
... provided by the applied force about the rotation axis biggest? In both cases the magnitude and direction of the applied force is the same. Remember torque requires F, r and sin f or the tangential force component times perpendicular distance ...
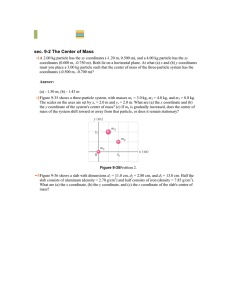
Chapter 02 Motion
... 20. A skateboarder pushes on the ground with her foot. She and the skateboard accelerate down the sidewalk due to the force A. she exerts against the ground. B. between the skateboard wheels and the ground. C. the ground exerts against her foot. D. of gravity acting on the skateboard. Accessibility: ...
... 20. A skateboarder pushes on the ground with her foot. She and the skateboard accelerate down the sidewalk due to the force A. she exerts against the ground. B. between the skateboard wheels and the ground. C. the ground exerts against her foot. D. of gravity acting on the skateboard. Accessibility: ...
Quiz 07-2 Rotation
... a) zero newtons b) 100 N c) 600 N d) 800 N e) 1000 N ____ 13. A string is wrapped around a pulley of radius 0.05 m and moment of inertia 0.2 kg • m2. If the string is pulled with a force F, the resulting angular acceleration of the pulley is 2 rad/s2. Determine the magnitude of the force F. ...
... a) zero newtons b) 100 N c) 600 N d) 800 N e) 1000 N ____ 13. A string is wrapped around a pulley of radius 0.05 m and moment of inertia 0.2 kg • m2. If the string is pulled with a force F, the resulting angular acceleration of the pulley is 2 rad/s2. Determine the magnitude of the force F. ...
F = ma, Important Equation, Big Mistake
... motion is ever proportional to the motive force impressed.” Taking these words to imply the important equation F=ma is perhaps the biggest mistake in the history of science. “Alteration,” in the Second Law is generally taken to mean the rate of change, or the derivative, of a thing with respect to t ...
... motion is ever proportional to the motive force impressed.” Taking these words to imply the important equation F=ma is perhaps the biggest mistake in the history of science. “Alteration,” in the Second Law is generally taken to mean the rate of change, or the derivative, of a thing with respect to t ...
AP Physics - Rose Tree Media School District
... Benchmark # 1 Describe and evaluate the motion of an object undergoing ANY kind of motion in a straight line. a. Define displacement, velocity, acceleration, surge, and alpha, beta (etc., terms of motion. b. Drive the universal equation for displacement in one dimension. c. Graph these quantities vs ...
... Benchmark # 1 Describe and evaluate the motion of an object undergoing ANY kind of motion in a straight line. a. Define displacement, velocity, acceleration, surge, and alpha, beta (etc., terms of motion. b. Drive the universal equation for displacement in one dimension. c. Graph these quantities vs ...
Mechanics 3 – Kinetics: A Level Maths Tutor
... When the particles are released from rest the 2 kg mass moves up the plane. i) what is the acceleration of the 2 kg & 5 kg masses? ii) What is the tension in the string? ...
... When the particles are released from rest the 2 kg mass moves up the plane. i) what is the acceleration of the 2 kg & 5 kg masses? ii) What is the tension in the string? ...
Patterns of Motion
... If you now apply a greater force on the pedals the extra force you apply is unbalanced by friction and air resistance. Hence there will be a net force greater than zero, and you will accelerate. You will accelerate during, and only during, the time that the (unbalanced) net force is greater than ze ...
... If you now apply a greater force on the pedals the extra force you apply is unbalanced by friction and air resistance. Hence there will be a net force greater than zero, and you will accelerate. You will accelerate during, and only during, the time that the (unbalanced) net force is greater than ze ...
Translational Motion
... When a horizontal force of 20 N is applied to this object, an equal and opposite horizontal force opposes the applied force. This opposing force is called the force of static friction, ƒÍ. The maxium value of ƒÍ is ƒÍMAX . The value of ƒÍMAX is a function of FN and the properties of the two material ...
... When a horizontal force of 20 N is applied to this object, an equal and opposite horizontal force opposes the applied force. This opposing force is called the force of static friction, ƒÍ. The maxium value of ƒÍ is ƒÍMAX . The value of ƒÍMAX is a function of FN and the properties of the two material ...
Real Life Examples in Dynamics
... In the horizontal direction (neglecting drag): s vx t 12 ax t 2 27 0.28 0 7.45 m so the slingshot has a range of almost 7.5m. (Note: potential energy gained in flight is (mgh = 0.0249.811.5 = ) 0.35J or 4% of the kinetic energy at launch). ...
... In the horizontal direction (neglecting drag): s vx t 12 ax t 2 27 0.28 0 7.45 m so the slingshot has a range of almost 7.5m. (Note: potential energy gained in flight is (mgh = 0.0249.811.5 = ) 0.35J or 4% of the kinetic energy at launch). ...
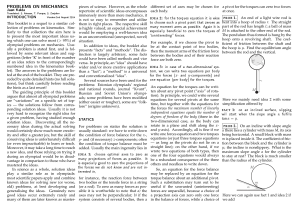
Rotational Motion
... discussed earlier in connection with circular motion in Chapter 5. Even in the case of uniform circular motion, where the speed and are constant and so atang ⫽ 0, there is a nonzero radially directed centripetal acceleration required to steer the object around the circle. If atang is not equal to ...
... discussed earlier in connection with circular motion in Chapter 5. Even in the case of uniform circular motion, where the speed and are constant and so atang ⫽ 0, there is a nonzero radially directed centripetal acceleration required to steer the object around the circle. If atang is not equal to ...